ALTE DOCUMENTE
|
||||||||
With IP multicasting, one device can send a single data stream that the network replicates only as necessary so that multiple devices receive the data. Because of the minimal overhead required to create the data stream and the low overhead on the network, multicast communication is particularly suitable for multiple-user multimedia applicat 24524v217y ions such as video conferencing, distance learning, and collaborative computing. You can also use multicast traffic to discover resources on the internetwork and to support datacasting applications such as file distribution or database synchronization.
Using the IP multicast components of the Windows Server 2003 TCP/IP protocol and the Routing and Remote Access service, you can send and receive IP multicast traffic from multicast-enabled portions of your intranet or the Internet and from remote access clients. You can use IP multicast to optimize server loading and network bandwidth.
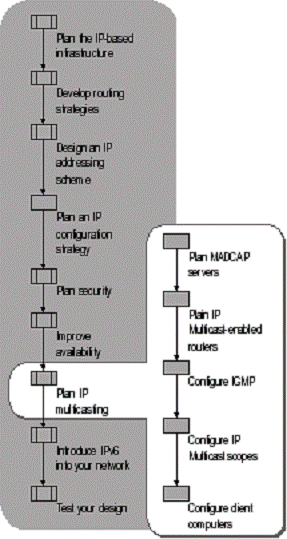
Figure 1.13 shows the tasks involved in planning IP multicasting.
Figure 1.13 Planning IP Multicasting
In multicast routing, routers communicate multicast group membership information to each other using multicast routing protocols, and forward data across the internetwork. Multicast forwarding refers to the process of forwarding multicast traffic to networks on which other multicast devices are listening. The multicast-capable portion of the Internet is referred to as the Internet multicast backbone, or MBone.
All computers running Windows Server 2003 can both send and receive IP multicast traffic. Windows Server 2003 TCP/IP can listen for IPv4 multicast traffic and use a multicast forwarding table to determine where to forward incoming multicast traffic.
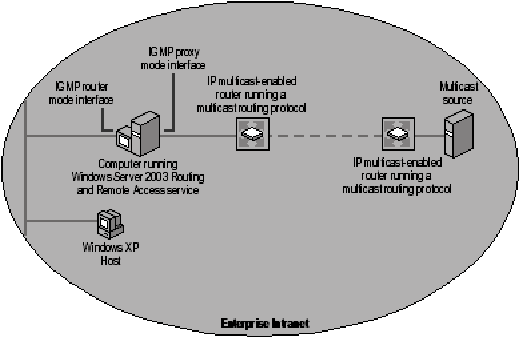
Figure 1.14 shows one common configuration of IP multicast components. For examples of a number of supported multicast configurations, see the Internetworking Guide of the Windows Server 2003 Resource Kit (or see the Internetworking Guide on the Web at https://www.microsoft.com/reskit).
Figure 1. IP Multicast Components
The Multicast Address Dynamic Client Allocation Protocol (MADCAP), built on a client/server model, enables a computer to request an IP multicast address from one or more multicast address allocation servers, known as MADCAP servers. If a client sends a message and does not receive a response, it can retransmit its request.
MADCAP as defined in RFC 2730, "Multicast Address Dynamic Client Allocation Protocol (MADCAP)," differs substantially and is separate from DHCP. However, the Windows Server 2003 DHCP service combines support for both the DHCP and MADCAP protocols for IPv4. Although MADCAP is packaged in the DHCP service, the DHCP and MADCAP services are independent of each other. A DHCP client might or might not be a MADCAP client, and a MADCAP client might or might not be a DHCP client.
To use the DHCP service to deploy MADCAP servers independently of DHCP servers, create one or more multicast scopes, but do not create other scopes or superscopes. The MADCAP server also functions as a DHCP server only if you configure other scopes or superscopes.
The IPSec protocol meets MADCAP requirements for client/server identification and integrity protection as described in RFC 2730, and requires no modifications to the MADCAP protocol. Therefore, when you require strong security, use IPSec to protect all of the unicast messages of the MADCAP protocol.
For more information about MADCAP, including how to use IPSec in conjunction with MADCAP, see RFC 2730, "Multicast Address Dynamic Client Allocation Protocol (MADCAP)."
|