![]() ADM326
Upgrade to R / 3 Enterprise
ADM326
Upgrade to R / 3 Enterprise
ADM326
|
Release 640 21.12.2005 |
|
|
|
|

ADM326 Upgrade to R / 3 Enterprise ..............
Copyright ...............
Course Prerequisites ............
The Need for an Upgrade ........
Content and Goals ...............
When Should a Customer Upgrade a Production System? .......
Upgrade Projects - Reasons Versus Concerns ........
R / 3 Maintenance Strategy ..
Most Critical Pain Points at a Glance ....
SAP Software Lifecycle .......
Focus on Gaps ..
Summary ............
Upgrade Documentation .........
Content and Goals ...............
Upgrade Documentation .....
Upgrade Documentation Structure .......
Filtering of Product-Specific Information .................
Integration of Parts ..............
Upgrade - Step by Step ......
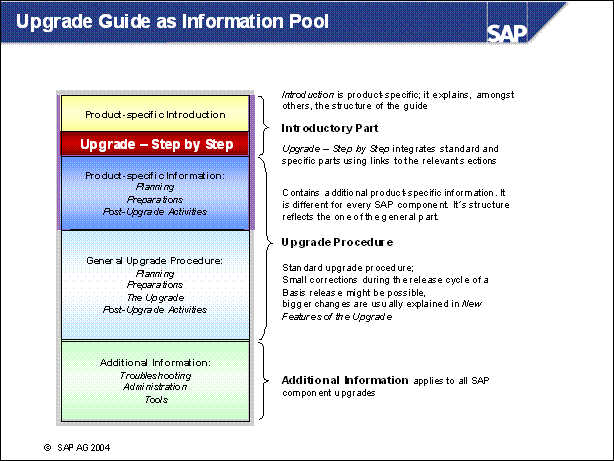
Upgrade Guide as Information Pool ......
Summary ............
Upgrade Tools ......
Content and Goals ...............
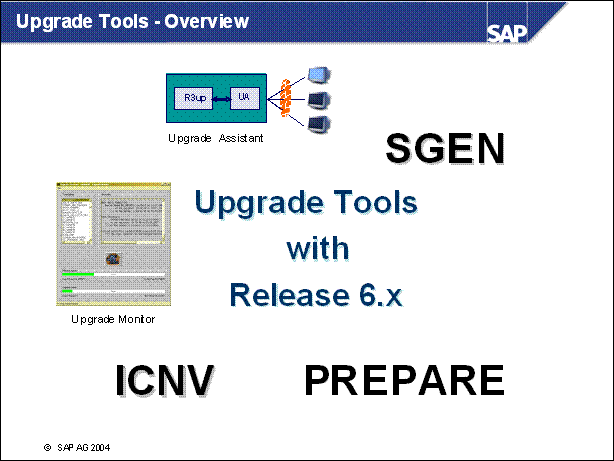
Upgrade Tools - Overview .
Upgrade Tools - PREPARE
Upgrade Tools - PREPARE
Upgrade Tools - Integration of Support Packages .
Incremental Table Conversion ...............
Upgrade Tools - Upgrade Assistant .....
Upgrade Assistant Server ..
Upgrade Tools - Upgrade Assistant ...
Upgrade Tools - Upgrade Assistant ...
Upgrade Tools - Upgrade Assistant ...
Upgrade Assistant Input Window ......
Upgrade Assistant Input Window ......
Upgrade Monitor ...............
Upgrade Tools - SGEN ......
Summary ..........
Phases of PREPARE .................
Content and Goals ...............
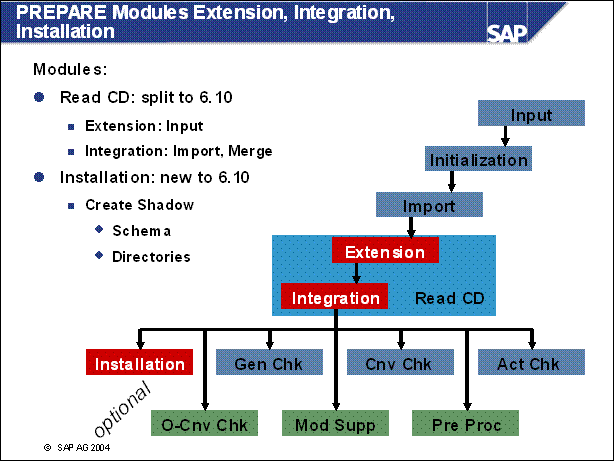
PREPARE Modules Extension, Integration, Installation ...........
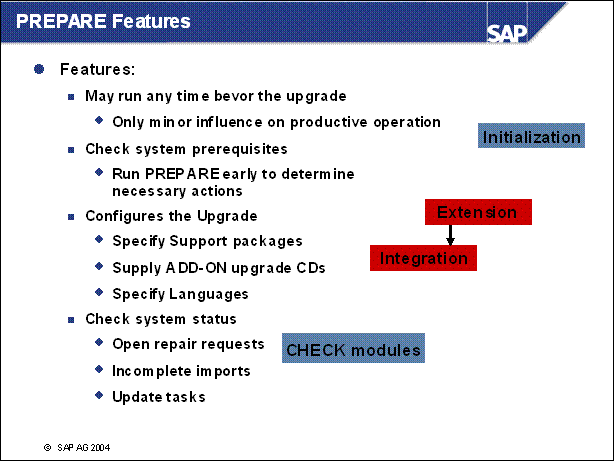
PREPARE Features ..............
PREPARE Handling .............
PREPARE Checks ................
PREPARE Modules Parameter Input, Initialisation
PREPARE Module Import ...
PREPARE Modules Extension, Integration .............
PREPARE Modules Installation ..........
PREPARE Check-Modules ...................
PREPARE Check-Modules ...................
PREPARE as a Part of the Upgrade .....
PREPARE Finished? -> Upgrade! ........
Summary ..........
Appendix: PREPARE Phase List ..........
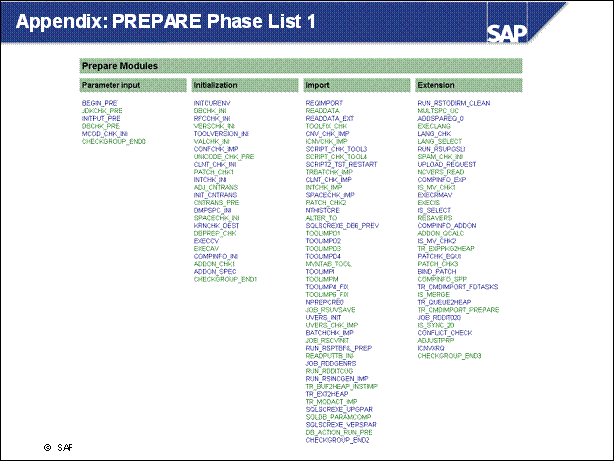
Appendix: PREPARE Phase List 1 .......
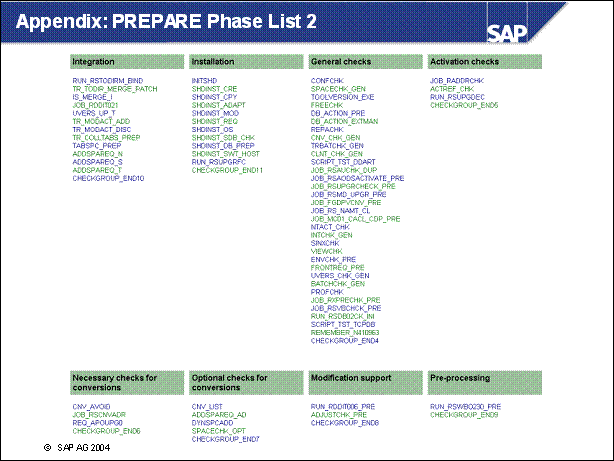
Appendix: PREPARE Phase List 2 .......
Modification Adjustment ........
Content and Goals ...............
Changing the SAP Standard ..................
Modification: Yes or No? ....
System Upgrade Process ....
Upgrade System Landscape ...................
Calculation of Modified Objects to be Adjusted ....
Preparation Aspects (1) ......
Preparation Aspects (2) ......
SPDD ................
SPAU ...............
Handling Change Requests During Adjustment ..
Change Requests: Notes ..
Modification Adjustment Transactions .................
Summary ..........
Phases of the Upgrade .............
Content and Goals ...............
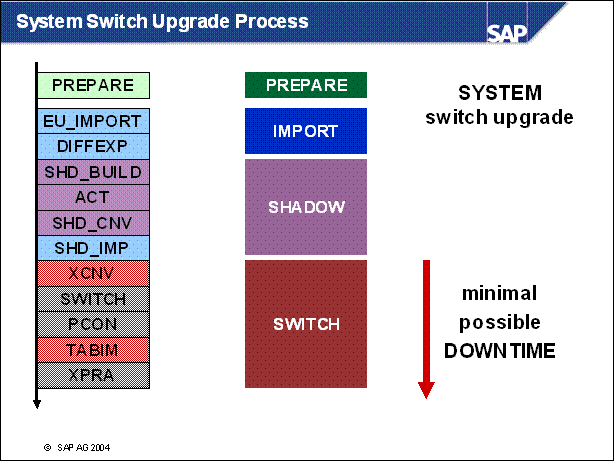
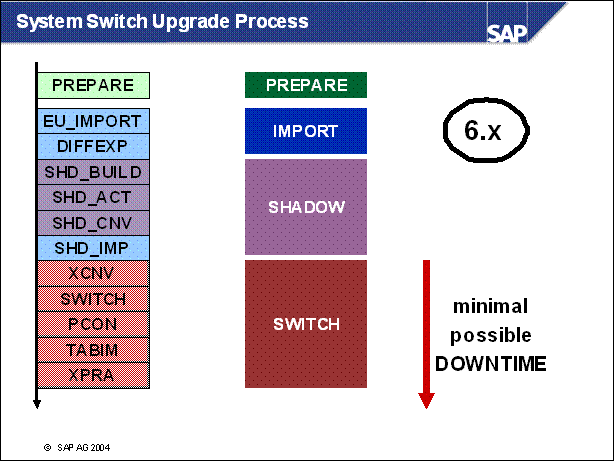
Repositors Switch vs. System Switch Upgrade ......
EU _ IMPORT .....
EU _ IMPORT .....
DIFFEXP ............
START _ SHDI _ FIRST .........
Activation .........
Shadow Import .
Switch ..............
Parallel Conversion ............
TABIM and XPRAs ..........
System Switch Upgrade Process .........
Upgrade Process ................
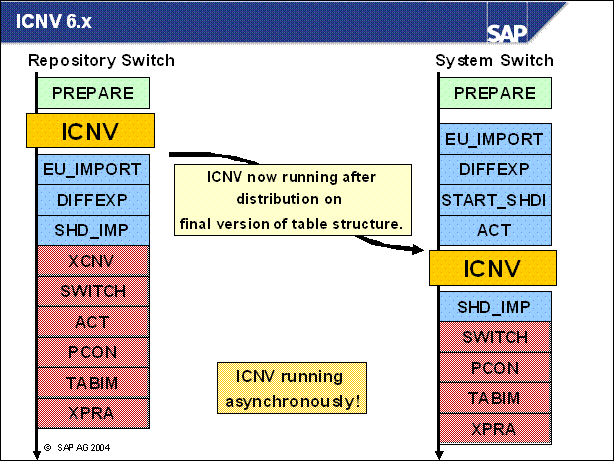
ICNV 6.x ...........
Summary ..........
Appendix: Upgrade Phase List ............
Appendix: Upgrade Phase List 1 .........
Appendix: Upgrade Phase List 2 .........
Troubleshooting ...
Content and Goals ...............
Overview: Upgrade Executables ............
Overview: Monitoring Upgrade Activity .................
Overview: Stop of the Upgrade .............
Overview: Phases .................
Job Phases: Control Flow ...
Job Phases: Log Files ..........
Job Phases: Strategy for Problems ........
Transport Phases: Control Flow (TABIM) ............
Transport Phases: Control Flow (ACT, XPRA) ....
Transport Phases: Logfiles ...................
Transport Phases: Strategy for Problems ...............
Bulk Import Phases: Control Flow .......
Bulk Import Phases: Log files and Strategy ...........
Log File Analysis ...............
Recomendations .................
Summary ..........
Upgrade Strategy ..
Content and Goals ...............
Planning the Upgrade Strategy: Purpose .................
System Switch Upgrade: Two Upgrade Strategies .
Upgrade Strategies: Overview 6.x ..........
Upgrade Strategies: Advantages & Disadvantages ..................
Upgrade Strategies from 6.x
Considerations .
System Switch Upgrade Process ...........
Summary ..........
Shadow Instance ..
Content and Goals ...............
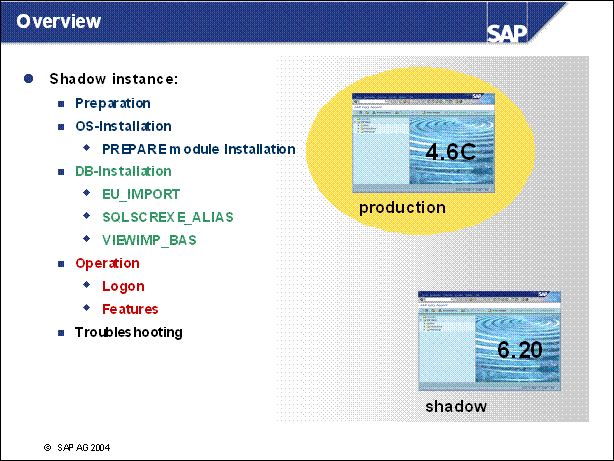
Overview ...........
Overview ...........
PREPARE ..........
PREPARE Module INSTALLATION 1 .
PREPARE Module INSTALLATION 2 .
System Switch Upgrade: The Process (1) ................
System Switch Upgrade: The Process (2) ................
Upgrade Phases EU _ IMPORT <n> ......
Upgrade ...........
System Switch Upgrade: The Process (3) ..............
Operation of Shadow Instance ............
Shadow Instance and SAP GUI ...........
Features of Shadow Instance ...............
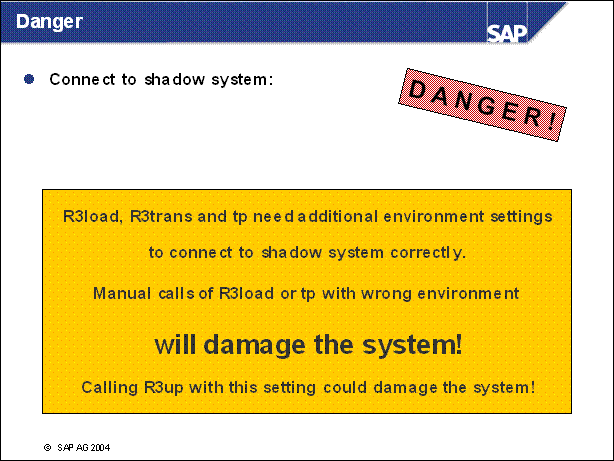
Danger .............
Summary ..........
Incremental Conversion .........
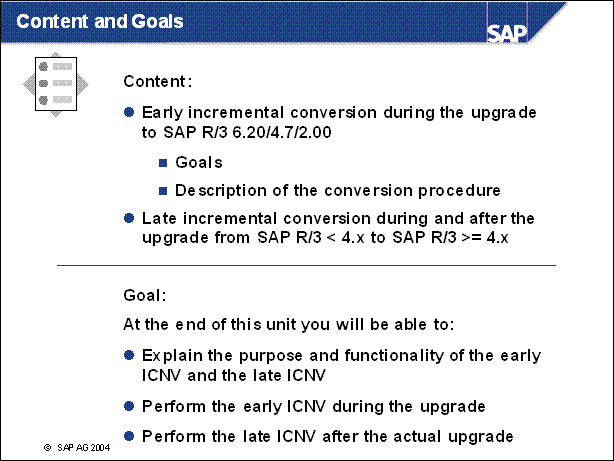
Content and Goals .............
Goals ................
Overview .........
Need for Logging Mechanism .............
Logging Mechanism (1) ....
Logging Mechanism (2) ....
Conversion of Residue During Downtime .............
Transaction ICNV: Selection of Candidates ..........
Transaction ICNV: Initialization and ICNV Assistant ............
Transaction ICNV: Performance Monitor .............
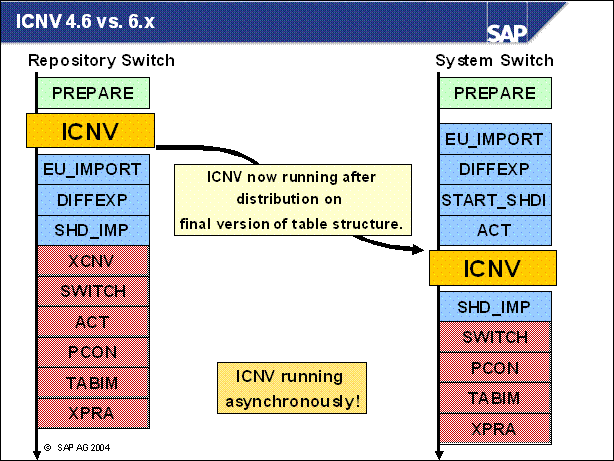
ICNV 4.6 vs. 6.x .................
Summary ........
Late ICNV ......
Late ICNV (Actions During Upgrade) ..................
Late ICNV (Actions After Upgrade) .
Late ICNV: Transaction ...
Summary ........
Support Packages and Add-Ons ..............
Content and Goals .............
Software Components with SAP Web AS 6.20 .....
Support Packages ..............
Support Packages ..............
Integration of Support Packages .........
Upgrade Configuration .....
New Features 6.x: Why Queue Calculation? ..........
Upgrade and Installation of Components ..............
New with Upgrade 6.20 ...
IS _ SELECT - Selection I .
Decision about Add-On ..
Phase BIND _ PATCH ......
BIND _ PATCH - Selection I ...............
BIND _ PATCH - Selection II ..............
BIND _ PATCH - Selection III ............
Downtime with System Switch Upgrade (6.x) ......
Binding Add-Ons and Support Packages ............
Summary ........
Upgrade Planning and Preparation ..........
Content and Goals .............
Major Upgrade Aspects at a Glance ..
Upgrade Planning: General Overview .
Aspects in an Upgrade Project ............
Organizational Aspects: Initial Project Planning ...
Business Aspects in Detail ..................
Technology Aspects in Detail .............
Towards SAP R / 3 Enterprise or mySAP ERP 2004 ...................
Available Upgrade Technology ........
Upgrade Environment .....
SAP R / 3 Technical Upgrade Procedure: Overview .................
PREPARE ......
Upgrade 1 ......
Upgrade 2 ......
Support Packages ............
Add On ..........
Shadow Instance ..............
Downtime ......
Factors Affecting Runtime and Downtime ...........
Steps to Minimize Upgrade Downtime .................
The History of Upgrade Downtime ...
System Switch Upgrade: Two Upgrade Strategies .................
SAP R / 3 Enterprise - Statistics and Facts ...........
Database Size vs. Upgrade Downtime (4.6C) .......
SAP R / 3 Enterprise - Statistics and Facts ...........
Hardware Requirements with SAP R / 3 Enterprise ..................
Frontend requirements for R / 3 Enterprise ............
- ...
Upgrade Improvements by SAP ........
SAP R / 3 Enterprise - Statistics and Facts ...........
Experience with Upgrades ..................
Experience with Upgrades ..................
Recommendations on Upgrades ........
Summary ........
Customer Based Upgrade ......
Content and Goals .............
Normal SAP Upgrade in a Three System Landscape ...............
CBU in a Three System Landscape .....
Upgrade Configuration .....
Customer Based Upgrade .
Customer Based Upgrade: Complete Process (1) ..
Customer Based Upgrade: Complete Process (2) ..
Customer Based Upgrade: Complete Process .......
Customer Based Upgrade: Complete Process .....
Customer Based Upgrade: Complete Process .....
Requirements
Benefits of CBU ................
Risks and Issues ..............
Optimization of CBU ........
Summary: Reasons for using CBU ....
Summary ........
SAP Upgrade Offerings .........
Content and Goals .............
Upgrade Projects - Reasons Versus Concerns ......
R / 3 Maintenance Strategy: Maximum Flexibility for Your Transition ........
Options: Upgrade, Extended Maintenance, Customer-Specific Maintenance .............
Justifying the Upgrade Project ............
Most Critical Pain Points at a Glance ..
Challenges of Upgrade Planning and Execution ...
Upgrade Challenges Along the Life Cycle .............
SAP Upgrade Offerings Along the Life Cycle .....
SAP Upgrade Evaluation Services in Detail ........
Safeguarding for Upgrade - Overview .................
Advanced Upgrade Services and Tools in Detail ...................
Upgrade Coach: Scope in Detail ........
SAP Upgrade Roadmap at a Glance ..
SAP Upgrade Road Map - HTML Version .........
SAP Upgrade Roadmap ..
SAP Upgrade Roadmap in SAP Solution Manager ................
SAP Solution Manager attacks known cost drivers ...............
Upgrading with SAP Solution Manager ...............
Critical Pain Point: IT Infrastructure ..
Hardware Sizing ................
Hardware load and capacity check ....
Data Management ............
Archive Quick-wins (for upgrade) .....
Front-End and Upgrade ..
Critical Pain Point: Modification Adjustment ......
Modification and Application adjustment ...........
Development News Browser ..............
Potential Issues after the Technical Upgrade ......
ASU ( Application Specific Upgrade) Tool .........
SAP Modification Clearing Service - Three phases ..............
Critical Pain Point: Testing .................
Motivation ....
Test Management Optimization Service ...............
Critical Pain Point: End user Training ...................
Knowledge Transfer Optimization Service ...........
Use SAP Tutor with SAP Solution Manager .......
SAP Tutor for Customers using SAP Solution Manager ......
Critical Pain Point: Technical Upgrade .................
SAP Upgrade Weekend Support .......
SAP Downtime Assessment: Sample Report .......
Safeguarding for Upgrades - Cost Savings ........
SAP Upgrade Info Center at a Glance ...................
SAP Upgrade Info Center ...................
Order Information .............
Summary ........
Deltas in Upgrades .................
Content and Goals .............
Delta - What is new with 6.x ? .............
New Features 4.6C / D - 6.x: ...................
System Switch Upgrade ....
Upgrade Strategies ............
Downtime 6.10
System Switch Upgrade ....
PREPARE ........
Phase List ......
4.6C - 6.20 .....
ICNV ...............
New Features 6.x ..............
New Features 6.20 (1) ......
New Features 6.20 (2) ......
New Features 6.20 (3) ......
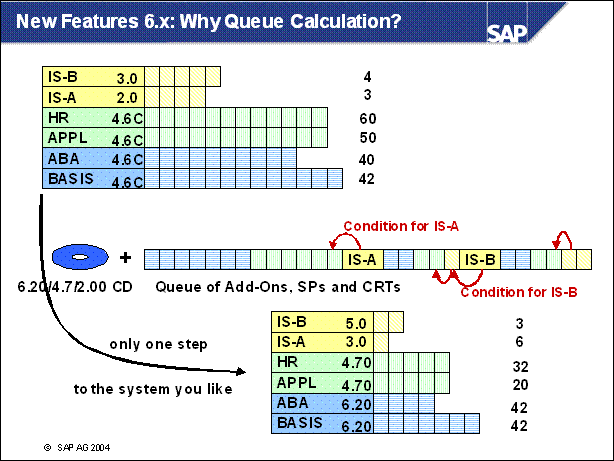
Queue Calculation ............
Improvements in Downtime Reduction ................
The evolution of SAP's upgrade technologies ...
The Evolution of SAP's Upgrade Technologies
Summary ........
MCOD Upgrade ..
Content and Goals .............
MCOD ..............
MCOD ..............
MCOD ..............
MCOD on Oracle ................
MCOD during Upgrade .....
MCOD Archiving ...............
MCOD Restore ...................
MCOD and Upgrade ........
MCOD: Summary .............
Summary ........
Appendix: MCOD on other Databases .................
MCOD on MSSQL / SAP DB .............
MCOD on DB6 .................
MCOD on DB2 .................
MCOD on Informix ...........
Unicode Conversion ..............
Content and Goals .............
What is Unicode? ..............
Languages supported in a Unicode system ..........
Application Impact - MDMP Restrictions ............
Unicode mySAP.com Status and Planning ............
Default Conversion Method ................
Important Notes .................
Prerequisites on the Source System 1 .
Prerequisites on the Source System 2 ...................
Prerequisites on the Source System 2 (MDMP) ..
Prerequisites on the Source System 3 ...................
Prerequisites on the Source System 4 ...................
Prerequisites on the Source System 5 ...................
Actions on the Source System ..........
Important Note for the Export ............
Transferring the Export Files to the Target Host
Actions on the Target System 1 ........
Actions on the Target System 2 ........
Final Activities 1 ..............
Final Activities 2 ..............
Final Activities 3 ..............
Further Information ..........
Summary ........
Appendix .......
Unicode Upgrade at a Glance .............
Unicode Upgrade - Preparation ........
Unicode Upgrade - Preparation ........
Unicode Upgrade - Preparation ........
Unicode Upgrade - Preparation MDMP ..............
Unicode Upgrade - Preparation MDMP ..............
Unicode Upgrade - Preparation MDMP ..............
Transaction UCCHECK ...
UCCHECK - Show Extended Error Messages ....
UCCHECK - Set the Unicode Flag ....
Unicode Upgrade - Conversion ........
Unicode Upgrade - Post-Conversion ...................
Dependencies ...................
Exercises ...............
Solutions ..............
Notes
n R / 3 4.7
n WEB AS 6.20
n 2005 / Q1
n

n Some software products marketed by SAP AG and its distributors contain proprietary software components of other software vendors.
n Microsoft, Windows, Outlook, and PowerPoint are registered trademarks of Microsoft Corporation.
n IBM, DB2, DB2 Universal Database, OS / 2, Parallel Sysplex, MVS / ESA, AIX, S / 390, AS / 400, OS / 390, OS / 400, iSeries, pSeries, xSeries, zSeries, z / OS, AFP, Intelligent Miner, WebSphere, Netfinity, Tivoli, and Informix are trademarks or registered trademarks of IBM Corporation in the United States and / or other countries.
n Oracle is a registered trademark of Oracle Corporation.
n UNIX, X / Open, OSF / 1, and Motif are registered trademarks of the Open Group.
n Citrix, ICA, Program Neighborhood, MetaFrame, WinFrame, VideoFrame, and MultiWin are trademarks or registered trademarks of Citrix Systems, Inc.
n HTML, XML, XHTML and W3C are trademarks or registered trademarks of W3C®, World Wide Web Consortium, Massachusetts Institute of Technology.
n Java is a registered trademark of Sun Microsystems, Inc.
n JavaScript is a registered trademark of Sun Microsystems, Inc., used under license for technology invented and implemented by Netscape.
n MaxDB is a trademark of MySQL AB, Sweden.
n SAP, R / 3, mySAP, mySAP.com, xApps, xApp, and other SAP products and services mentioned herein as well as their respective logos are trademarks or registered trademarks of SAP AG in Germany and in several other countries all over the world. All other product and service names mentioned are the trademarks of their respective companies. Data contained in this document serves informational purposes only. National product specifications may vary.
n These materials are subject to change without notice. These materials are provided by SAP AG and its affiliated companies ("SAP Group") for informational purposes only, without representation or warranty of any kind, and SAP Group shall not be liable for errors or omissions with respect to the materials. The only warranties for SAP Group products and services are those that are set forth in the express warranty statements accompanying such products and services, if any. Nothing herein should be construed as constituting an additional warranty.

n The question in this position should really be: What advantages would an upgrade to the new release bring for me? Does the new release offer me functions that are currently missing or that I urgently require?
n This is a central question, as you should not automatically upgrade as soon as a new SAP R / 3 release comes on to the market.
n The question can be answered with a definite YES, if, thinking strategically, you believe that the release that you are currently using will shortly no longer be supported. Equally, the question can be answered with a definite NO if you are satisfied with the current release.
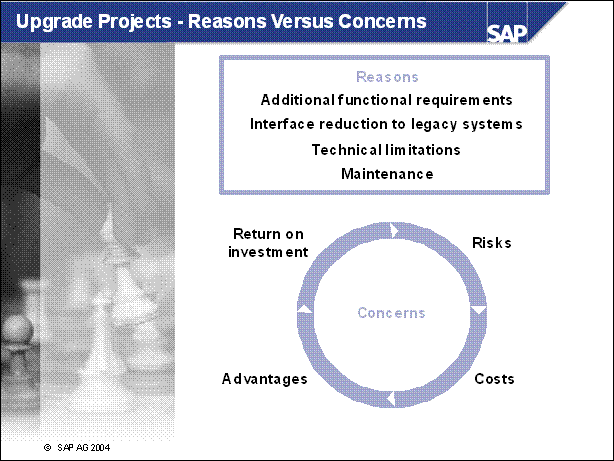
n There are a lot of reasons to upgrade, which can result in direct business benefits. New functionalities in higher releases can potentially replace lots of your modifications, which cost a lot of money to maintain. Furthermore, new functionalities can make your business more efficient.
n Additional functions: SAP R / 3 Enterprise as well as SAP ERP Central Component provide a lot of new functionalities in the application area.
n Technical limitations: The technology is becoming increasingly important in discussions about TCO. But besides this there are other things to consider. An old SAP R / 3 release with older technologies has limitations like addressing bandwidth of memory, performance in general, and so on.
n Reduction of interfaces: Staying with TCO, one of the biggest cost drivers is the number of interfaces used. Non-standard interfaces in particular cost a lot to maintain. With an upgrade to a higher release, many customers see potential in reducing their non-standard interfaces by replacing existing non-SAP systems with the functionality provided. Furthermore, SAP Exchange Infrastructure, which also comes with SAP NetWeaver can help customers to significantly reduce the TCO on the interfacing area.
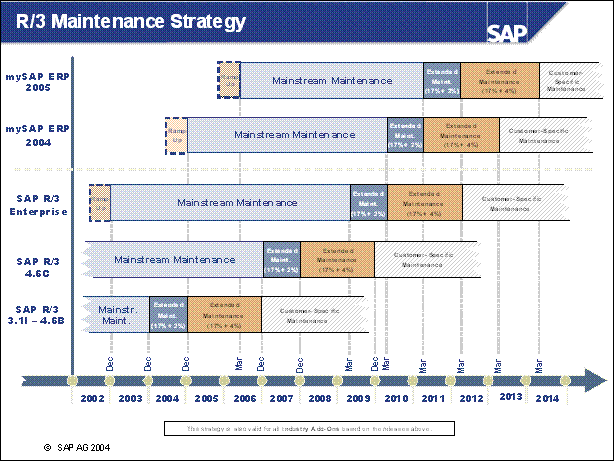
n Maintenance: Finally, the maintenance might also be a driver for some customers. SAP certainly does a lot to ensure that customers are aware of a lot of the reasons already mentioned. But even if the other areas currently offer no benefit to the individual customer, the customer might not need to do an upgrade if the mainstream maintenance has ended. There is also the option to extend the maintenance for a specific timeframe. Customers should consult https: / / service.sap.com / maintenance for more details.
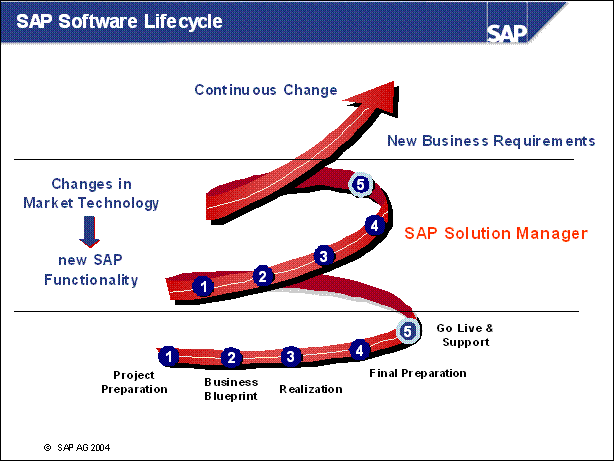
n Change and improvements are integral parts of today's business environment. SAP R / 3 supports and embraces the process of continuous change as:
New SAP functionality becomes available
Market technology changes
New business requirements are defined
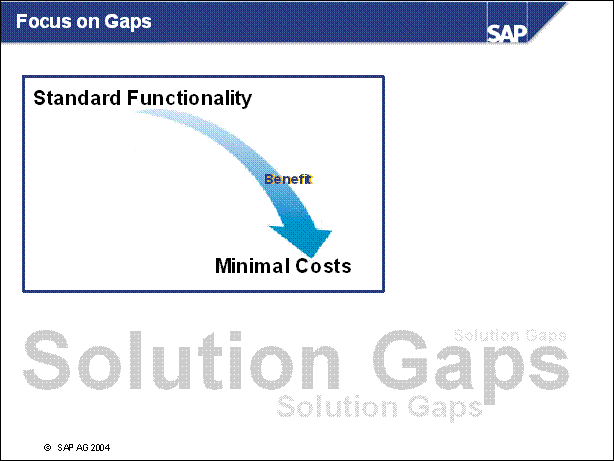
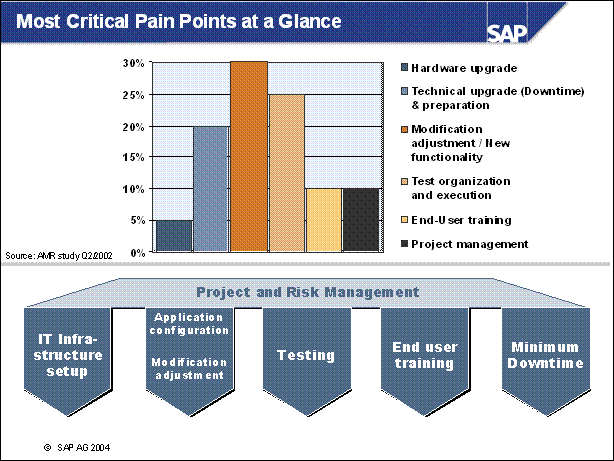
n Focus on the typical problem areas such as solution gaps:
Assuming the customer documented their initial implementation, one of the
easiest things to evaluate during upgrade planning is if any of the original
gaps can be replaced by standard
functionality in the target release
n The benefit to this approach is that it can be done relatively quickly, for a minimal cost. It also aims at an area that is very easy to quantify into tangible savings.
n Review each component of new release functionality. Determine how these enhancements can add value to the customer's operations.

n This documentation describes the upgrade and provides you with additional information on upgrade topics. The information in this documentation is intended for SAP system administrators with operating system, database, and SAP Basis knowledge.
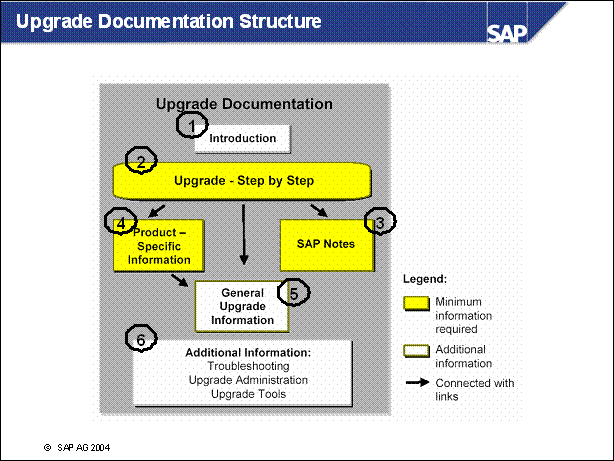
n Introduction:
- New Features in the SAP R / 3 Enterprise Upgrade
n Upgrade
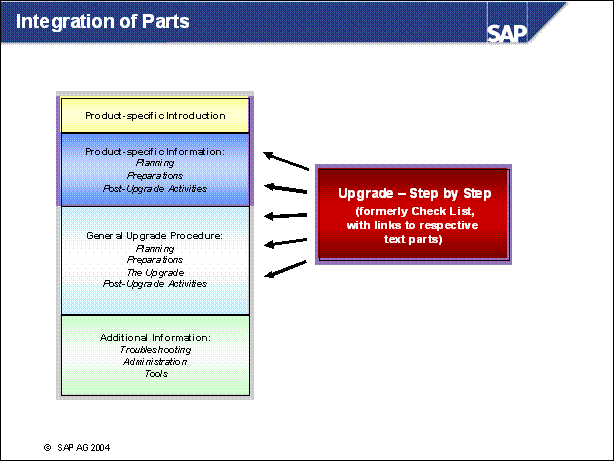
- Step by Step: this section is the core of the documentation.
- Important information, such as user entries
- Links to a detailed description of the action
- Links to any product-specific information about the action
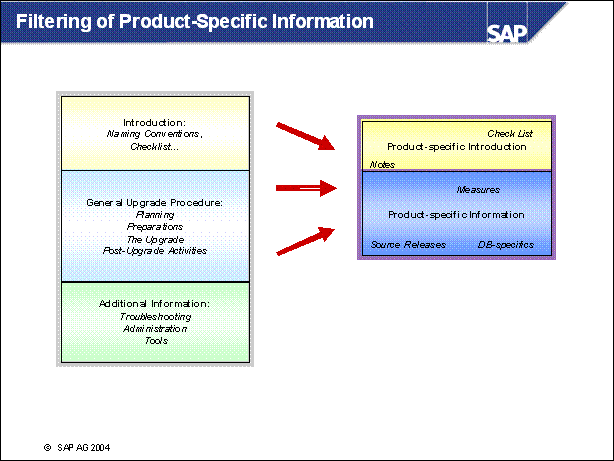
n Product-Specific Information for the SAP R / 3 Enterprise Upgrade: This part of the documentation contains additional information or restrictions on the descriptions in General Upgrade Information, which only affect this specific SAP product. The headings of the sections are the same as the corresponding sections in General Upgrade Information. Each product-specific text contains a link to the general description of the action.
n General Upgrade Information: This part of the documentation is a general description of the upgrade of an SAP system. It contains procedures and background information about the upgrade process flow and the individual actions. However, it does not contain all the information you need for the upgrade of your specific SAP product. For information on any extra details about the upgrade of your product, see the Product-Specific Information part of the documentation.
n Additional
Information: Troubleshooting, Upgrade Administration, Upgrade Tools
These sections contain information on troubleshooting, the administration tasks
you need to perform before and after the upgrade, and the tools that you use to
upgrade the system.
n You can find more detailed information about PREPARE in the Phases of PREPARE unit
n Upgrade Assistant is a graphic-based tool which has been available since SAP R / 3 4.6
n Upgrade Monitor is a new feature of SAP R / 3 4.6. The idea for it comes from the ASCII-based upgrade monitor in SAP R / 3 3.x
n SGEN is a new transaction in SAP R / 3 4.6. It replaces the post-upgrade action with the old report rddgenld. SGEN is redesigned with 6.x
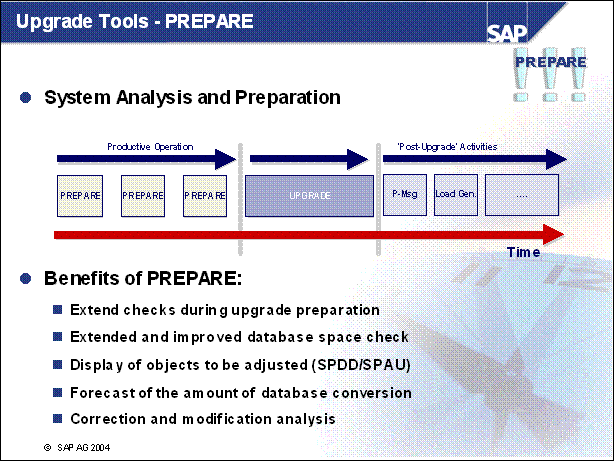
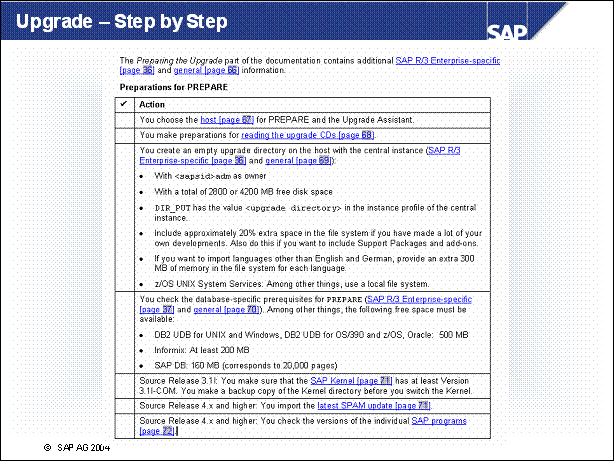
n Careful preparation of the upgrade is the best guarantee that it will run without errors. Extensive checks are required for the upgrade. The PREPARE program uses a series of checks to support the preparation of the upgrade without affecting productive operation. PREPARE can be used entirely on its own and at a different time from the upgrade. Prerequisite: You have finished planning the upgrade.
n Use the PREPARE program to prepare your SAP system for the upgrade.
You can execute this program while the system is running.
It checks the requirements for the upgrade and provides further information when executing the optional module.
Import a number of tools into your database.
It copies data and programs to the upgrade directory.
n PREPARE is based on R3up. Whenever PREPARE is started it starts R3up in a special PREPARE mode.
n PREPARE can always run during production operation.
n PREPARE performs the majority of the required checks automatically. Afterwards, you must also check the operating system, database and SAP R / 3 system manually as well.
n IMPORTANT: PREPARE can reduce performance during operation.
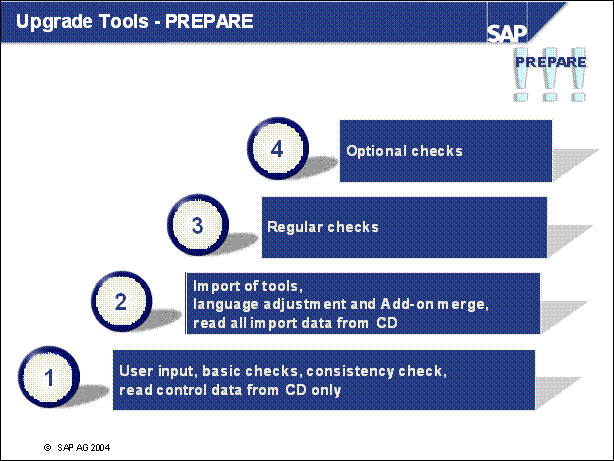
n PREPARE is divided into 4 levels.
n Level 1 can be started at any time
n Level 2 is performed only once
n Level 3 includes all checks requiring short run times
n Level 4 includes long running jobs:
Calculate modification adjustments
Calculate repository transfer
Calculate future inconsistencies in the ABAP Dictionary
Run an extended free space check
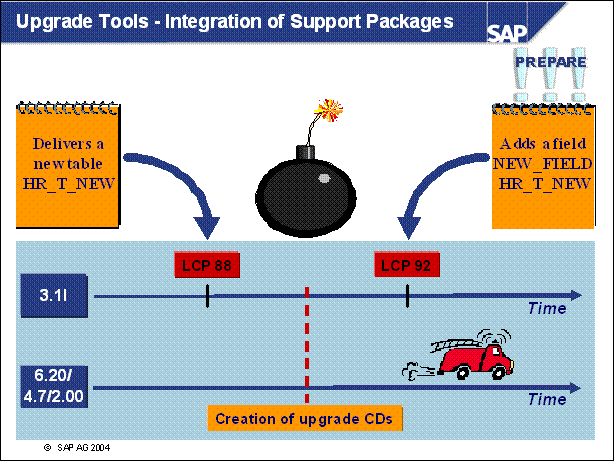
n The motivation for integrating Support Packages into the upgrade is demonstrated by the following scenario:
SAP R / 3 3.1I Legal Change Patch 88 delivers a new table HR _ TAB _ NEW, belonging to the HR module
The table HR _ TAB _ NEW is also used in SAP R / 3 6.20 / 4.7 / 2.00
At a specific point in time, the SAP R / 3 6.20 / 4.7 / 2.00 upgrade CDs are created
Later on, SAP R / 3 3.1I Legal Change Patch 92 adds a field NEW _ FIELD to HR _ TAB _ NEW (for example, because of changed tax requirements).
The upgrade CDs still contain the old version of HR _ TAB _ NEW without field NEW _ FIELD delivered. Therefore the upgrade (SAP R / 3 3.1I, LCP 92 to SAP R / 3 6.20 / 4.7 / 2.00) assumes that the field NEW _ FIELD is obsolete and it will delete NEW _ FIELD without any comment.
=> Corresponding SAP R / 3 6.20 / 4.7 / 2.00 HR Support Packages must be integrated into the upgrade
n Data loss is possible if you ignore this fact.
n For Support Packages other than HR Support Packages it is assumed that there are no structural changes and the possibility of data loss is very small.
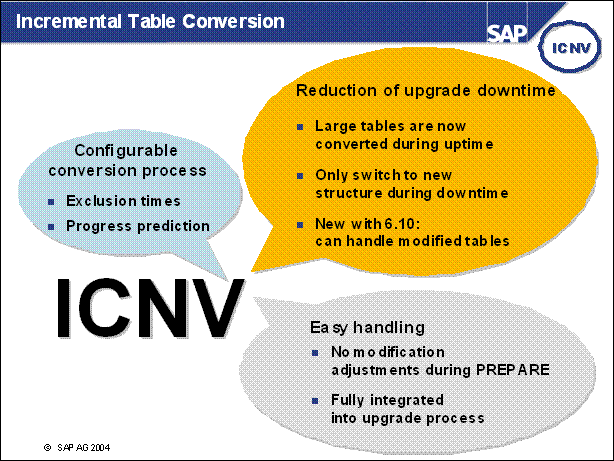
n With each new release, the structure of the tables in your database changes. These table conversions used previously only occured during the upgrade downtime (e.g. phase PCON). By using incremental conversion, you can convert many of these data records before the upgrade. Advantages of ICNV:
Reduced downtime during the upgrade, because a large number of tables will be converted during uptime.
You can return to the SAP standard more easily for modified tables.
You can use incremental conversion for large tables as well.
n Incremental table conversion is performed using transaction ICNV. You can use the following functions:
Display the tables determined by PREPARE (tables for conversion with ICNV)
Choose which tables you want to convert incrementally.
Start the conversion.
Monitor the conversion.
Estimate the runtime of the conversion.
n You can define the time during which ICNV should not be executed.
n ICNV gives you information about the progress prediction
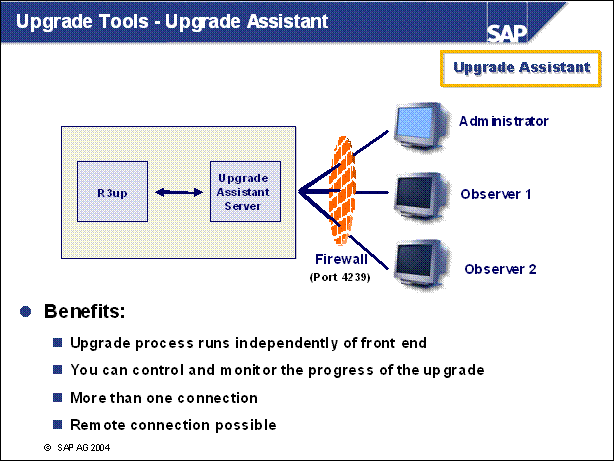
n Functions:
You can control and monitor the progress of the upgrade from a number of different places.
Front end and upgrade processes are divided into separate components so that the entire upgrade does not terminate if a connection fails. This provides optimal support for a remote upgrade.
You have an alert mechanism that lets you start an external program.
Optimal support for a remote upgrade.
Standard TCP / IP ports for the Upgrade Assistant are 4239 (Http) and 4241 (locally installed version)
n Prerequisites: The Upgrade Assistant (server and GUI) is implemented in Java. This means that it requires a Microsoft Virtual Machine for execution (Version 1.1x or preferably higher).
Microsoft SDK for Java (Microsoft Virtual Machine)
Requirements for the server of the Upgrade Assistant (Server) Make sure that the Microsoft Virtual Machine is installed on the host on which you want to start the server.
Requirements for the user interfaces (GUIs) of the Upgrade Assistant Make sure that the Microsoft Virtual Machine is installed on the host on which you want to start the GUI. The Upgrade Assistant GUI can also be executed in a Java-1.1-compatible browser. If you want to use this option, make sure that Microsoft Internet Explorer 4.0 is installed on the host on which you want to start a GUI.
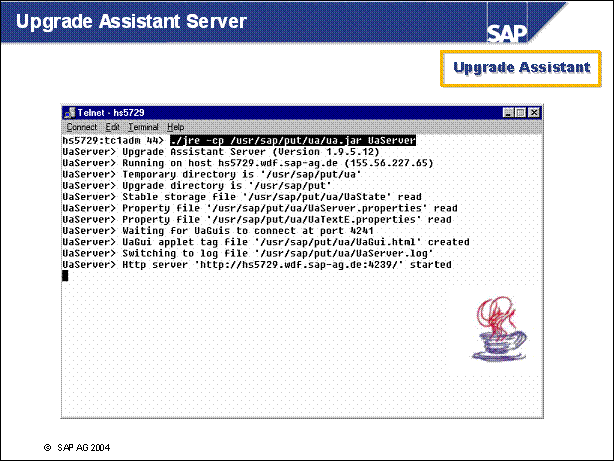
n To get the Upgrade Assistant tools, you must start PREPARE once directly from the CD.
The tools will be unpacked to the directory / usr / sap / put / ua
n Once you have started the server, you can start an Upgrade Assistant GUI. We recommend calling the GUI from the Internet browser.
n To start the Upgrade Assistant Server, proceed as follows:
Change to the drive where the directory <UpgDir> is located.
When using the Microsoft Virtual Machine for a UaServer and a UaGui, enter the following:
jview / cp <UpgDir>\UA\ua.jar UaServer
n The assistant server process should be started as long as you use the Upgrade Assistant GUI
n Once you have started the server, you can start an Upgrade Assistant GUI. Start the GUI as follows:
When using the Microsoft Virtual Machine:
jview / cp <UpgDir>\UA\uagui.jar UaGui
When using Microsoft Internet Explorer:
In the field Address, enter the following address:
https: / / <host _ name>:4239
<host _ name>: Name of the host on which the Upgrade Assistant is running.
n To display a description of the Upgrade Assistant with all its functions, choose Help Introduction in the main menu.
n Once you have started the server, you can start an Upgrade Assistant GUI. Start the GUI as follows:
When using the Microsoft Virtual Machine:
jview / cp <UpgDir>\UA\uagui.jar UaGui
When using Microsoft Internet Explorer:
In the field Address, enter the following address:
https: / / <host _ name>:4239
<host _ name>: Name of the host on which the Upgrade Assistant is running.
n To display a description of the Upgrade Assistant with all its functions, choose Help Introduction in the main menu.
n You can log on to Upgrade Assistant with different roles.
n Administrator:
Power user gets full functionality of Upgrade Assistant
Standard password is "admin"
This user can be logged in once
If the administrator logs on, another active administrator will be switched to user observer
n Observer:
This user can only monitor the upgrade
User standard password is "observer"
This user can be logged on several times
An observer can take over the administrator role
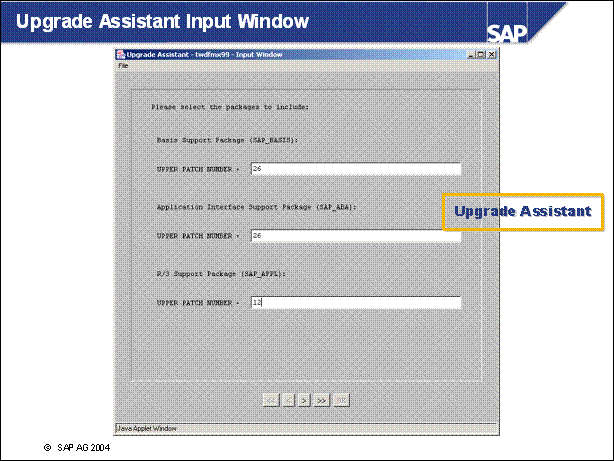
n Each time the upgrade needs input, an input window will appear and wait for input.
n The slide shows the input window for the PREPARE Phase BIND _ PATCH.
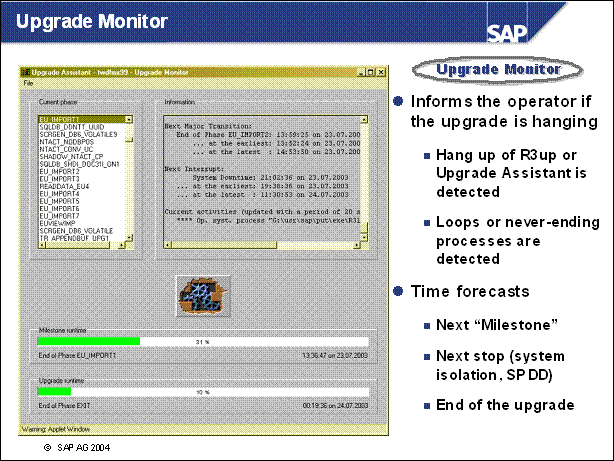
n The Upgrade Monitor lets you monitor the upgrade, and helps you recognize any processes that have stopped. It contains the following functions
The monitor estimates the time when the upgrade will end, as well as other important stages (milestones).
These estimates are based on SAP reference times and the runtimes of upgrade phases that have already completed. The more advanced the progress of the upgrade is, the more precise the estimates are. If possible, the runtime estimate also includes any runtime that is lengthened for systematic reasons, however this is subject to restrictions. Systematic fluctuations can also occur if the upgrade phases run more quickly than expected. This means that the end of the upgrade cannot be estimated precisely.
n The total runtime of the upgrade and the runtime of the next milestone appear as bar graphs. As long as the runtime has not been exceeded, the bar appears in green. If the runtime has been exceeded, the bars appear first in yellow and then in red.
n An animated graphic displays the activity of the upgrade processes. If the graphic is not moving, one of the upgrade processes is stopped. This may be the Upgrade Monitor, the Upgrade Assistant or the R3up program.
n The upgrade processes that are running appear under Current activities. The monitor does not recognize any subprocesses of these processes, and therefore cannot display them. Note that the process bar is updated only every 60 seconds.
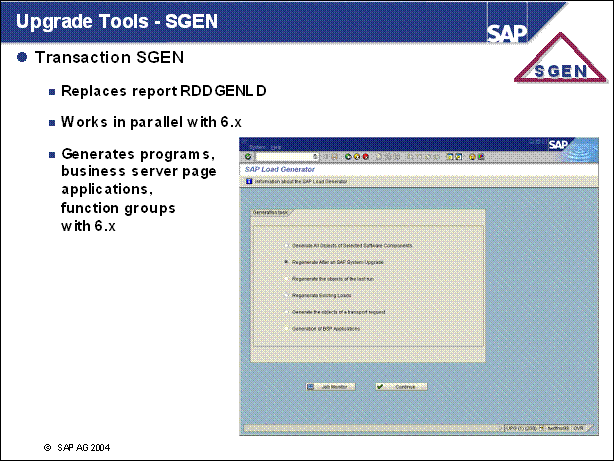
n With SAP R / 3 4.6, the report RDDGENLD is replaced by transaction SGEN.
n With SAP 6.x SGEN generates loads in parallel. In addition to programs SGEN can now generate business server page applications, function groups etc.
n The most important ABAP loads for the Basis system are upgraded with the new release. However, there are not yet any generated ABAP loads for all of the transactions from the different SAP application areas. When you call a program, a load is automatically generated if it does not already exist. This may, however, reduce production system performance. To avoid this, you can use transaction SGEN to generate the missing loads.
n Recommendation: If possible, generate the loads directly after the upgrade.
n For a detailed description of the features, see the online documentation in transaction SGEN by choosing Information on the SAP Load Generator, or in the Job Monitor by choosing Job Monitor.
n For more information on the free space requirements in the load tables, see SAP Note 18606

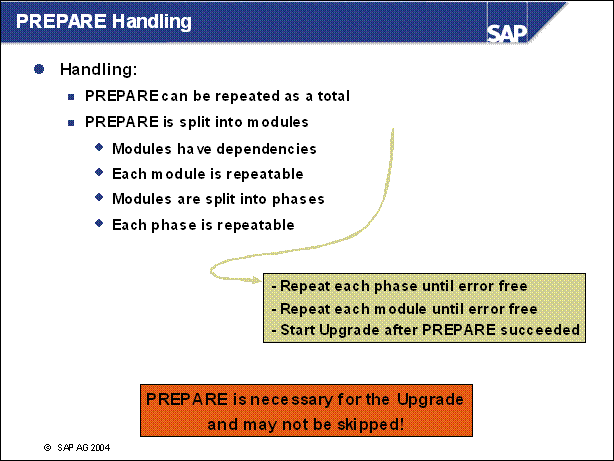
n PREPARE can be repeated as often as you want. Even if a previous PREPARE completely finished successfully.
n In some few cases, errors can be ignored. For example, if PREPARE complains about lacking space in Oracle Tablespace but the AUTOEXTEND is switched on für these tablespaces.
n If a phase stopped with an error message you have to repeat the phase. If a module finished with the status , failed' you have to reselect it and execute it again.
n All modules have to be finished successfully before you can begin with the upgrade.
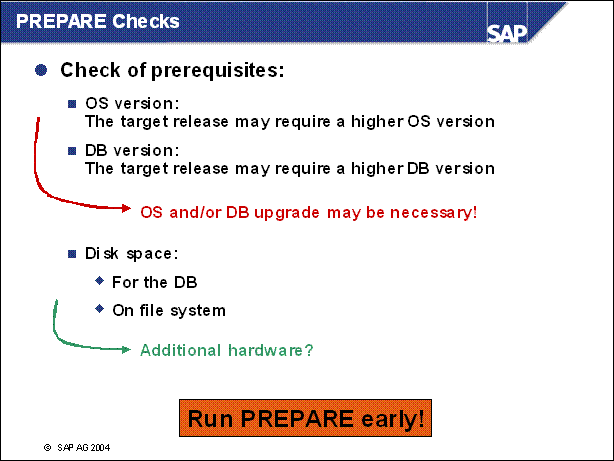
n A possible reason for the failure of a module may be the requirement of higher OS or DB version. Also it may be necessary to enlarge your file system or to add files to the database. That's why we recommend to run the Prepare early that you have enough time to react.
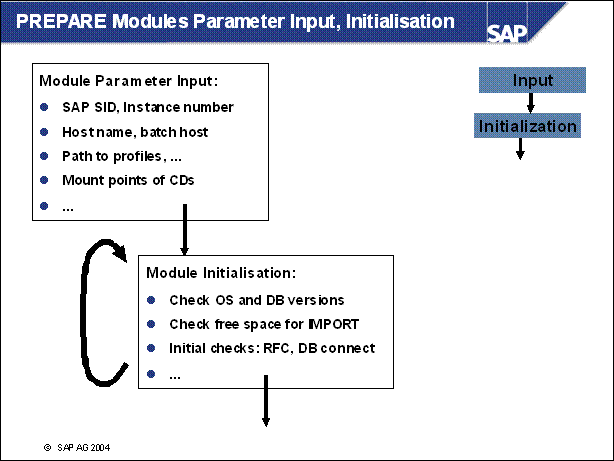
n The parameters you enter in the module , parameter input' you can change afterwards by calling R3up with the option set param. After the parameters are entered, the module 'initialization' starts the first checks.
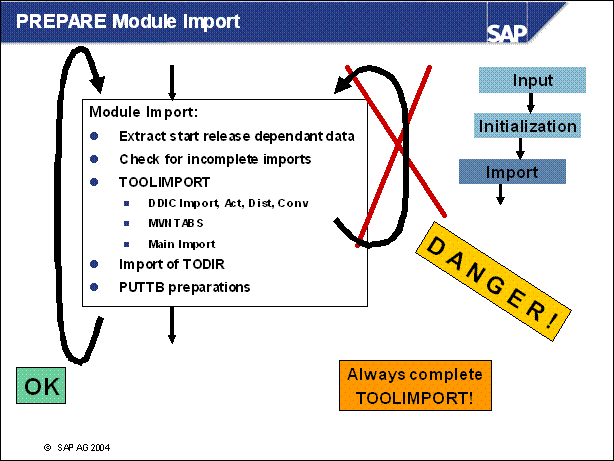
n To the module 'import' we can say that it is very important to complete the tool import. If an error occurs you must not reselect the module.
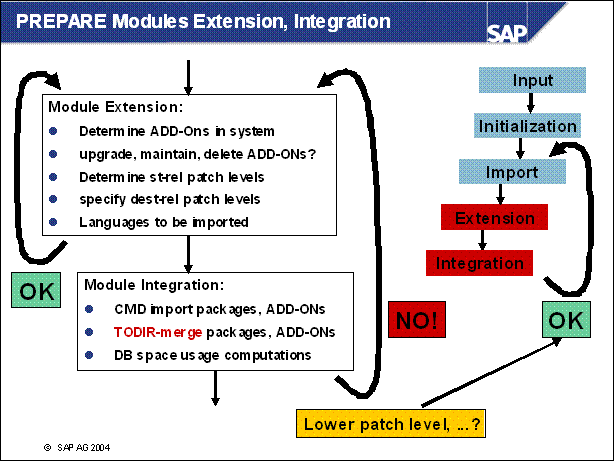
n If you have entered the wrong patch level of Support Packages you want to bind to the upgrade, you can repeat the module extension. If the module 'integration' is already finished then you must also repeat the module 'import'.
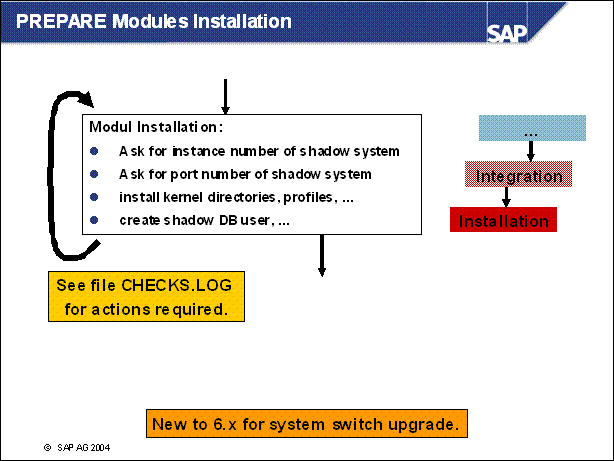
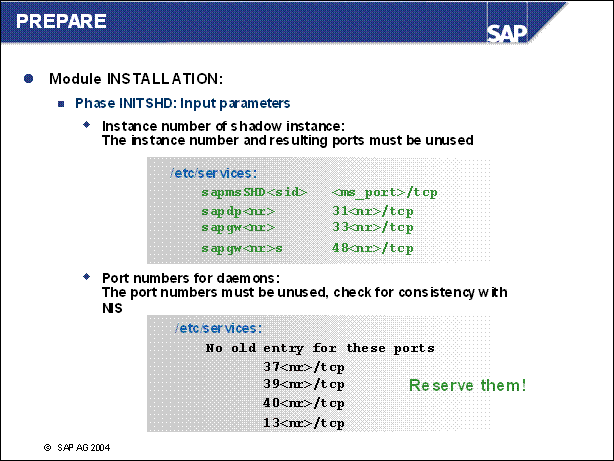
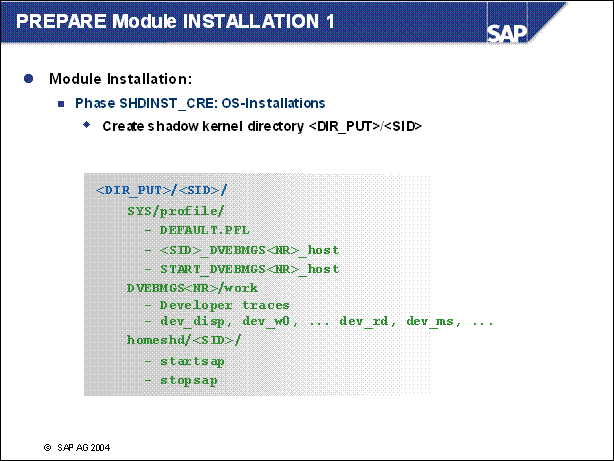
n This is the new module installation. In here you are asked for the parameters of the shadow instance. The shadow instance will then be installed and the shadow schema will be created in the database.
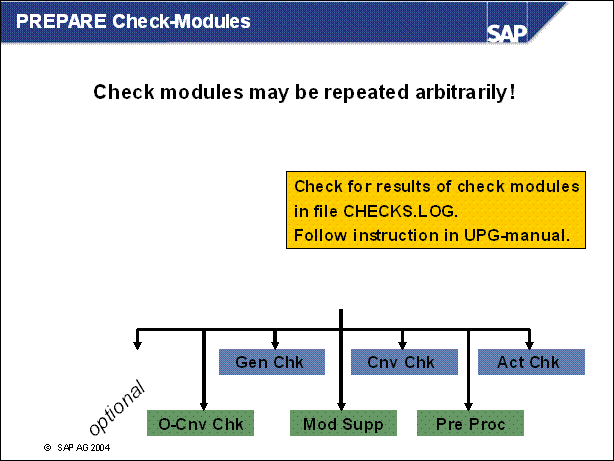
n You can execute every check module as oft as you want. You don't have to comply with a special order. The results are listed in the file CHECKS.LOG.
n although some modules are classified as 'optional', they should be executed in any case. They contain important checks, you don't want to miss.
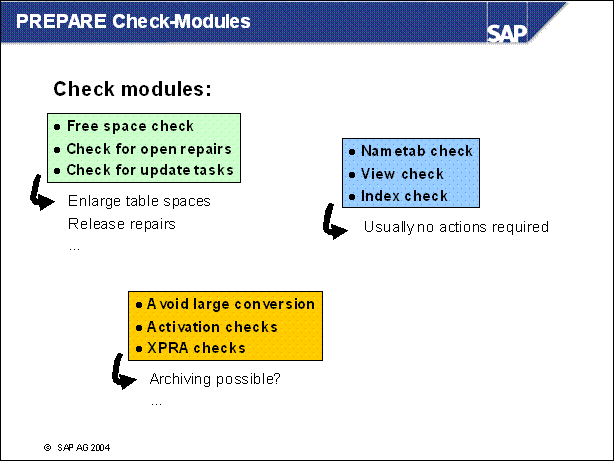
n Check the SAP system for open or erroneous updates (via transaction SM13)
n If an outstanding upgrade is not executed successfully before the upgrade, it might not be postable after the upgrade. For example, when the tables being used in the respective update tasks have been converted during the upgrade (PCON Phase)

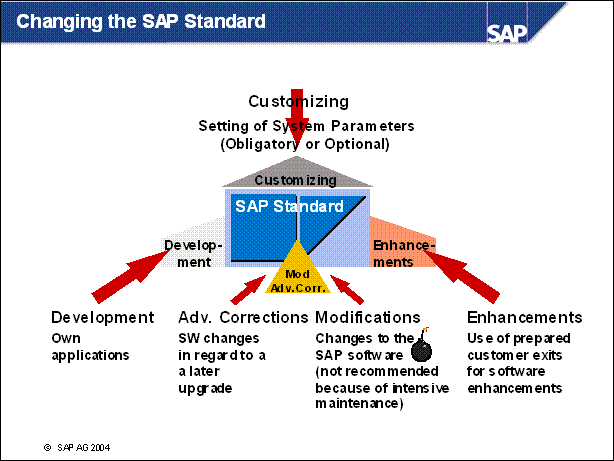
n There are five types of SAP R / 3 system changes:
Customizing:
Involves setting system parameters using the special Customizing transaction.
Changes are scheduled and organized in advance. Customizing is mandatory before
using the SAP system in a live environment.
Customer developments:
Creation of customer-specific objects according to naming conventions.
Enhancements:
Customer changes to SAP Repository objects without the need for modifications.
Modification:
Customer-specific changes to SAP Repository objects. When SAP objects are
changed, the customer version has to be modified to match the new SAP version.
Advanced correction:
Apply bug fixes from SAP directly to the SAP system. The SAP Online Correction
Services (OCS) provides SAP Support Packages to avoid having customers modify
SAP objects manually.
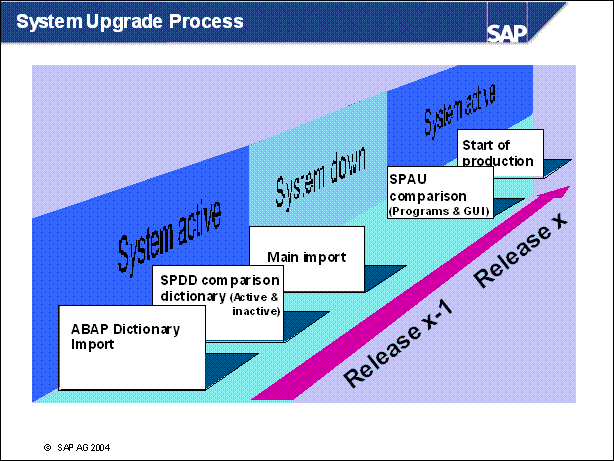
n The start of the upgrade process involves the transfer of new data to the system from the shipped CDs. SAP Repository objects are imported into the system and the customer objects are compared. All SAP ABAP Dictionary objects that have been modified by customers must be compared to the new SAP standard during this upgrade process.
n In order to avoid loss of data and table fields that customers may have created, conflicting structures must be merged before the mass activation of Dictionary objects in the upgrade process.
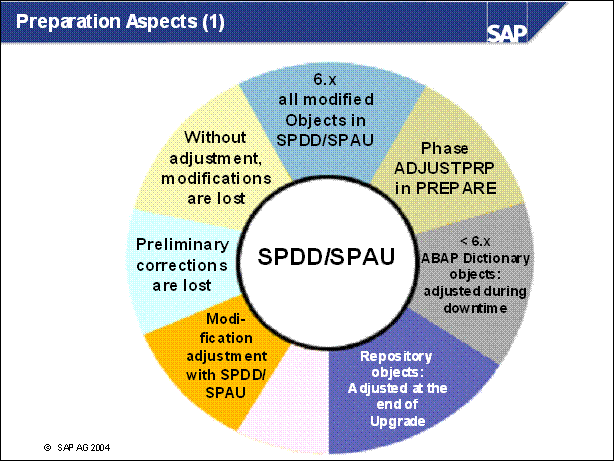
n If objects need to be adjusted, use the transactions SPDD and SPAU. All modifications made by customers are then merged with the new SAP object versions to retain data; otherwise, the new SAP version will be activated and data may be lost.
n Upgrades to < 6.10: The system is not available during the activation phase. During this time, data tables are converted and activated. Depending on the data volume, this transfer of data and mass activation may take several hours.
n Upgrades to >= 6.10: The system is available during the activation phase. The activation takes place on the shadow instance.
n After the activation phase is completed, the system has been adjusted to the new release. The new Repository objects and the new SAP Kernel are active.
n When the upgrade is completed, the SAP system is successfully running at the new release level. Customer developed objects and modifications have been preserved.
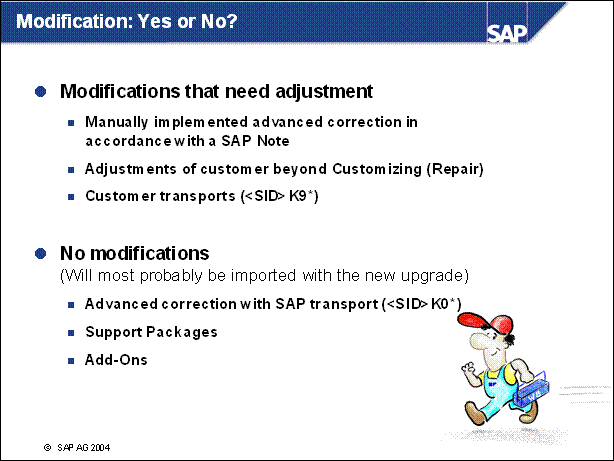
n When you upgrade the system, you lose any modifications you made to objects that conflict with SAP modifications. The modification adjustment lets you make your modifications to the appropriate new objects in the upgrade.
n You can identify modifications as repairs to the SAP standard or as imports of SAP objects. Requests in the customer namespace (number range 900000 to 999999) "modify" the SAP objects included in them. All other requests are dealt with as preliminary corrections.
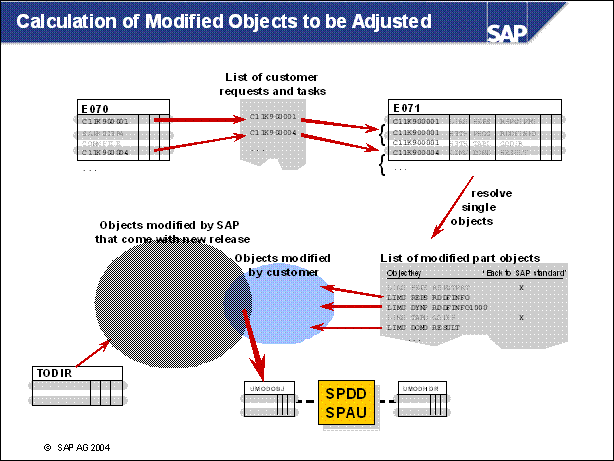
n The list of objects that have to be adjusted in your SAP R / 3 System is determined in the ADJUSTPRP phase. This phase is executed in the PREPARE module Modification Support, and runs in the upgrade between the import of the substitution set and the end of the production period. You must consult the authors of the modifications named in the log UMODPROT. <SID> in the sub-directory log of your upgrade directory to get background information on the changes made.
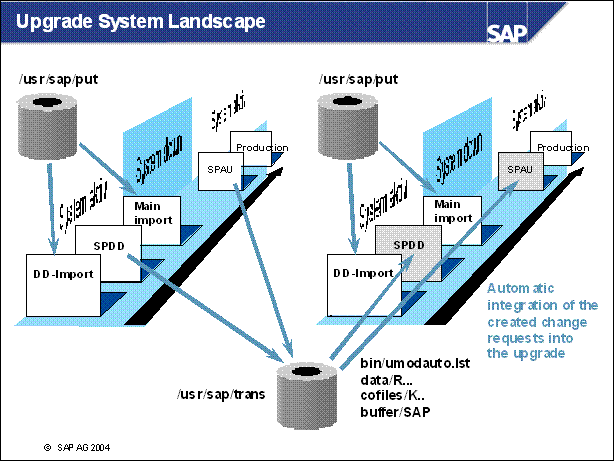
n The ABAP Dictionary objects (tables, data elements, domains, and so on) are adjusted during downtime before the activation of the ABAP Dictionary. The adjusted objects are collected in a repair that is released to a transport request. You cannot release this transport request; instead it must be flagged for export in transaction SPDD. Towards the end of the upgrade, R3up exports this transport request into the transport directory / usr / sap / trans (UNIX), and then registers it for transport in the file umodauto.lst.
n Repository objects (reports, screens, and so on) are adjusted towards the end of the upgrade. At this stage, the import of SAP objects has already been completed. However, the old, modified version is still available in the versions database. As with ABAP Dictionary objects, all adjustments are released to a transport request that is noted and then exported and registered by R3up.
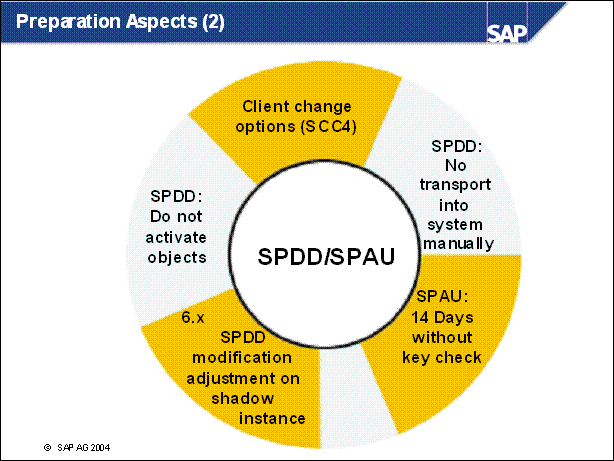
n SPDD: Any requests for automatic adjustment from previous upgrades can be included in this upgrade only in the PREPARE phase ADJUSTPRP.
n Do not attempt to import adjustment transport requests into the system manually during SPDD. This leads to the loss of data in customer fields.
n Upgrades to < 6.10: Transaction SU01 does not work now. If you want to create a user for the adjustment at this point, use the report program UPGADDUSR. You still need the authorization for creating users. UPGADDUSER creates the adjustment user upg _ tmp _ user with the password init in the client where you run the report. This user is valid for a week.
n Do not activate any objects. Activation is carried out automatically after the adjustment.
n If errors are reported when you activate your own developments after executing this phase, you can correct these here, since R3up stops when errors occur. However, you also have the option of choosing Ignore to temporarily ignore these errors. You do not need a password to do this. If you chose Ignore here, you must activate these objects after the upgrade.
n After you have completed the upgrade you have a maximum of 14 days to execute transaction SPAU without a key check (SAP Software Change Registration) for the objects that you changed.
n For further information, see the upgrade manual and online application help for SPDD / SPAU
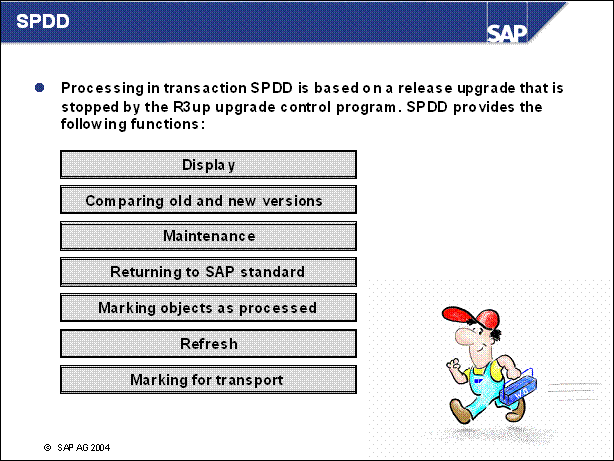
n Display Within individual development classes or corrections, the objects are displayed according to type. To view a changed object, select it with a double-click. You are automatically shown an overview of all existing versions of the selected object.
n Comparing Old and New Versions Selecting an individual object lets you view all existing versions of the object stored in version management. The display is the same as the one with which you are presented when you compare two objects in version management. The information reflects the status of the objects after their activation. For example, a comment in a table field indicating deletion means that the field will be deleted after activation, provided no maintenance is carried out beforehand.
n Maintenance Transaction SPDD lets you compare the most important attributes of old (customer) and new (SAP) versions of domains and data elements. This helps you to decide how to proceed. Perform the adjustments required in transaction SE11, preferably in a second window.
n Returning to SAP Standard If, after comparing the results of the analysis, you conclude that you do not wish to retain previous modifications, choose Return SAP stand. for the object in question. For example, you may need this function if you have patched an object by hand. When SAP delivers the same patch, together with other corrections in the next upgrade, you can revert to the SAP standard because you no longer need your own modification.
n Marking Objects as Processed To facilitate work with the generated object list, you can assign the status Completed to each object. Selecting the function changes the status of the object and indicates this by highlighting it with a different color. The completed flag is meant only to assist you in organizing your work and has no other internal function.
n Marking for Transport The Select for transport function helps you to adjust other SAP systems
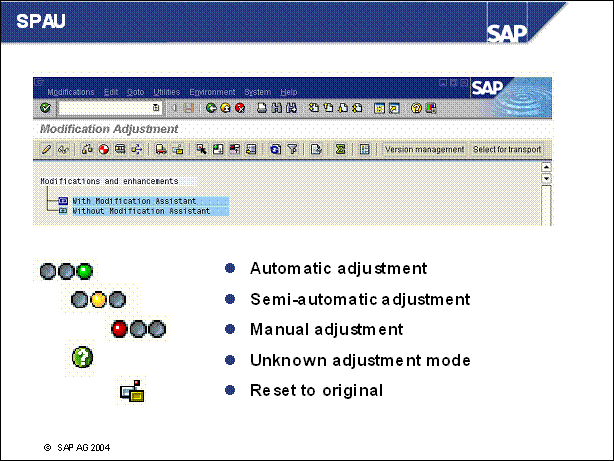
n Automatic adjustment Customer modification can be automatically adopted. Clicking on the icon causes the system to automatically adjust the object. (Only With Modification Assistant category
n Semi-automatic adjustment Semi-automatic means that each tool will individually offer you support during the adjustment process. When adjusting programs, the splitscreen editor is called, whereas in the other tools any entries made in the collision dialog box lead to the necessary adjustments being made automatically. As with the green traffic light, the semi-automatic adjustment icon only appears in the with Modification Assistant category
n Manual adjustment Objects in the Without Modification Assistant subtree can only be post processed manually after the adjustment process. Manual adjustment means that you must make modifications without any special support from the system. Use the log as a help. Using Version Management, you can retrieve old versions or use your recordings to process the newly imported objects. In rare cases, the red traffic light may also appear in the With Modification Assistant category
n Unknown adjustment mode The adjustment mode (manual, semi-automatic, automatic) for at least one of the objects in question could not be determined for modification adjustment with the Modification Assistant. If this is the case and you start transaction SPAU, a dialog box informs you that you can start a background process by choosing the appropriate pushbutton which determines the adjustment modes for all objects.
n Reset to original If you choose Reset to original for an object displayed in the overview, no modifications are adopted for this object. The original is the version that was last imported into the SAP R / 3 system during an upgrade or the application of a Support Package.
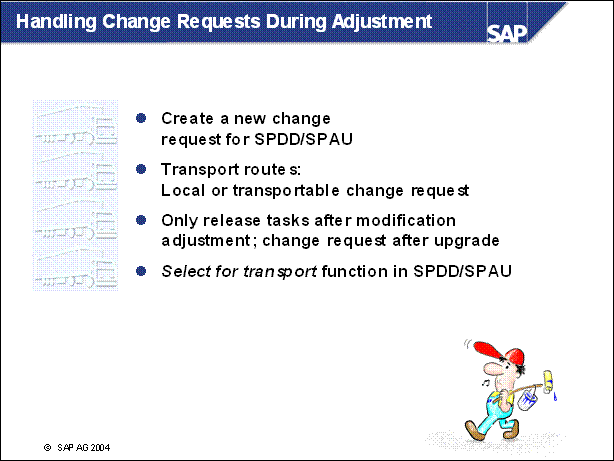
n The configuration of the transport routes in the SAP system determines whether changes to objects during modification adjustment are recorded in a local or transportable change request. You cannot and must not change these settings during the upgrade. In all cases, the change request can still be used for automatically transferring modifications to a subsequent system. For this procedure, the change requests are not released in the normal way, but handled specially. Do not change the configuration of the transport routes in your system group during the upgrade.
n When modification adjustment has been completed, release your tasks. The tasks are the repairs and / or corrections that were automatically assigned to you when the change request was created. Do not release the change request at this point if you want to use it to automatically transfer the modification adjustments to subsequent systems During the adjustment of the ABAP Dictionary objects, releasing requests is locked until the edited objects have been activated. Do not release these requests until after the upgrade.
n To automatically transfer modifications to a subsequent system when you have completed modification adjustment, use the Select for transport function in SPDD or SPAU. If your modifications are recorded in several change requests, you first have to place all entries in a single request. Several requests cannot be marked for transfer.
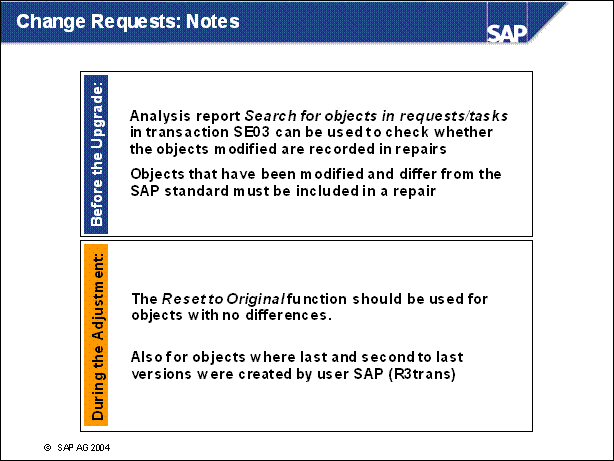
Before the upgrade:
n You are not sure whether all modifications to SAP
objects were carried out with the system change option All objects (with
correction system).
Check whether the objects you modified are
recorded in repairs. To do this, you can use analysis report Search for objects
in requests / tasks in transaction SE03.
n No repairs or customer transports are displayed by the Transport Organizer (SE01) and the Workbench Organizer (SE09), although you know that objects have been modified in the SAP system Indicate the objects that have been modified and differ from the SAP standard by including them in a repair and subsequently releasing it.
n During the adjustment:
n No differences are found when you compare the second to last and third to last versions: During the last upgrade you did not perform adjustments to retain changes you had made to objects. Indicate that modifications to these objects are no longer needed with the Reset to original function.
n The last and second to last versions were created by user SAP (R3trans): During the last upgrade you did not perform adjustments to retain changes you had made to objects. Indicate that modifications to these objects are no longer needed with the Reset to original function.
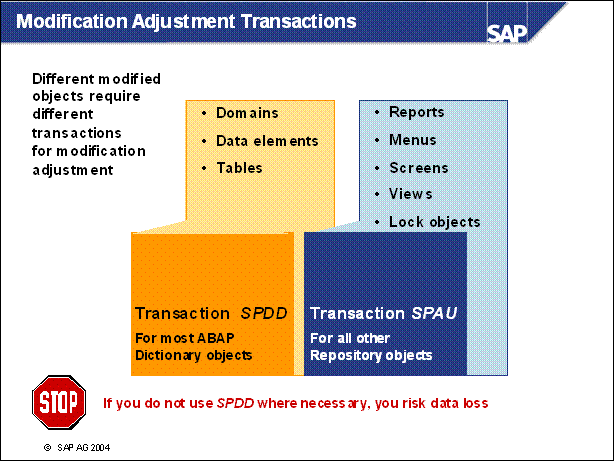
n Transaction SPDD is used to perform modification adjustment to certain ABAP Dictionary objects such as domains, data elements, table structures, transparent tables, pooled tables, cluster tables, and table technical settings. Not performing modification adjustment for these objects would cause data loss.
n After activating the new Repository, transaction SPAU is used to perform modification adjustment for objects for which not performing modification adjustment would NOT lead to data loss. These objects include:
Some ABAP Dictionary objects (lock objects, views etc.)
All other Repository objects (such as module pools, ABAP programs, function modules, menus, and screens)
After running transactions SPDD and SPAU, all modifications have been incorporated into the new SAP release.
n As of SAP R / 3 4.0, pre-upgrade use of PREPARE to upgrade tools to check which modified objects need adjustment enables you to better plan the time required for using transactions SPDD and SPAU.
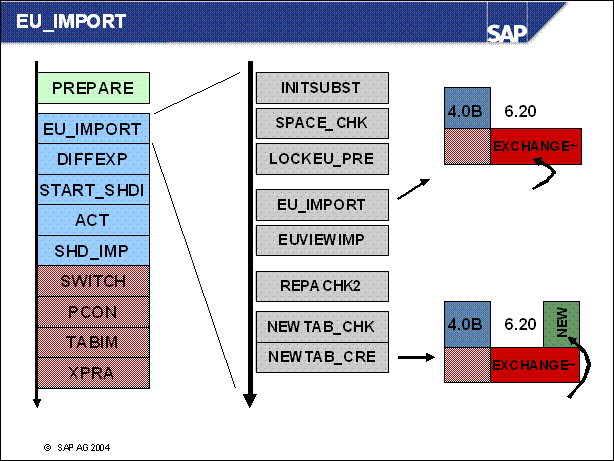
n INITSUBST: initialization of the system switch upgrade
n SPACE _ CHK: check of free space in the database
n LOCKEU _ PRE: asks for the point of time when the Workbench has to be locked
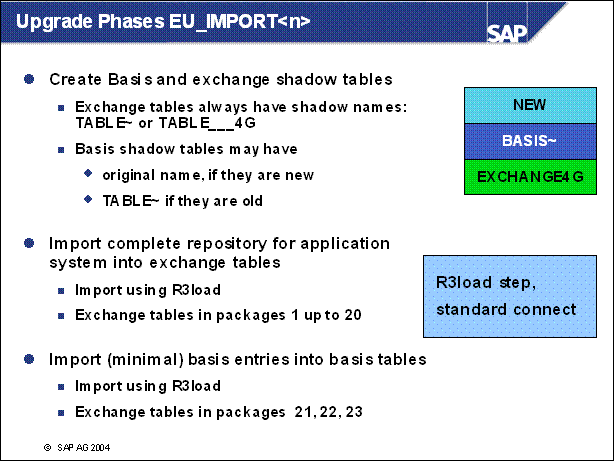
n EU _ IMPORT: tables which can be exchanged are imported into the shadow
n EUVIEWIMP: views are imported into the shadow
n REPACHK2: determination of locked SAP objects
n NEWTAB _ CHK: determination of new tables in this system
n NEWTAB _ CRE: tables that don't exist in the current repository are created
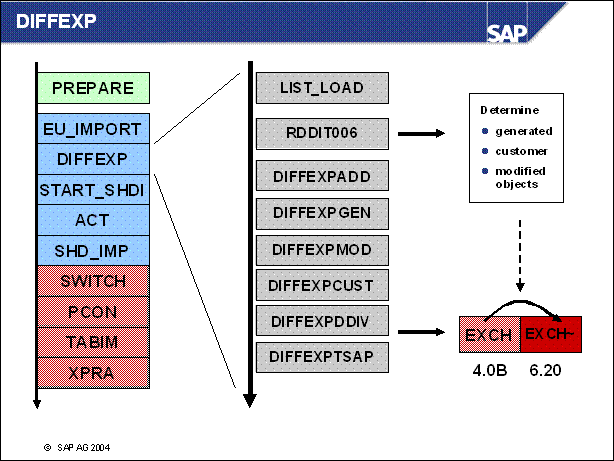
n LIST _ LOAD: creation of a list which programs have to be generated
n RDDIT006:
determination of the objects which have to be adopted
This job calculates which objects of the current repository will be copied to
the shadow and which are saved for modification adjustment.
n DIFFEXPADD: transfer of dictionary parts of add ons
n DIFFEXPGEN: transfer of dictionary parts of generated objects
n DIFFEXPMOD: transfer of dictionary parts of modified objects which are not changed in the target release
n DIFFEXPCUST: transfer of dictionary parts of customer objects
n DIFFEXPDDIV: transfer of inactive ABAP-Dictionary versions
n DIFFEXPTSAP: transfer of local private objects and test objects of the SAP name space
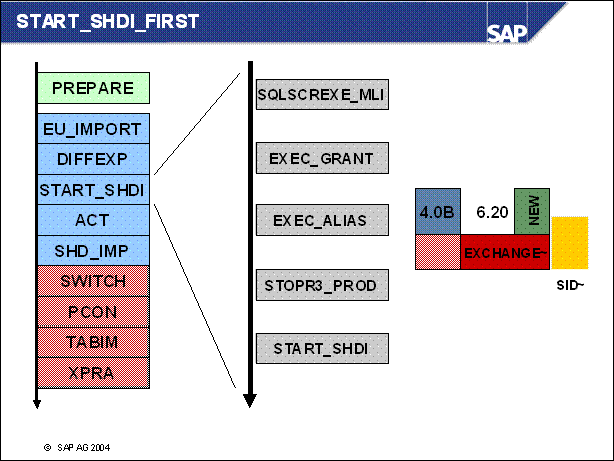
n SQLSCREXE _ MLI: installs the license for the shadow instance
n EXEC _ GRANT: specifies the grants for the user of the shadow instance
n EXEC _ ALIAS: creates the synonyms and aliases in the shadow schema
n STOPR3 _ PROD: for the resource minimized strategy this is the point where the producive system is stopped
n START _ SHDI _ FIRST: now the shadow instance is started
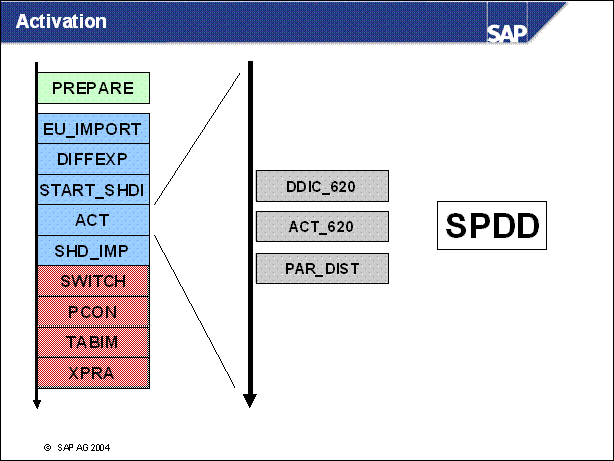
n In phase DDIC _ 620 you are asked for a transport with the result of SPDD of maybe the DEV system.
n In phase ACT _ 620 the customer objects are activated. Maybe this needs adjustment via SPDD.
n PAR _ DIST starts the distributor. The distributor makes entries in table TATAF for every database object which can be changed by an SQL Statement. For every table that has to be converted it makes entries in table TBATG.
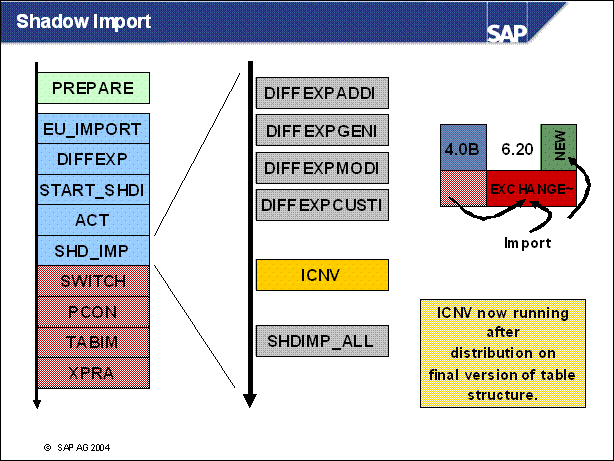
n Here in this DIFFEXP phases the main import of generated and customer objects takes place. These are imported from the current repository.
n Very important. The ICNV is running now when the final structures of the tables are defined. This means that not only large tables that go back to SAP standard are converted, but also tables that are changed by Support Packages of customer modifications.
n SHDIMP _ ALL imports new data into the new tables and the data of Support Packages and add ons into the exchange tables.
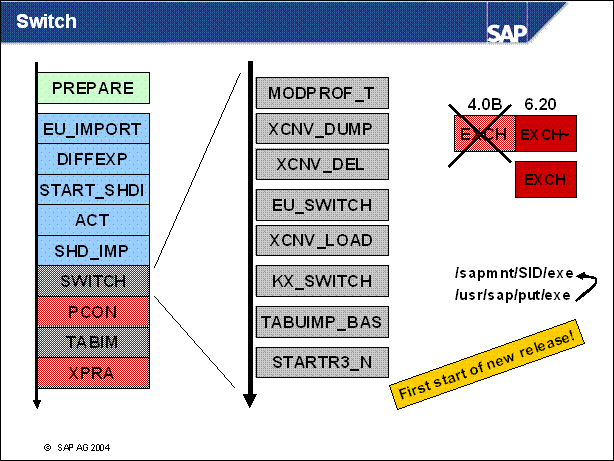
n With the downtime minimized stragety the production system is stopped in phase MODPROF _ TRANS.
n To convert basis tables the system has to be down, but then the conversion can not be done by an ABAP program. So, first these tables are exported to the filesystem in the phase XCNV _ DUMP. After the successful export these tables are deleted in phase XCNV _ DEL. Now the system switches to the new repository. This is done in EU _ SWITCH. In phase XCNV _ LOAD these tables are converted by an external porgram an imported into the new repository. The kernel gets exchanged in phase KX _ SWITCH, some basis tables are imported in TABUIMP _ BAS and the new release starts the first time with STARTR3 _ NBAS.
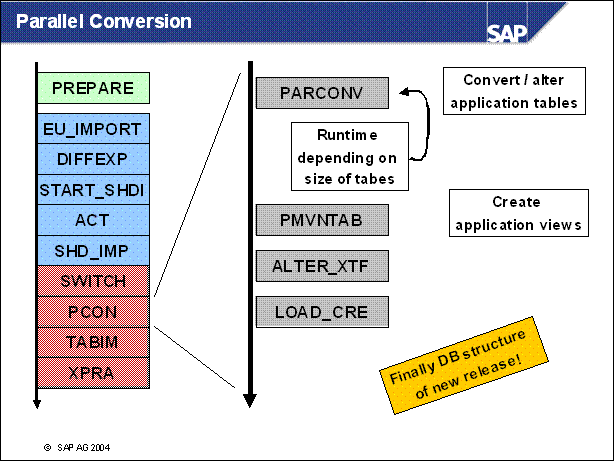
n Phase PARCONV _ UPG ist the new PCON. Here are application tables converted which cannot be changed by an ALTER TABLE statement.
n In PMVNTAB _ UPG some application views are converted and the remaining name tab entries are activated.
n LOAD _ CRE creates new ABAP load tables.
n Now on the database layer the structure is in its final state.
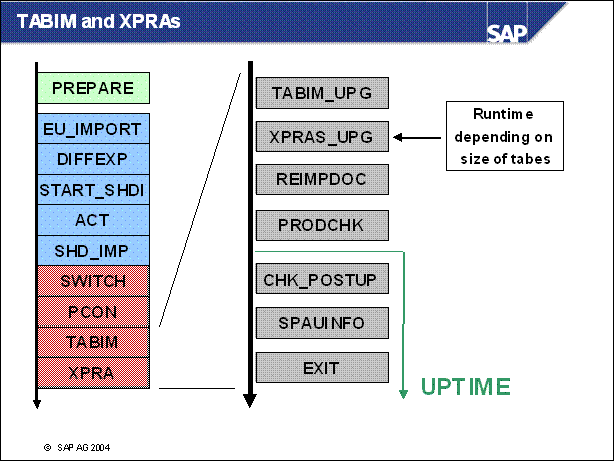
n In phase TABIMP _ UPG data is imported into control tables.
n Phase XPRAS _ UPG starts XPRA programs which create entries in changed tables.
n REIMPDOC imports documentation which was changed or created by the customer.
n In phase PRODCHK the requirements for productive operation are checked.
n Phase CHK _ POSTUP formerly known as LONGPOST shows errors with a P mark. These are errors you can remove after the upgrade.
n Phase SPAUINFO remembers to adjust objects in transaction SPAU.

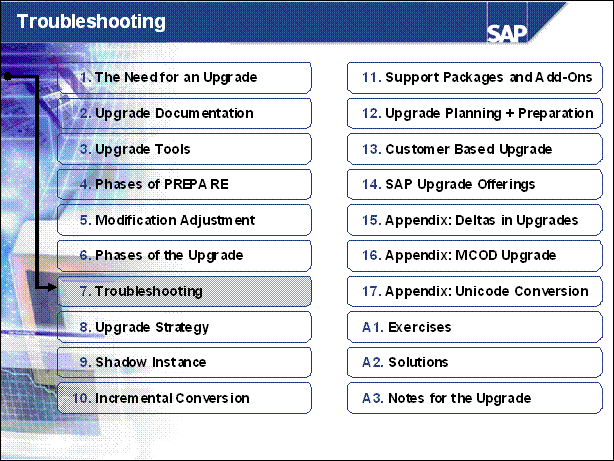

n The user interface is described in the upgrade manual.
n UaGui or special versions of a SAP system executable like tp, R3trans,
or R3load are used for the upgrade special executables such as R3up and
UaServer.
Do not exchange a special upgrade tool like tp or R3trans for a regular one
from the start or the target release unless advised explicitly to do so by an
SAP Note.
n The version of most SAP executables can be determined with the option
-V.
For those tools which connect to the database, a value in the DB library line
indicates that the corresponding DB library can be loaded. Additional
documentation can be found in SAP Note 193616.
n R3up can run in server mode (recommended) or in scroll mode. In server mode, the Upgrade Assistant Server must also be running to receive the standard output of R3up. The Upgrade Assistant GUI does not require a permanent connection to the server.
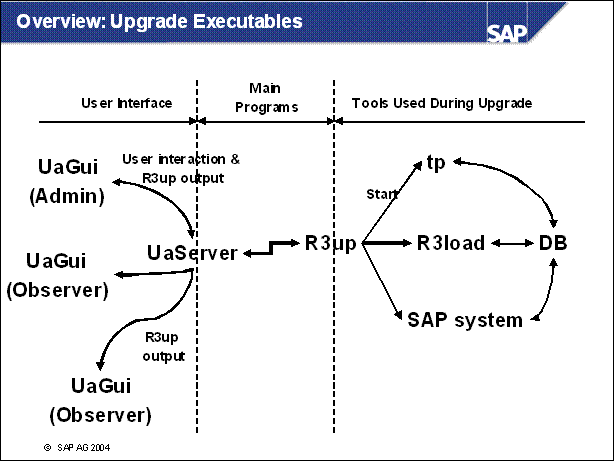
n You can use the above tools to see the upgrade activity.
n If input is required, the upgrade will stop. A file, upalert.log, is then written to DIR _ PUT / tmp. You can also use the alert functionality of the Upgrade Assistant to start a command (for example, to send a mail), when the upgrade process stops.
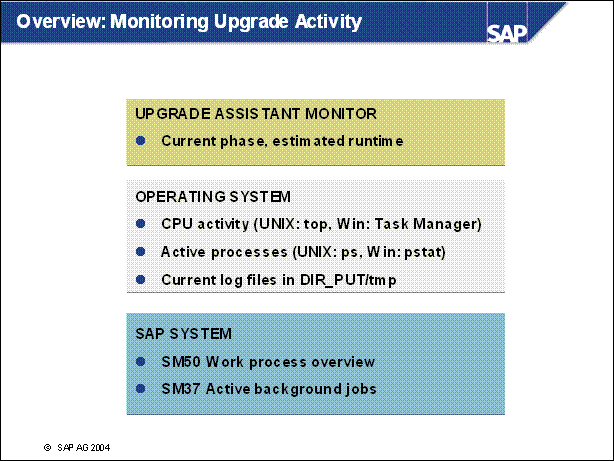
n Steps
1-3 should be processed to find what caused the upgrade to stop.
The current phase is the last in R3up.log (upgrade) or R3upchk.log
(PREPARE).
n Under UNIX, the most recently written log files can be found in DIR _ PUT / log with >ls -ltr | tail
n Additional logs can be created in transactions SM21 and SM37 for activities inside the SAP R / 3 System.
n The database alert file can contain special DB-related errors such as archiver stuck.
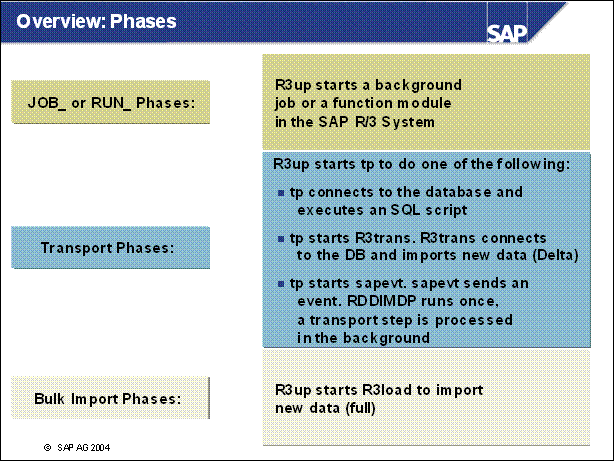
n Info : An upgrade to SAP R / 3 46C contains approximately 200 different phases. Most of the phases fit into one of three described classes.
n R3up itself cannot connect to the database. To read or change information in a database table, R3up needs a tool that can access the database. In each of the three classes, R3up chooses different tools. Details of these classes are described on the following pages.
n During upgrade phases with names like JOB _ or RUN _ , R3up starts a function module in the system using RFC to schedule and start a background job. After the job had finished, the result is evaluated from the log file.
n Phases with names such as TABIM, TABUIMP, VIEWIMP, PORT _ IMP,
TOOLIMP, and so on are classical import phases. tp starts R3trans,
R3trans imports data.
Phases like DIFFEXP or SHADOW _ IMPORT are similar phases, except
that R3trans imports into the shadow tables.
n The EU _ IMPORT phases are the bulk import phases during which the
new Repository is imported into the shadow tables invisible to the production
SAP R / 3 System.
Most of the data in the Repository is not unique to the system, therefore an
exchange is more efficient than a import of the delta. In contrast, Customizing
is unique to each system, and therefore only the delta is imported.
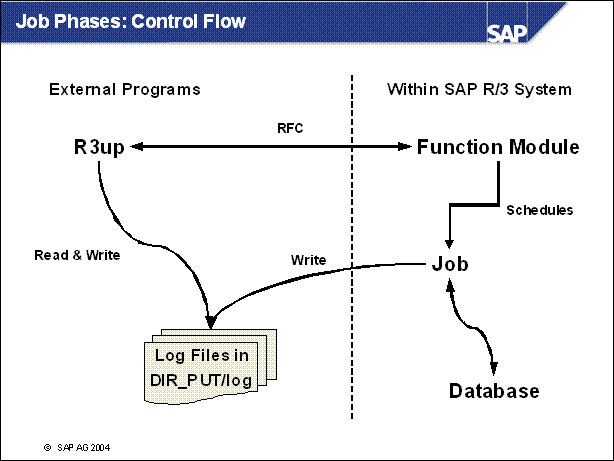
n R3up starts a function module in the SAP system as user DDIC in client 000 (SUBST _ START _ BATCHJOB).
n This function schedules a background job for the phase.
n R3up regularly checks the status of this job with a new RFC call (SUBST _ CHECK _ BATCHJOB), until the job has finished.
n The log file written by the job in DIR _ PUT / tmp is analyzed and evaluated by R3up.
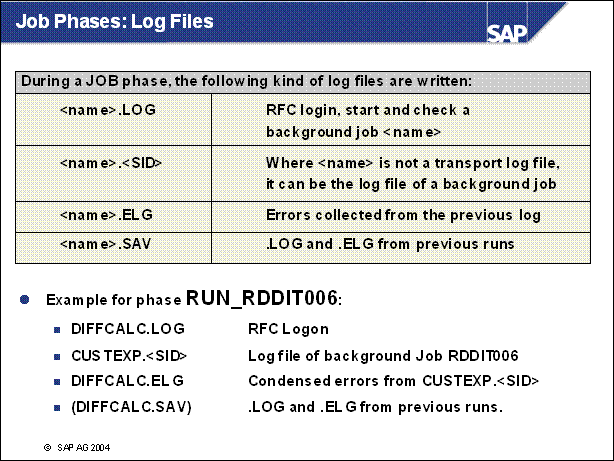
n The first RFC phase is RFCCHK _ INI in PREPARE. Only the RFC logon is performed during this phase, and no background jobs are started (RFCCHK _ INI.LOG).
n The check of the background job functionality is made during BATCHCHK phases (for example: BATCHCHK _ IMP.LOG).
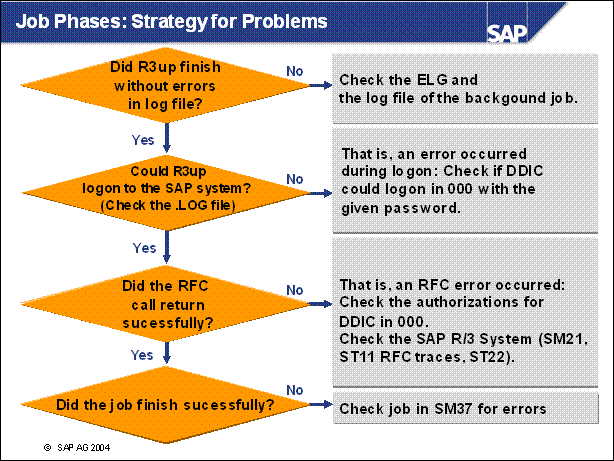
n Point 2: If DDIC could not logon, update the password known to the
upgrade with
> R3up set DDICpwd
and exit, then restart R3up. Using SU01 to change the password from within the
system does not always work during the upgrade.
n Point 3: A similar strategy could be used for phases, where R3up does only a RFC call into the system.
n Point 4: If the job finished successfully and R3up could not find the log file, check if the DIR _ PUT on the instance on which the job has run points to the upgrade directory in AL11.
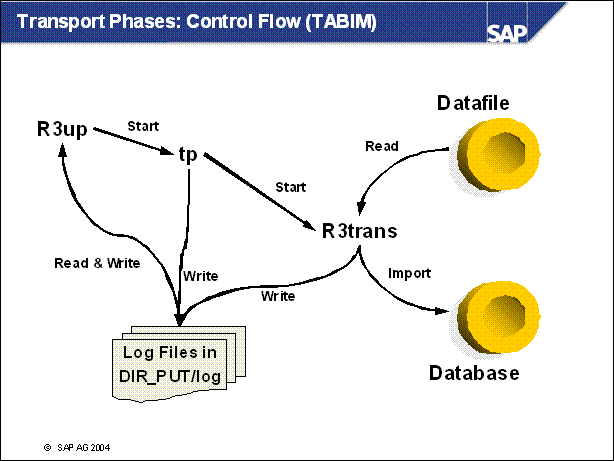
n This is also valid for TOOLIMP, DIFFEXP* and other import phases.
n During the DIFFEXP* phases, R3trans reads from the source release tables and writes into the target release tables (copy to shadow).
n R3up evaluates a direct return code from the tools (finished) and evaluates an indirect returncode from the written log files.
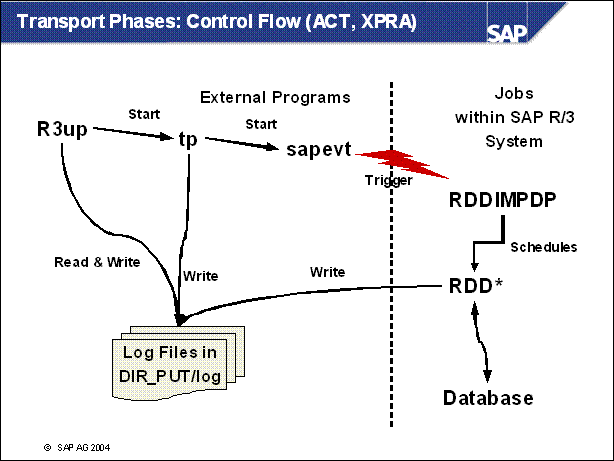
n Instead of R3trans, a transport background job might also be started for actions such as activation.
n The start of RDDIMPDP works differently from the start of a job during a JOB phase.
n PCON (parallel conversion) is similar to this, but R3up starts the transport background jobs (distribution, conversion) itself, and in parallel. After distribution, an additional check is made for lost fields (FDSAVPROT). R3up then starts tp only for movenametab (execution of DDLs).
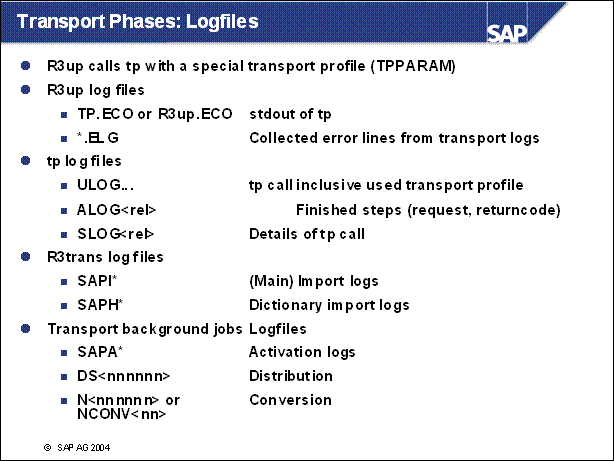
n The special upgrade log files are .ECOs for standard output and .ELGs, where errors from other log files are collected. A line in a transport log is transfered if it contains an E in the second column.
n The log files for tp differ only in the naming from the usual transport log files.
n Additional PCON log files are:
FDSAVPRT. <SID> Check for lost fields
PA <date>. <SID> Only nametab activated
PD <date>. <SID> Activate and alter table (add field or similar)
PL <date>. <SID> Delete table and remove nametab
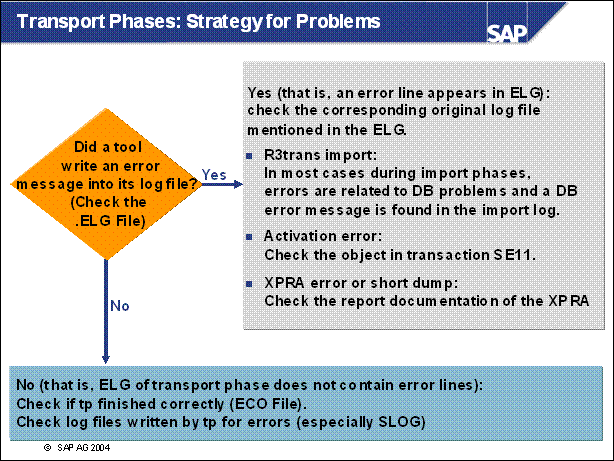
n Activation errors should be resolved or classified as non-critical. Otherwise, there is a chance that data in PCON will be lost.
n In ACT, XPRA and ADOIMP, a return code of 8 means that individual objects were not processed successfully. You could repeat the phase at your own risk with >repair severe errors. If you do this, then only return codes larger than 8 will stop the phase.
n Check for lost fields fails in PCON :
Verify that this is correct (SAP Note). Data might be lost if the phase is
repeated with Do not repeat checks.
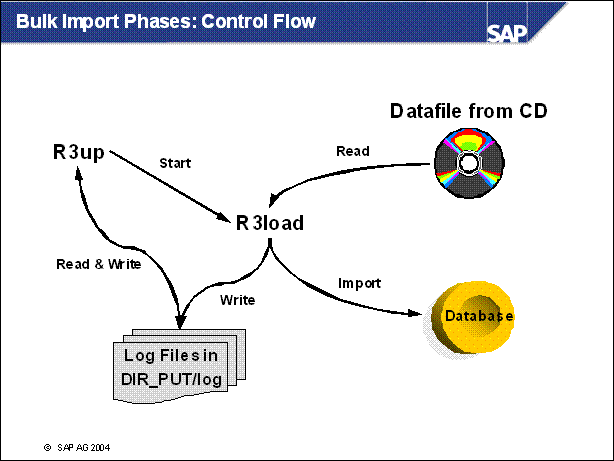
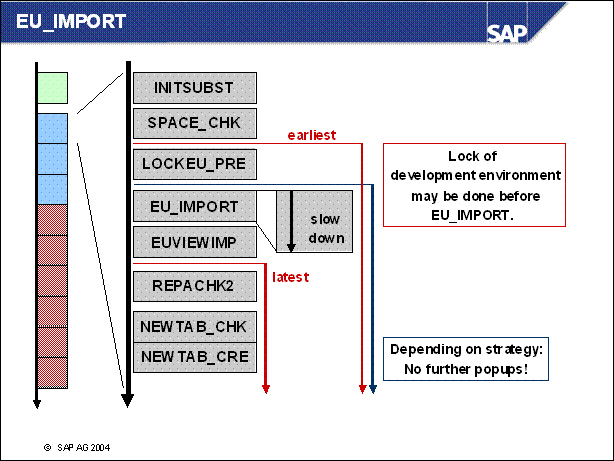
n If the system is productive during EU _ IMPORT phases, you can slow down the R3load process so that the performance of the SAP R / 3 System is not affected.
n If the system is not productive during EU _ IMPORT, the SAP R / 3 System is shut down during EU _ IMPORT and several parallel R3load processes are started.
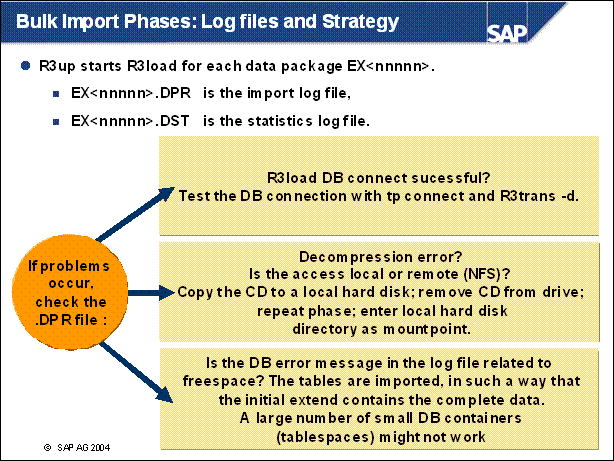
n The statistics log file contains only the number of imported bytes and the total number of bytes in this data package.
n The restart of an EU _ IMPORT phase with init first removes all previously imported tables and then starts R3load to import all tables again.
n The restart of an EU _ IMPORT phase with repeat just starts R3load to restart from the point where the error occurred.
n Duplicate keys during the creation of a index are caused by CD read problems. The recommended solution is init of the phase with the CD copied to disk.
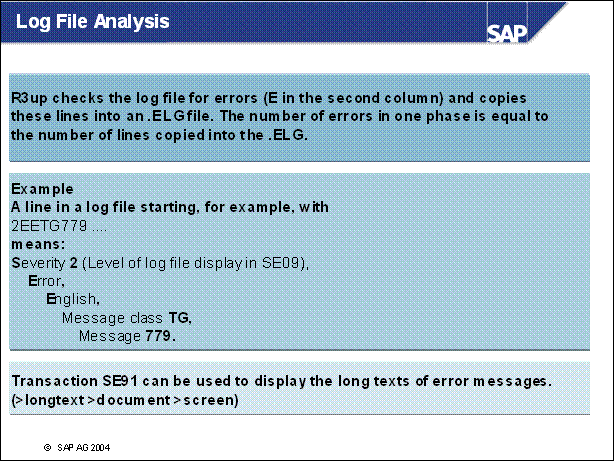
n SE91 can also be used to identify the development class of the message. The development class has a component assigned. Especially for XPRAs, the customer message can be opened directly on this component.
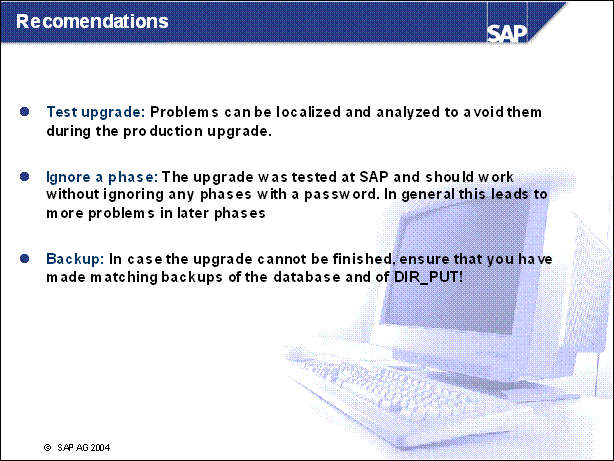
l
During a test upgrade, problems can be
localized and analyzed, so that they can be avoided during the production
upgrade.
l
The upgrade was tested at SAP and
should work without ignoring any phases. To ignore a phase with a password
will, in general, lead to more problems in later phases, Therefore passwords
are given only by Software Logistics Development Support.
l In the very rare case that the upgrade cannot be finished, ensure that you have made a backup of the database and of DIR _ PUT as descibed in the upgrade manual. The database and the upgrade directory must have a matching state.

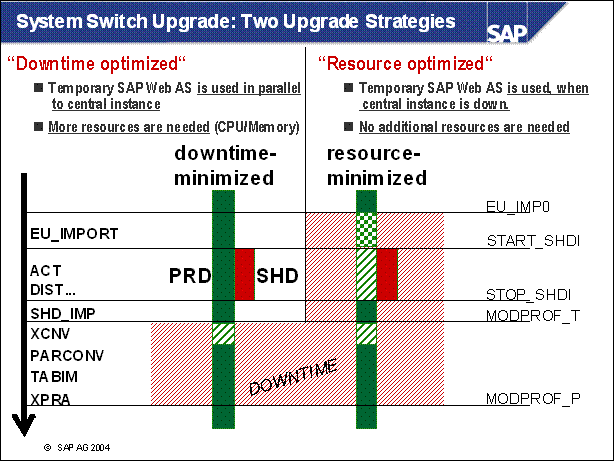
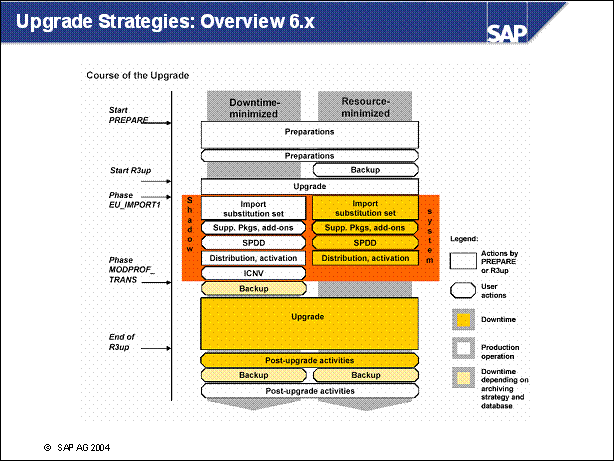
n The upgrade strategy is one of the main factors in determining the runtime of the upgrade and how much downtime is involved.
n The graphic shows the course of the upgrade for the various strategies. It does not show the differences in the duration of the upgrade. The upgrade is divided into phases.
n EU _ IMPORT1 and MODPROF _ TRANS are important phases, since they mark the start of downtime (depending on the chosen strategy).
n The course of the upgrade is identical in all strategies up to the EU _ IMPORT1 phase. The resource-minimized strategy starts the downtime in the EU _ IMPORT1 phase. For the downtime-minimized strategy, downtime begins in the MODPROF _ TRANS phase.
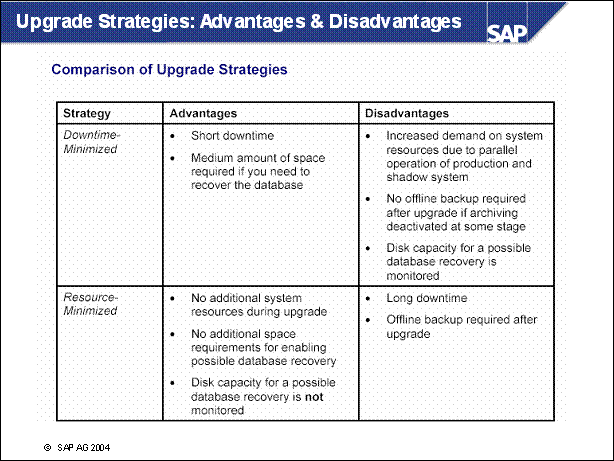
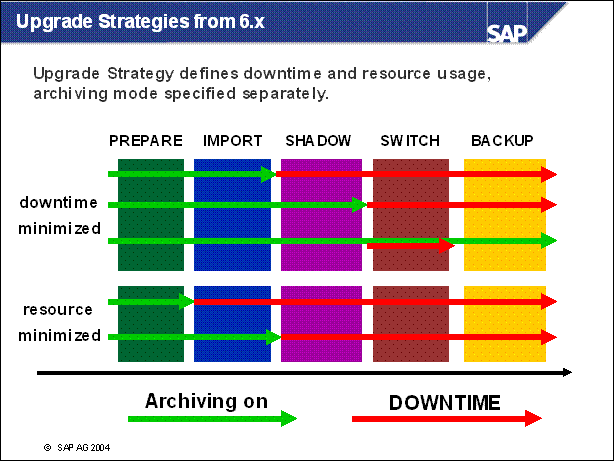
n Two upgrade strategies are possible, the archiving (and thus downtime) is only loosely related to the strategy. The possible (and meaningful) combinations are listed on the screen.
n Downtime-Minimized: All Actions are adusted to reduce the downtime to a minimum. This strategy requires more memory and cpu than resource-minimized. The load on the system during uptime is reduced, thus the total runtime of the upgrade is longer.
n Resourece-minimized: the shadow system (see below) is started not in parallel to the production system. The prodictive operation needs to be stopped before the shadow system is started.
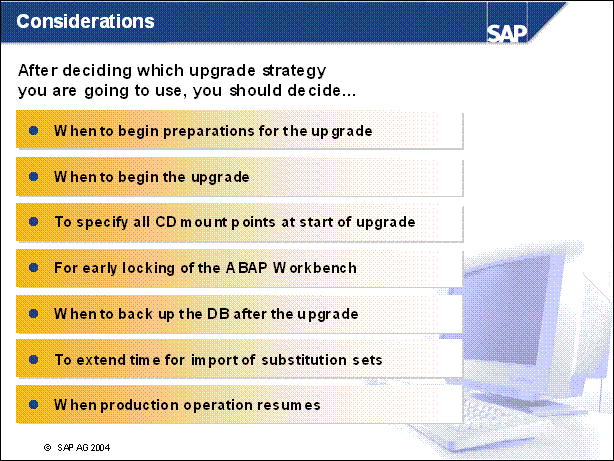
n At the latest, start preparing for your upgrade a week before starting the upgrade.
n You need approximately 4 hours to import the substitution sets. To avoid lowering system performance, extend this time. Set the time required for the import so that it ends at least 5 hours before the planned shutdown of production operation. At the latest, system downtime begins in the MODPROF _ TRANS phase. The earliest you can resume production operation is approximately 10 hours later. The SAP R / 3 system is started up several times during this time.
n If possible, do not resume production operation until all of the necessary post-upgrade activities have been performed. The same applies to the complete backup of the database, which is a requirement for resuming production operation. This has the advantage that all database changes resulting from post-upgrade activities are included in the complete backup. The earliest possible point for continuing with production operation is PRODCHK _ <release>.
n During the system switch upgrade, several phases work on the shadow system / tables.
n Using the strategy with the shortest possible downtime, these phases are stil uptime.

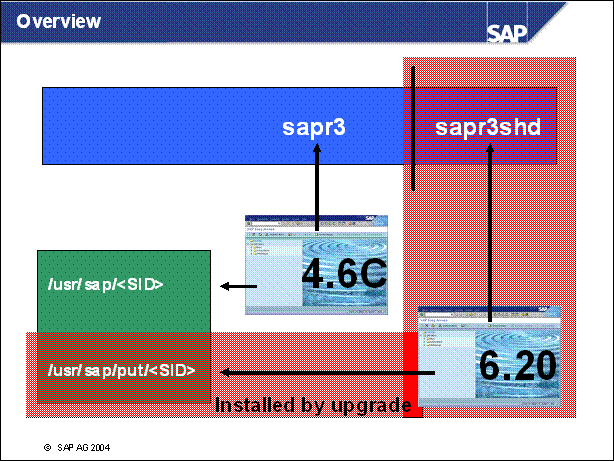
n User sapr3 is used to connect to the productive system database (4.6C in this example)
n User sapr3shd is used to connect to the database scheme of the shadow instance (6.20 in this example)
n The productive system central instance is using the executables and profiles from the / usr / sap / <SID> directory
n The shadow instance is using the executables and profiles from the / usr / sap / put / <SID> directory
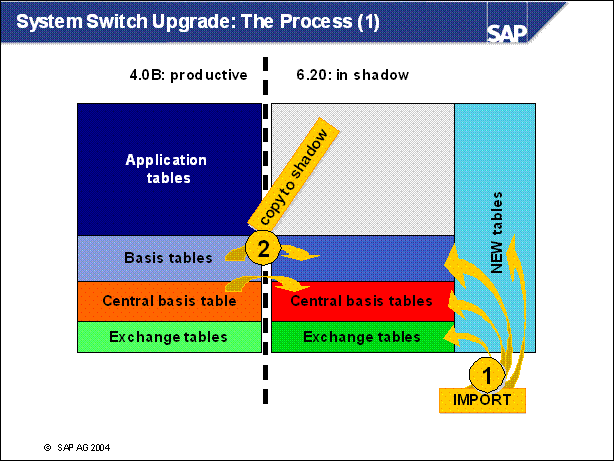
n Let's have a look onto the process.
n At first we import the SAP standard target repository and create tables which are new in the target release.
n Now we can copy the central basis tables and the basis tables to the shadow.
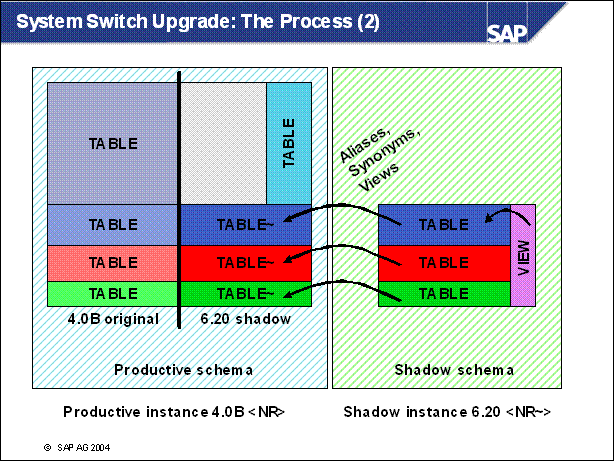
n What we do now is that we create aliases, synonyms and views in another schema on the database. These aliases guide to the physical table in the shadow of our productive schema.
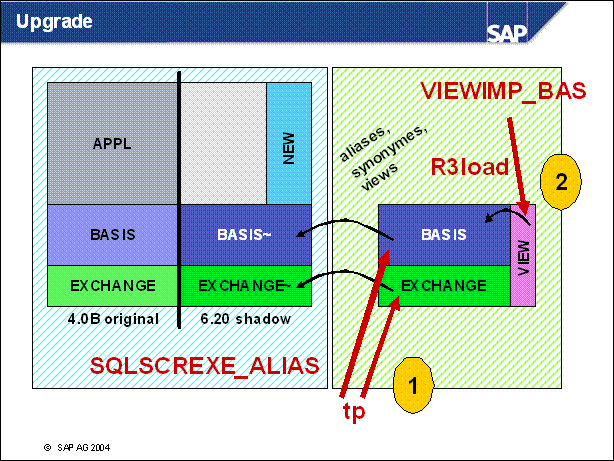
Phase SQLSCREXE _ ALIAS: tp
step, shadow connect
Create alias / synonym / view for shadow user on shadow table of original user
Example for Oracle:
connect as sapr3shd:
create synonym sapr3shd.DD03L for sapr3."DD03L~"
connect as sapr3:
grant all on sapr3."DD30L~" to sapr3shd
Phase VIEWIMP _ BAS: R3load
step, shadow connect
Create view on alias / synonym / view
Example for Oracle:
connect as sapr3shd:
create view DD90V ...as select ... from DD90T ...
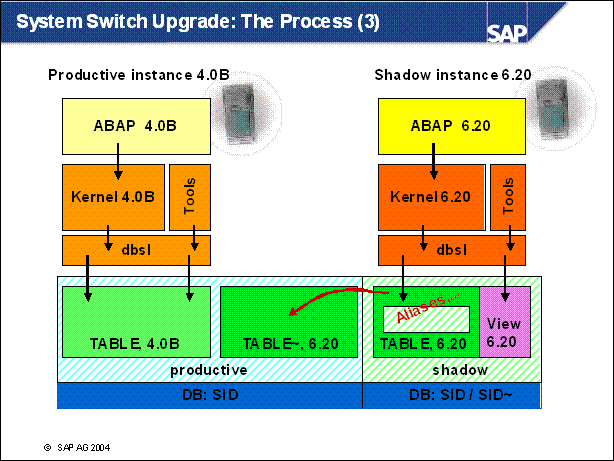
n Now we are able to start an instance with the new kernel. This kernel connects to the shadow schema and accesses the shadow repository via the aliases in its schema.
n We cannot go further in detail here. In fact the location of these tables depends on the particular database. Here is important to understand that it is possible to execute ABAP code for the target release with the target kernel during the production system is still working.
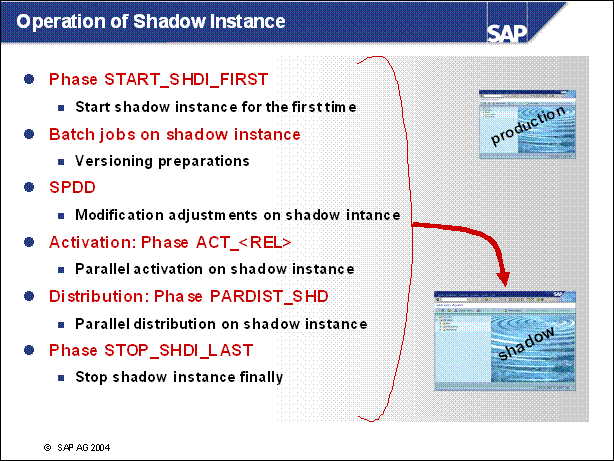
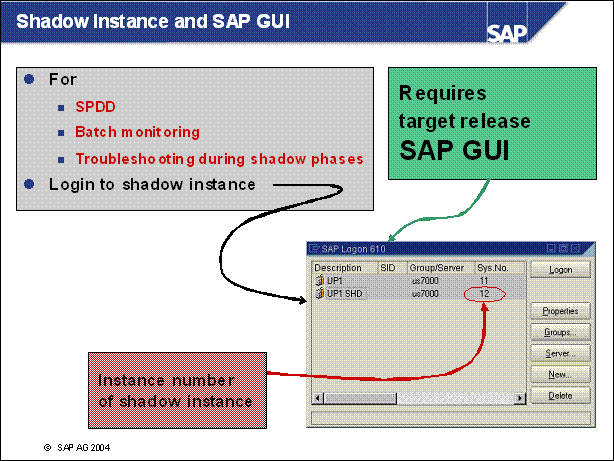
n A login to the shadow instance is possible during the upgrade
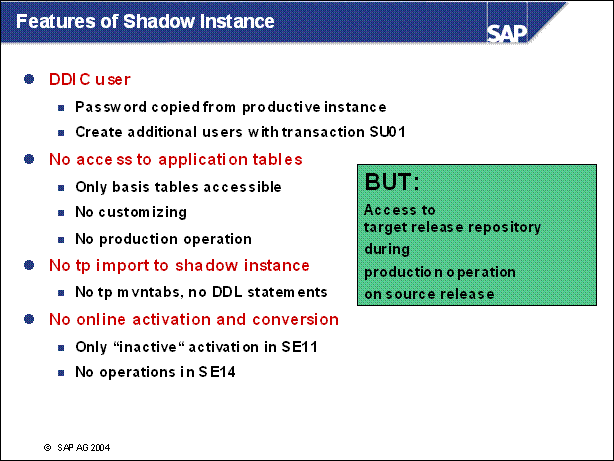
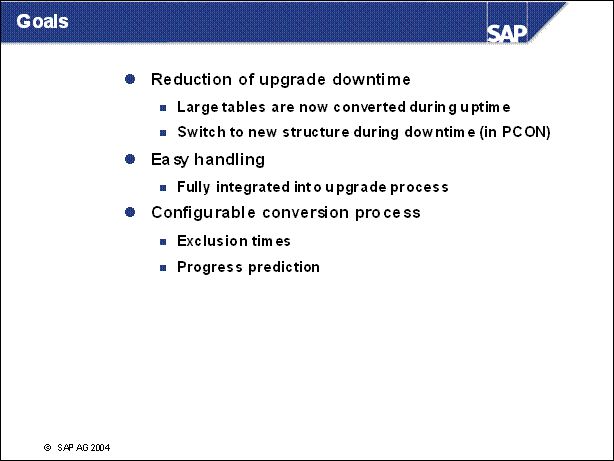
n The main goal of the ICNV is to reduce the downtime during an upgrade.
n The procedure should not be too complicated and it should be fully integrated into the upgrade process.
n The conversion process is executed during uptime. The database load is expected to be higher during this process. Therefore it should be possible to define exclusion times during which no ICNV processes are running.
n The user should be informed about the estimated end of the process to be able to plan the upgrade accurately.
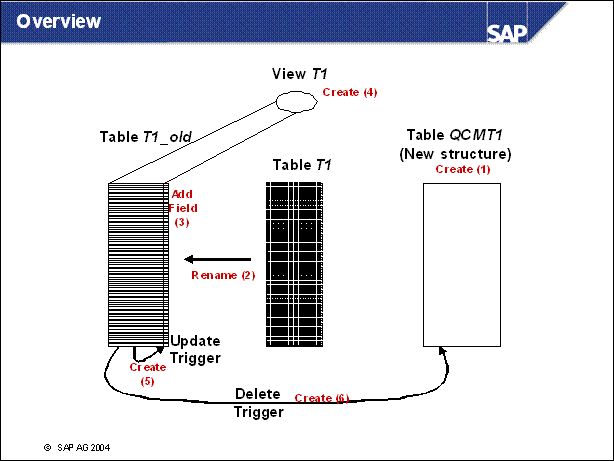
n Here is the sequence of steps during an incremental table conversion:
The conversion table candidates are selected.
(1) A QCM table with a new structure is created.
(2) The table T1 is renamed to T1 _ old.
(3) An additional status field is added to T1 _ old.
(4) A view on the old table structure is created. The applications access the view from now on. To log these changes the update (5) and the delete (6) trigger is needed
The table content is copied (low priority copy) to the shadow table QCMT
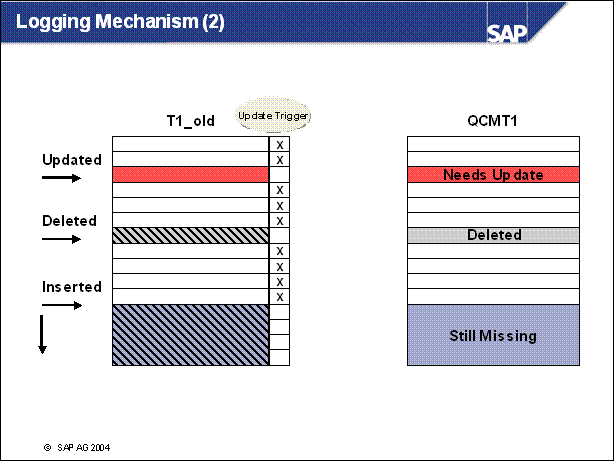
QCMT1 is filled by periodic runs
n After the start of an upgrade, only a few conversions remain. The downtime due to table conversion is significantly reduced.
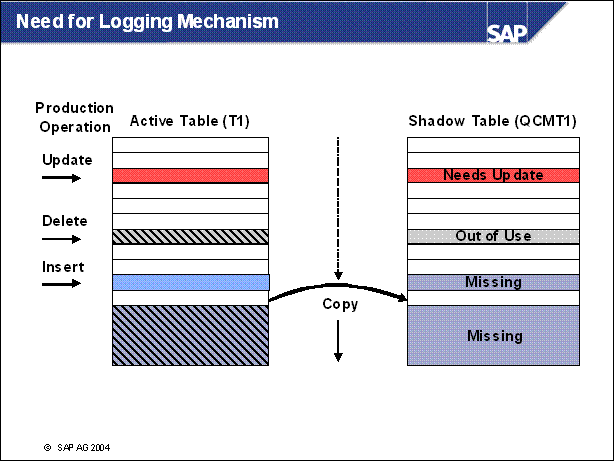
n A shadow table named QCMT1 with is created the new structure.
n The data from the original table T1 is copied using a background process during uptime to the shadow table QCMT1.
n T1 is still accessible by the applications. Therefore the changes during the data transfer must be logged and also be executed on the shadow table.
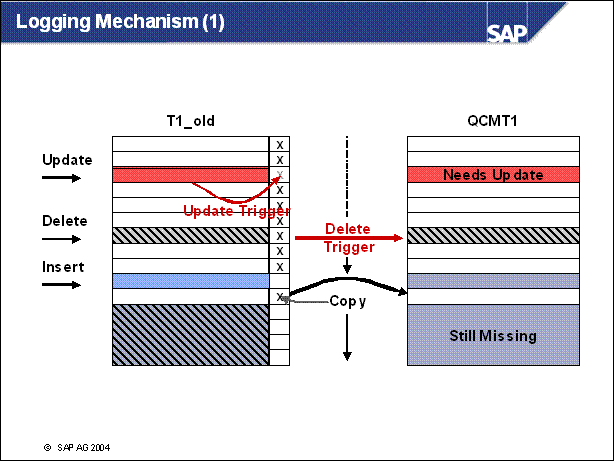
n T1 is modified by creating a flag field. This field indicates if this entry was already copied to the corresponding fields in QCMT1.
n Programs still work on the original table T1. To allow this, T1 is renamed to T1 _ old and a view T1 on the table T1 _ old without the flag field is created.
n A short pre-downtime for the Add Field operation is necessary
n Programs can perform updates, deletes and inserts on T1 _ old.
Update of already converted entry: The 'x' in the flag field is erased by the update trigger.
Deletion of already converted entry: The corresponding entry in the new table is directly deleted by the delete trigger.
Insert: The flag field for this entry is left empty.
n Every entry in table T1 _ old with an empty flag field is copied to QCMT1
n Periodically, the copy is repeated for all new rows since the last copy
n This could be the situation right after beginning of downtime:
Some rows are updated or inserted but not copied yet (empty flag field)
There can be a part of the old table which has not been transferred to QCMT1 (empty flag field)
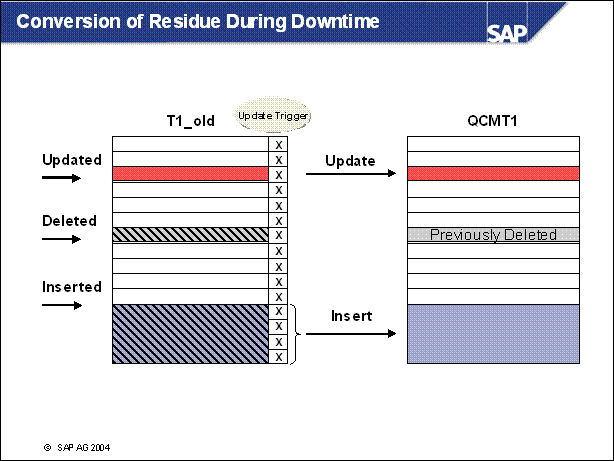
n The latest insert / update operations and the remaining conversion will be processed during downtime
n Inserting rows is possible without an additional load at that point in time, because no insert trigger is used.
n The update trigger is very efficient, because the additional load just consists of filling the flag field.
n Delete operations must be executed in both tables and are therefore inefficient.
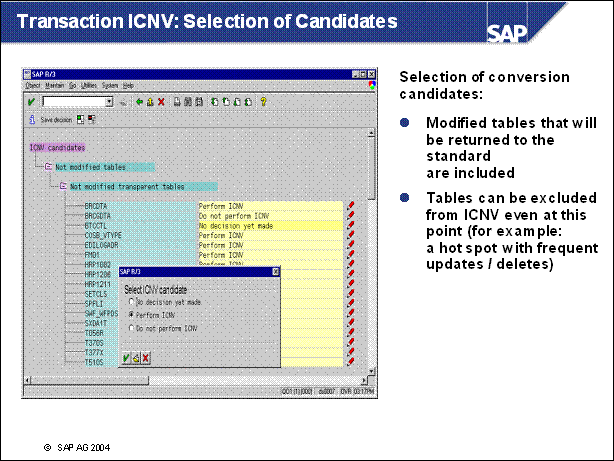
n By calling transaction ICNV, all potential candidates are displayed with their current selection status. You can decide which of the preselected tables should be processed by ICNV.
n Tables can be excluded from being processed by ICNV with Do not perform ICNV. This should be used for tables with a high number of updates and / or deletes, because in this case the ICNV can be inefficient. The delete operations are especially critical. The load on the database is doubled by performing a delete on a table processed by ICNV.
This efficiency check must be done manually. There is no tool that excludes "hot spot tables" automatically!
n The screen also shows tables modified by the user, which would be converted during a return to the SAP standard. The user can decide whether a table should return to the SAP standard or whether it should be presented again in SPDD. Tables that are not to be returned to the SAP standard, but to another user-defined structure cannot be processed by ICNV.
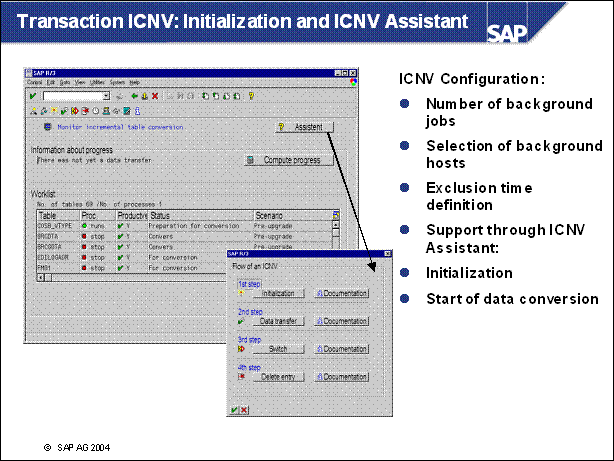
n ICNV offers several features to configure the incremental conversion process
Batch hosts can be specified
The number of running batch processes is adjustable
Exclusion times for processing can be specified for each table (This enables you to run conversion job at times with relatively low table I / 0).
The log files of the conversion processes for each table can be acessed
n See online documentation in ICNV
n After deciding about all tables, the user can choose to be guided through the necessary steps by an ICNV Assistant. For the upgrade scenario, there are two steps needed to be started manually:
Initialization
Extension by flag field
Build of an index on the flag field
Creation of update and delete triggers
Replacement of table by a view and renaming table
Start of the data transfer
n The remaining steps (switch and delete entry in ICNV) are then performed by R3up !
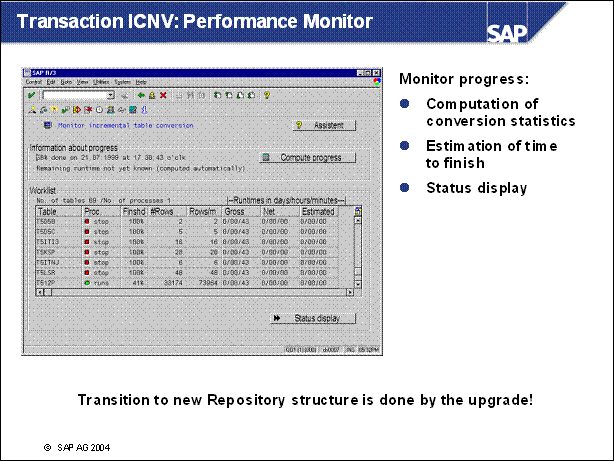
n The progress of the data conversion can be monitored by ICNV. The monitor displays the following information:
Table name
Number of runs
Number of processes working on the table (currently restricted to one)
Number of data records which were transferred by the current / previous / first run
n After the incremental conversion starts, dictionary definitions for the relevant tables cannot be changed until the upgrade ends. This affects changing, deleting or adding field definitions. Transaction SE11 is locked for these tables.
n If you use incremental table conversion, do not start an SAP archiving program for these tables in parallel, since this can lead to performance bottlenecks. Therefore, archive as much as possible before starting the conversion.
n Incremental conversion requires sufficient background work processes. Ideally, there should be one process for each table to be converted. If you cannot have one process for each table due to a large number of tables, you can still convert the tables since transaction ICNV distributes the tables by itself to the available background processes. However, completing the incremental conversion takes longer, and therefore more time is needed before beginning the upgrade downtime.
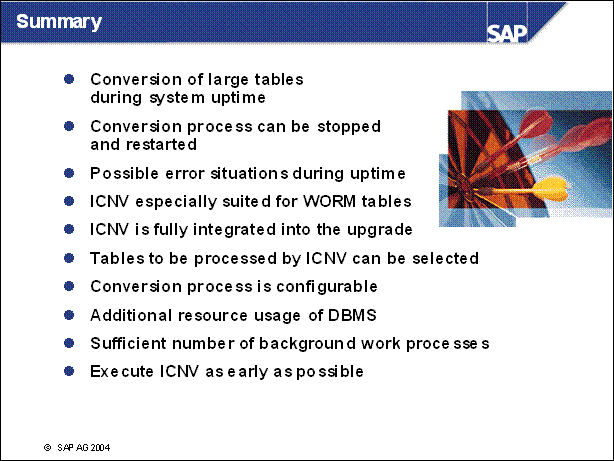
n Because most data is converted before the beginning of downtime, downtime can be reduced by several hours. The actual reduction depends on the table size. The dependence of downtime on the database size is also strongly reduced.The downtime can be predicted more accurately.
n The conversion process can be stopped and restarted at any time without loss of converted data.
n Error situations like table space overflow or reaching of maxextends due to the incremental conversion occur during uptime.
n ICNV is especially suited for large Write Once Read Many (WORM) tables
n Pay special attention to the resource usage of your database management system to detect bottlenecks early.
Incremental conversion requires double the space in the relevant database container (tablespace, dbspace, and so on) for each affected table during the conversion.
Due to the continuous data transfer, there are more transactions. Therefore, you should also monitor the space for the rollback information.
n Incremental conversion eventually requires more background work processes.
n Begin the downtime of the upgrade if at least 95% of the entire amount of data to be converted has been converted.
n Often, very large datasets are contained in tables CDCLS and EDIDOC so that a conversion would take too long during the phase PCON.
n The late ICNV can only be applied to special tables and is used only by SAP.
n During the upgrade, the incremental conversion is only prepared. The data transfer is performed after the upgrade.
n In SAP R / 3 4.x, the tables CDHDR and PCDHDR contained in CDCLS are made transparent.
n In addition, EDIDOC is replaced by EDI40.
n The procedure for CDCLS during the upgrade is as follows:
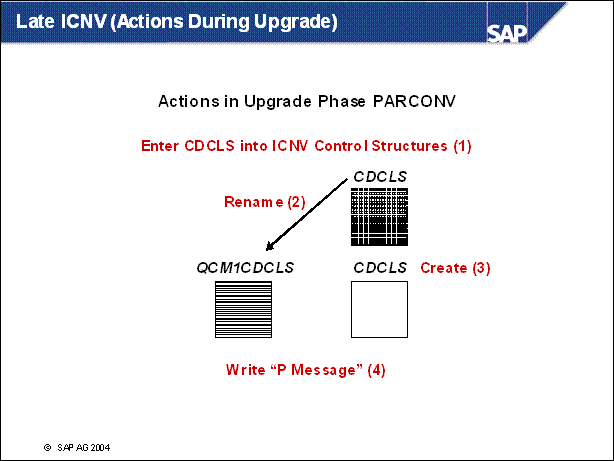
(1) In PARCONV the table cluster CDCLS is added to the control structure of ICNV.
(2) The old table cluster CDCLS is renamed in QCM1CDCLS and then not directly accessible any more.
(3) A new table cluster named CDCLS is created which includes all logical tables and which is empty immediately after the upgrade.
(4) A post-upgrade message is displayed in upgrade phase CHK _ POSTUP and written to LONGPOST.LOG to use the transaction ICNV to convert CDCLS before the next upgrade.
n The procedure for EDIDOC is similar.
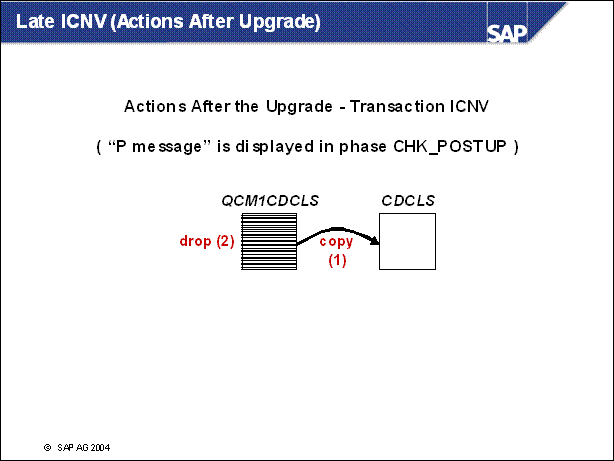
n Procedure after the upgrade:
After starting the data transfer for CDCLS in ICNV, the data is transferred step-by-step by the incremental converter and deleted from QCM1CDCLS.
If immediate read access is required to old data records that have not yet been transferred, this can be carried out using program RSSCD900.
New entries are only written to the new table CDCLS and therefore these change documents are immediately and unlimitedly available.
After switching to the new structure and deleting the entries in ICNV, all help objects and logs are removed and the conversion is carried out completely.
n The only difference for EDIDOC is as follows:
Data records which were not yet transferred can only be accessed in read mode.
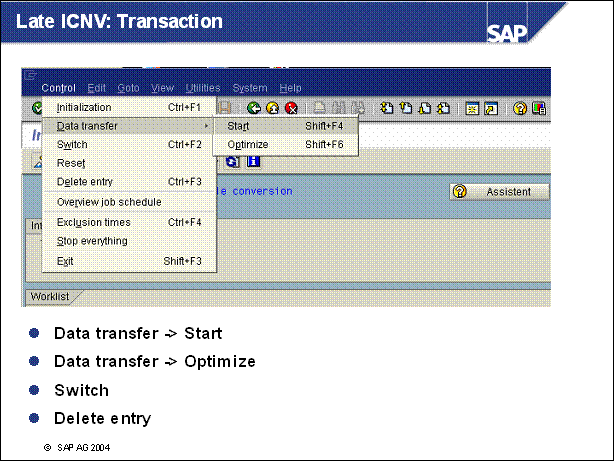
n Switch to the new tables at 100% (SAP R / 3 4.0 or 4.5) or 95% (SAP R / 3 4.6 or higher) progress
Only perform the switch when the data transfer process automatically stopped running (only SAP R / 3 4.0 or 4.5). Select the tables for the switch and choose Control -> Switch. During the switch a possible remaining dataset is transferred.
n Delete entry
Select the completely converted tables (see key) and choose Control -> Delete entry. The tables disappear from the list. Now, the conversion is performed completely. You must have deleted all entries before the beginning of the next release upgrade.

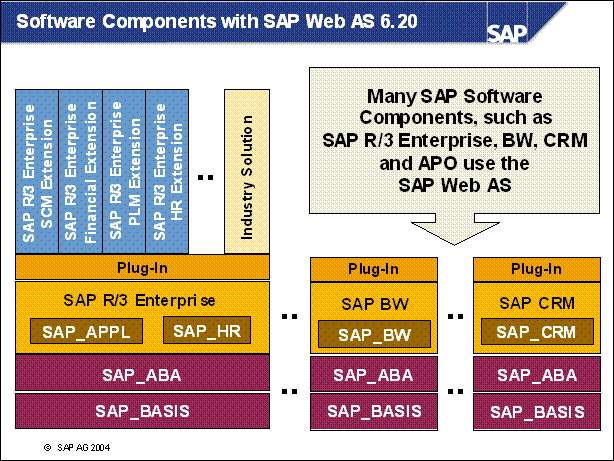
n BASIS: Basis Functionality
n ABA: Cross Application
n APPL: Central Applications without HR
n HR: Human Resources
n BW: Business Information Warehouse
n CRM: Customer Relationship Management
n These software components are independent from each other. Upgrading or patching one of them should not influence the others. There are, however, dependencies between the various components. For details see respective SAP Notes.
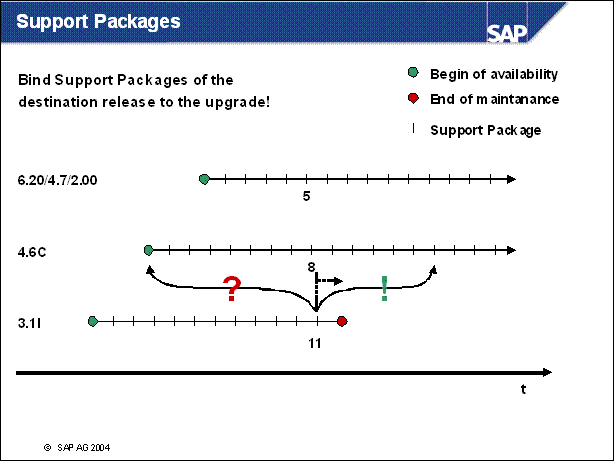
n Support packages on the start release are produced also after a potential destination release has been shipped.
n 3.1I Support Package 11 f.e. has been shipped after the shipment of 4.6C.
n On each potential destinatin release, Support Packages are availabel too.
n There is some relation between the Support Packages: usually fixes have been mad at the same time for different releases (here eg 6.20 / 4.7 / 2.00: 5, 4.6C: 8 and 3.1I: 11)
n An Upgrade from 3.1I support lackage level 11 to 4.6C Support Package level 0 would parially downgrade the system
n But: it is possible to bind packages to the upgrade: you can go directly to 4.6C Support Package 9 or higher (in this example)
n Advantages:
No need to supply the package on the destination release after the upgrade
No (temporary) downgrade
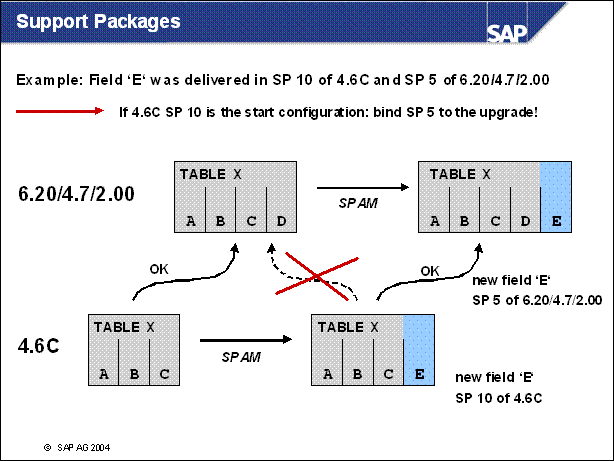
n An example, why binding Support Packages (e.g. legal change patches) is necessary:
Imagine, the field , E' has been shipped in 4.6C Support Package 10 and 6.20 / 4.7 / 2.00 Support Package 5.
If the start release is 4.6C with Support Package level higher than 10 (e.g. 11) an upgrade to 6.20 / 4.7 / 2.00 Support Package level lower than 5 wold drop the field! The data would be lost. Even if the Support Package 5 of 6.20 / 4.7 / 2.00 was applied after the upgrade, the data of field , E' is lost.
An Upgrade of 4.6C Support Package level > 10 should got to 6.20 / 4.7 / 2.00 Support Package level > 5.
The corresponding Support Package levels can be determined via the release date of the package (or a note in case HR patches need to be bound)
An reference information, which packages are at an idential level, will be supplied with the packages in future releases.
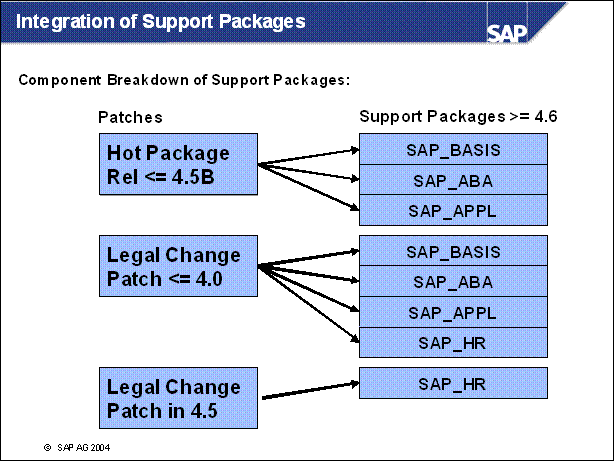
n SAP R / 3 3.1I, SAP R / 3 4.0B:
All Support Packages (SPs) are included in the Legal Change Patch Collection (LCP). Therefore the customer must decide whether to use SPs or LCPs.
n SAP R / 3 4.5B:
LCPs and SPs are separated. The customer can apply LCPs and / or SPs.
n SAP R / 3 4.6B / C: For the SAP R / 3 core there are four different kinds of Support Packages:
SAP _ BASIS : Basis Support Package
SAP _ ABA : Application Interface Support Package / Cross-Application Basis
SAP _ APPL : SAP R / 3 Support Package
SAP _ HR : HR Legal Change Package
n Further Support Packages are:
FFDP: FCS Final Delta Patch
NDI Support Packages (APO, BW, BBP, CRM...)
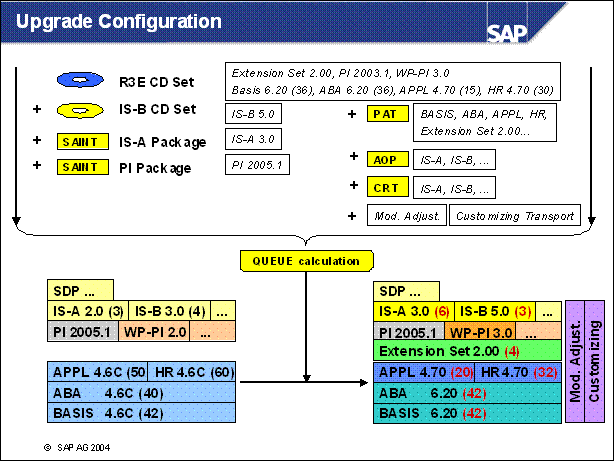

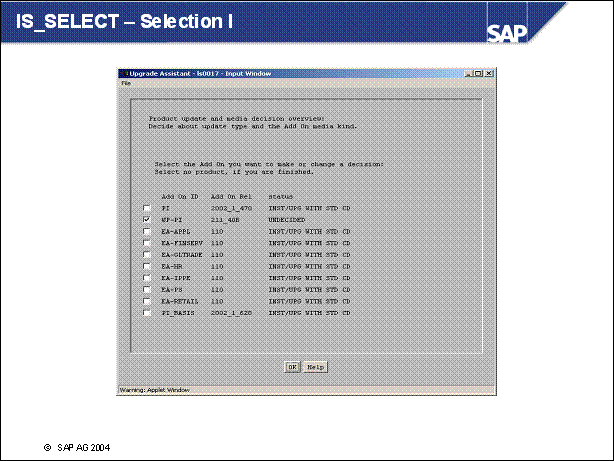
n UPG STDCD (upgrade to version on standard upgrade CDs)
Only possible for Add-Ons
that are delivered with the upgrade
(This is the default selection for these Add-Ons.)
Must be changed only if a newer version is available and you want to include it (usually for PI and PI _ BASIS Add-Ons)
n UPG CD (upgrade with Add-On CD)
Add-On upgrade with supplement CD (must be mounted)
If the supplement CD contains a SAINT attribute package (AOS), it is handled by the Add-On queue calculation (phase ADDON _ QCALC)
n UPG SAINT (upgrade with SAINT package)
Add-On upgrade with SAINT package (AOU)
Package must be available in <EPS> / in directory and is automatically uploaded
Add-On upgrade is handled by the Add-On queue calculation (phase ADDON _ QCALC)
n KEEP (with vendor key)
Add-On transferred unchanged to new release
Vendor key must be entered
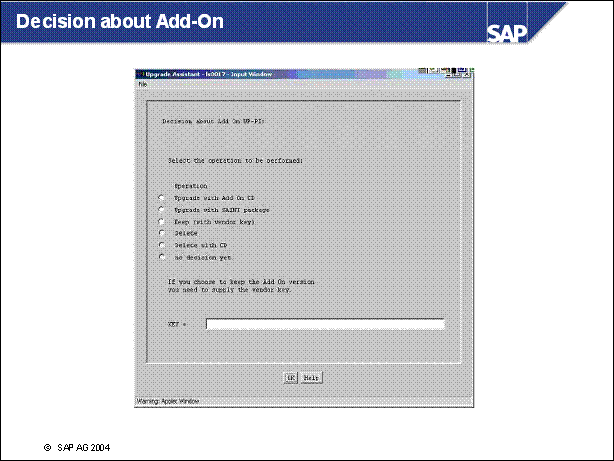
n KEEP YOURS (keep your version)
Component upgrade only
Only possible for Add-Ons
that refer to components that remain unchanged in the upgrade
(This is the default selection for these Add-Ons.)
Add-On is transferred unchanged to new release
No vendor key needed
n DEL (delete)
Passive deletion
Only possible if the Add-On is not protected (that is, listed in file <putdir> / bin / IS _ PROTECT.LST)
n DEL CD (Delete with CD)
Active deletion with a deletion CD (must be mounted)
n UNDECIDED (no decision yet)
Decision is needed
Default selection for all optional Add-Ons
Phase can be finished successfully only when all Add-Ons have been determined
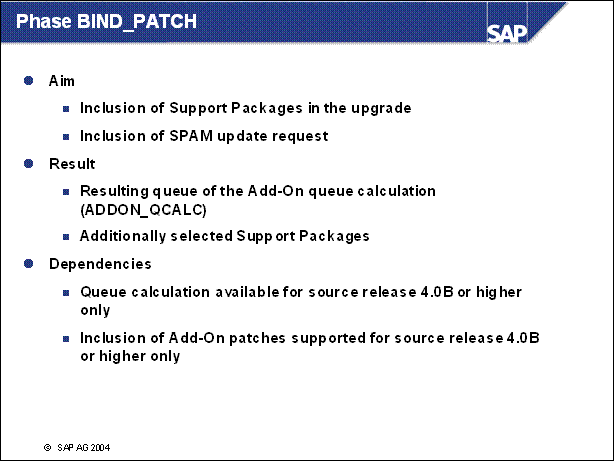
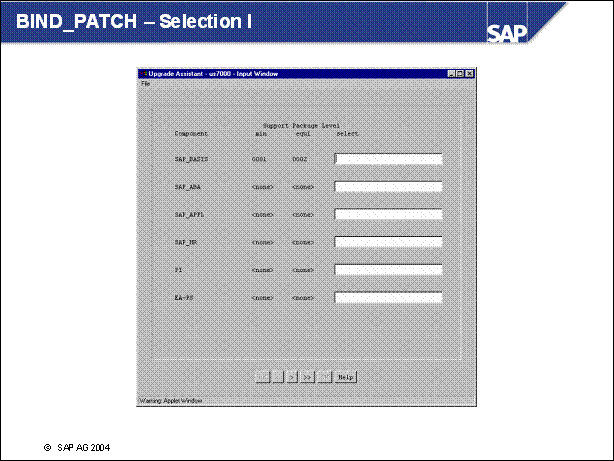
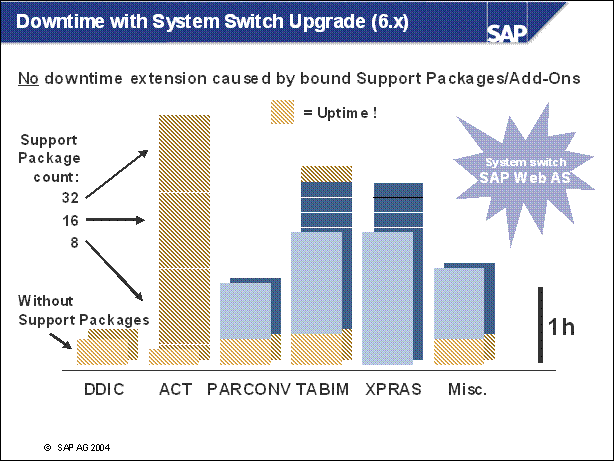
n With the system switch technology most of the upgrade activities are moved into uptime (marked in green).
n The amount of bound Support Packages has no impact on the downtime.
n Some upgrade phases still have to be processed in downtime, especially phase XPRA.

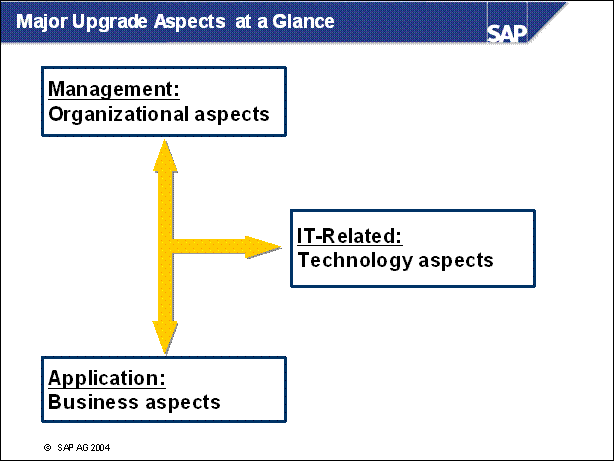
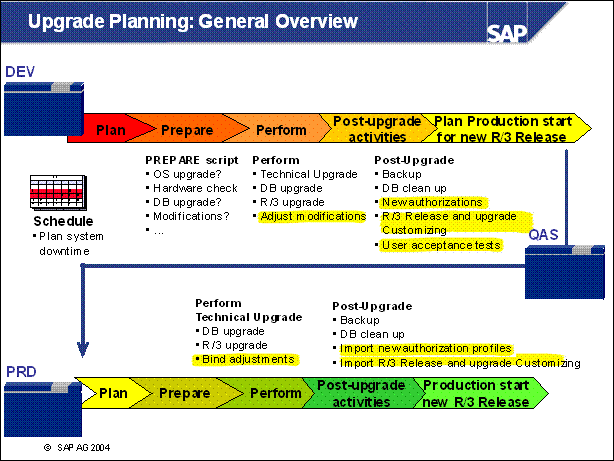
n In the standard three-system landscape, each of the systems is updated in the standard transport sequence. Tasks such as Customizing, applying patches, and performing modification adjustments, are performed in the development system and transported to the quality assurance and production systems.
n As described in the upgrade guideline documentation, mandatory tasks prior to an R / 3 Release upgrade include checking relevant OSS notes, performing backups, possibly installing new frontend software and deleting redundant clients to reduce upgrade time.
n One of the most important pre-upgrade tasks is running the PREPARE script to automatically perform many important checks (see appendix of this unit).
n One of the most important tasks during upgrade is performing modification adjustments using Transactions SPDD and SPAU.
n Post-upgrade tasks include:
Applying OCS patches the new R / 3 Release
Operating system backup
Customizing for the new R / 3 Release
Testing the new R / 3 Release and possibly distributing new authorizations
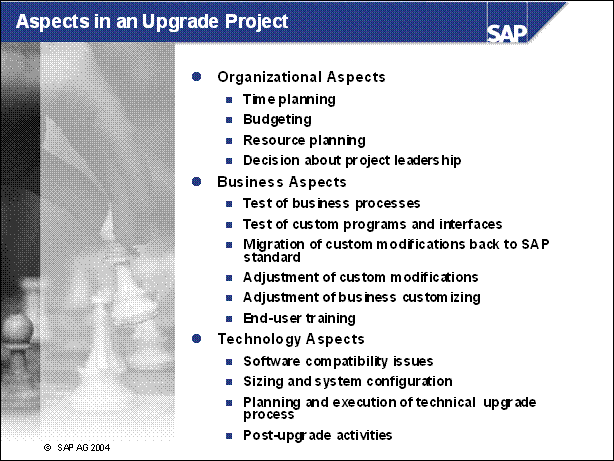
n Organizational challenges: Even if this sometimes rates as not so important, the organizational view is an important factor for the success of an upgrade project. Besides time and budget planning, resource planning is also important. In searching for team members, the upgrade skills should be considered. If the team members have never done an upgrade project, you should at least train this team and / or request assistance, e.g. project coaching.
n Business processes: It is clear that business processes are affected in
the upgrade project. A big opportunity is the potential to bring customer
modifications back to standard or to replace customer programs since their
functionality scope is in the SAP standard now.
Every modification, even customer programs cost money to maintain. Bringing as
many as possible back to the SAP standard, means maintenance of those objects
gets done by SAP in the future.
One point which has to be mentioned here is the testing effort. SAP has made a
lot of enhancements in the last years to reduce activities within an upgrade
project. However, testing is still a task which has to be done thoroughly. With
SAP ERP Central Component or SAP R / 3 Enterprise and their SAP Web Application
Server, a new test tool can be used which is e-CATT. Please make use of this to
minimize efforts in testing.
n Technology: In the area of technology several things have to be done too. Beside the execution of the technical upgrade itself, detailed planning of the technical activities as well as the sizing and configuration of the systems is an absolute must. Finally, post-activities are necessary like reviewing the existing backup and high availability setup.
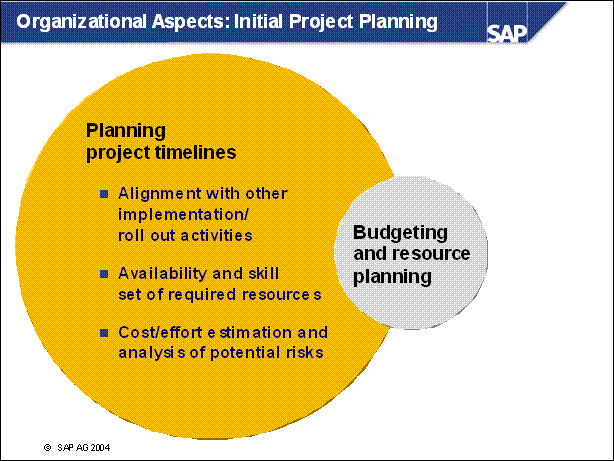
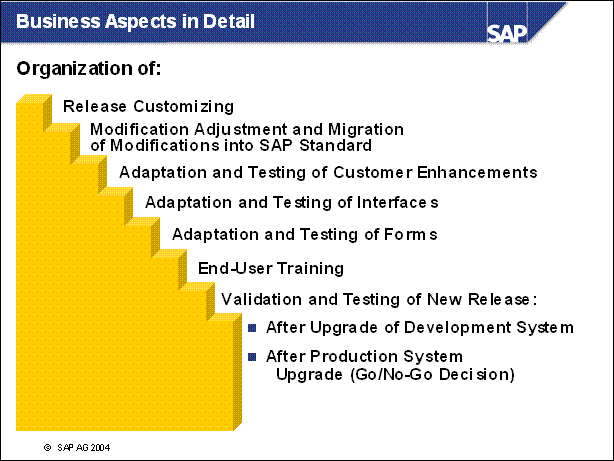
n The biggest part of the upgrade project represents the adaptation of the current business processes to the new features of the new SAP system. There are not only changes to the customizing and the repository. There are also changes for the end users, how to work with the new applications. When the development system has been Upgraded to the new release it can still be necessary to develop bug fixes for the productive system which is still working with the start release.
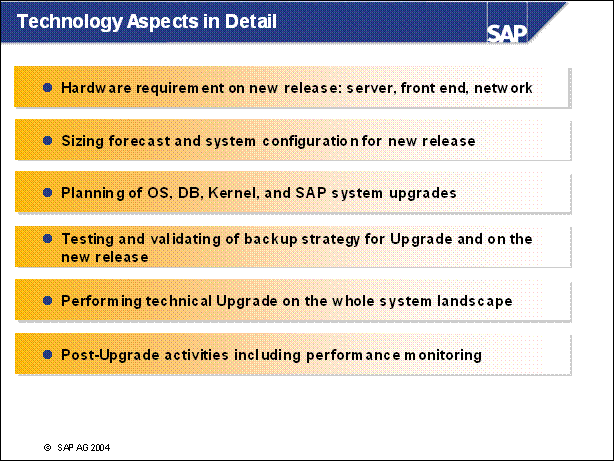
n Since the requirements of the new release are changing we need a sizing forecast which in turn requires changes to the configuration. Finally the whole environment is concerned, for example the server hardware, the client hardware, the network, the operating system and the database. Especially when changing the operating system other software on this computer has to be tested. For example the backup software has to be tested.
n Because of the new requirements, performance monitoring gets more important after the Upgrade.
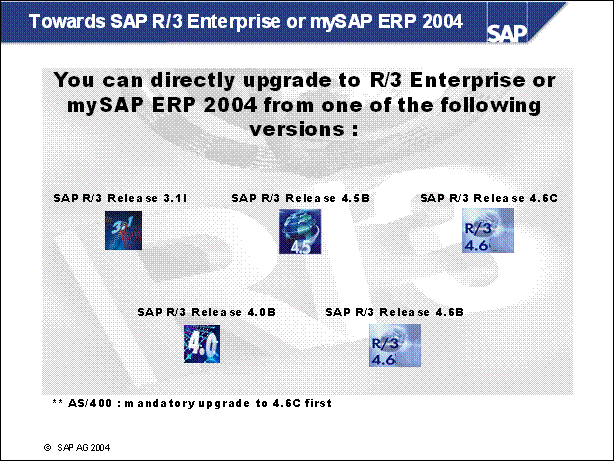
n All these SAP R / 3 Releases can be directly Upgraded to SAP R / 3 Enterprise.
n Note: The lower the start release, the higher the effort of the Upgrade project (for example, Enjoy SAP from 3.1I to SAP R / 3 Enterprise). Additional time for the Upgrade project has to be calculated.
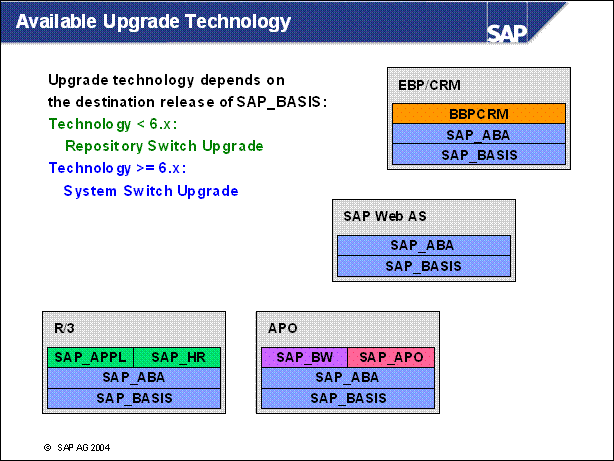
n The Upgrade technology provided depends mainly on the release of the SAP Technology (the Software component SAP _ BASIS) Currently we provide two different Upgrade procedures:
Repository Switch Upgrade for destination releases 3.x and 4.x
System Swtich Upgrade for destiantion releases 6.x
n For the repository switch Upgrade several new features have been developped during the releases. Here also the features depend on the destination release of SAP _ BASIS
4.6B: language transport with R3trans, "import to shadow" of Support Packages
4.6C: 'import to shadow' fo Upgrade transports into new tables, parallel mass activation
n For the system swith Upgrade, even for support releases on the same SAP _ BASIS release, new features are developed.
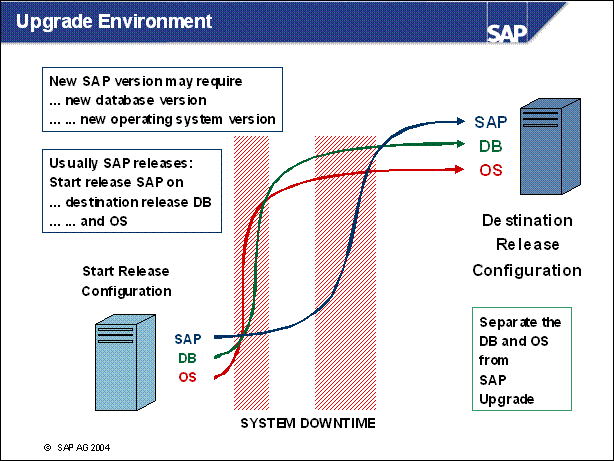
n The new SAP version usually needs a newer DB version and OS version. Thus an Upgrade of SAP usually also requires an Upgrade / migration of the operating system and the database. The usual dependencies are:
n SAP system is developed on the latest DB versiones,
n The latest DB versions usually are release only on newer OS versions
n SAP usually releases also 'older' SAP releases on DB and OS versions higher than those used initially
n This enables customers to run an SAP release on the latest DB and OS versions if required. Thus the maintainance periodes of SAP releases can be enlarged.
n During the Upgrade of a SAP, DB OS combination this feature may be used to split the system downtime (eg to two different weekends):
First do the Upgrade of DB and OS to the version required by the destination release of SAP system.
Second Upgrade SAP system to destinatin release.
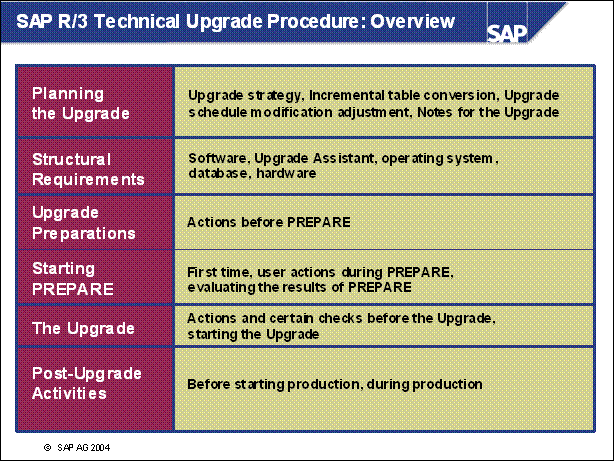
n This list consists of six parts. Each part describes a different activity that must be performed as part of the system Upgrade
n In planning the Upgrade, the customer should take decisions concerning the Upgrade strategy and incremental table conversion. An exact Upgrade schedule should be drawn up. The customer has to plan the Modification Adjustment carefully to reduce Upgrade downtime
n Certain requirements (software, hardware, operating system, database) must be met before you can Upgrade the SAP R / 3 System
n Careful preparation of the Upgrade is the best guarantee that it will run without errors.
n After you have performed the preparations for PREPARE, you can start it
n PREPARE automatically checks if your system is properly configured for performing the Upgrade. However, you must perform many tests and actions manually before starting the Upgrade
n Post-Upgrade activities include all actions necessary for completing the Upgrade. SAP recommends completing the actions in the order given in the Upgrade guidelines.
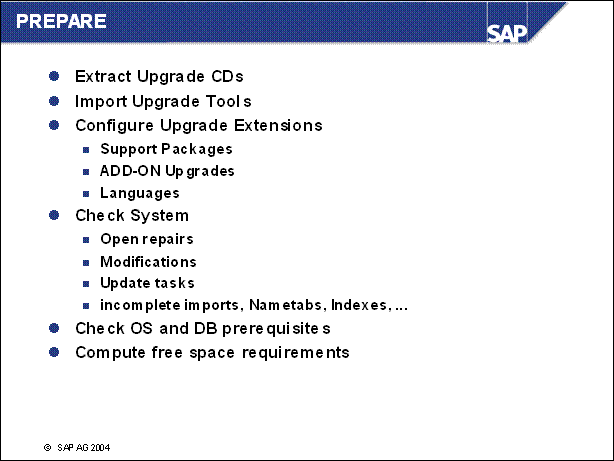
n During prepare:
n The CDs are read, all DATA needed during downtime is transferred to hard disk
n The tools needed during the Upgrade are imported into the system (TOOLIMPORT)
n The new kernel is extracted to disk
n The Upgrade can be configured:
Bind Support Packages to the Upgrade
Bind Add On Upgrades to the Upgrade of the underlying SAP system
Configure the languages that shall be availabe after the Upgrade
n PREPARE checks the system:
Open repairs (need to be released before they can be transferred into the new system)
Modifications
Update tasks
n Compute the free space requirements. Additional space is needed in the DB (both temporary and permanent!). This depends on:
The start release
The DB vendor
The number of clients in the system
The number and size of tables that need to be converted
The number of languages
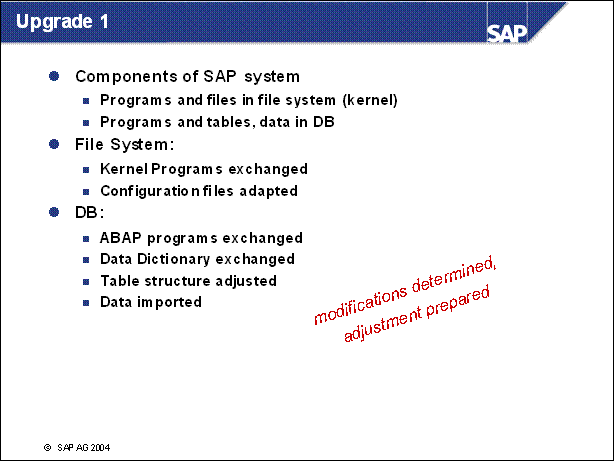
n During the Upgrade we
Exchange programs and files on the file system
the kernel and external tools
adapt profile settings
Operations on DB level:
Creation of new tables and views
Altering of existing tables
Operations refering to the content of tables:
Exchange ABAP programs and DDIC definitions
Import new customizing data
Import new texts in all required languages
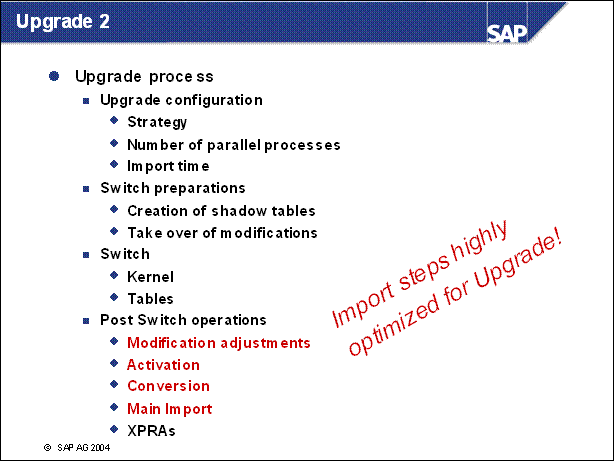
n The Upgrade process may be configured to adapt to the customer situation and hardware:
Different strategies (usually depends on the downtime requirements)
Number of processes run in parallel / usually depending on hardware)
Import time during productive operation may be slowed down to reduce system load and not affect the running system
n A first overview of the steps performed during the technical Upgrade istelf:
Switch preparation
Switch
Post processing
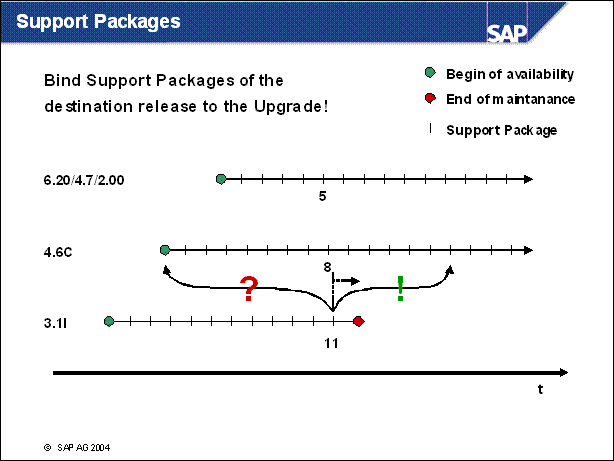
n Support packages on the start release are produced also after a potential destination release has been shipped.
n 3.1I Support Package 11 f.e. has been shipped after the shipment of 4.6C.
n On each potential destinatin release, Support Packages are availabel too.
n There is some relation between the Support Packages: usually fixes have been mad at the same time for different releases (here eg 6.20 / 4.7 / 2.00: 5, 4.6C: 8 and 3.1I: 11)
n An Upgrade from 3.1I Support Package level 11 to 4.6C Support Package level 0 would parially downgrade the system
n But: it is possible to bind packages to the Upgrade: you can go directly to 4.6C Support Package 9 or higher (in this example)
n Advantages:
No need to supply the Support Package on the destination release after the Upgrade
No (temporary) downgrade
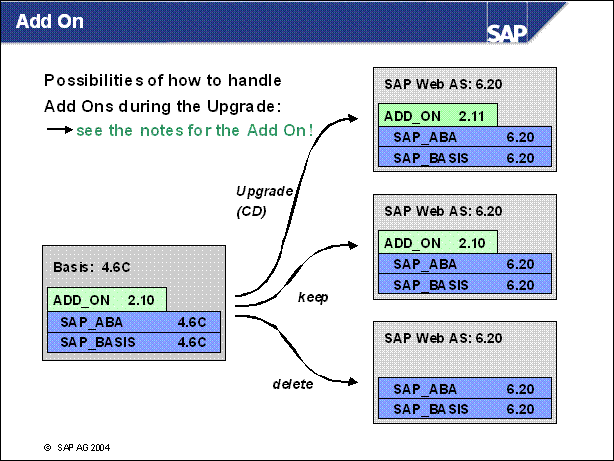
n Add Ons in the system:
n They are detected by R3up, a decision about the handling of the package during the Upgrade is requested:
Upgrade: there is an Upgrade CD provided by the Add On vendor. This CD can be bound to the Upgrade process, so also the Add On will go to a new release.
Keep: keep the add on version of the start release. This is not always possible since the Add On may use functionality of the system, and the system version changes. If it is possible, the Add On vendor publishes an Upgrade-Key. The key is required.
Delete: the add on software can be deleted from the system during the Upgrade. Modifications by the add on are removed. Tables on the DB are not deleted!
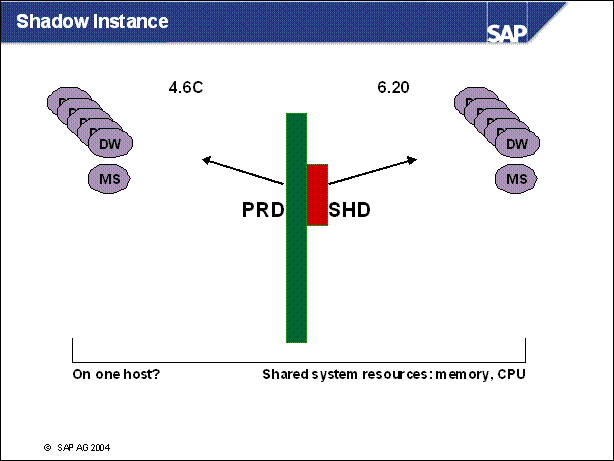
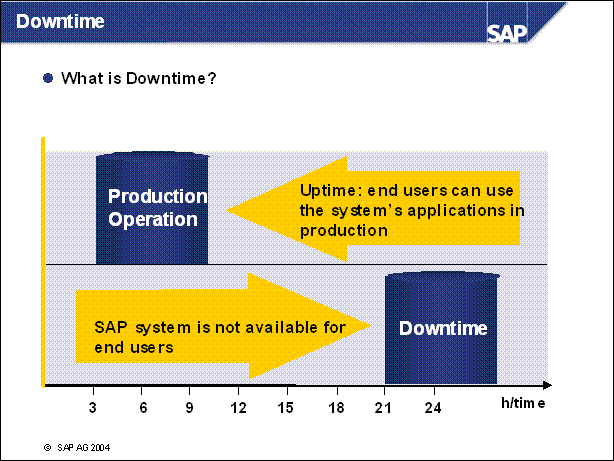
n Downtime is the duration, in which a user cannot use the systems applications in production.
n Why downtime?
The big advantage of SAP's Upgrade
technology is, that we allow our customers to adapt, extend and modify SAP
software, and these extensions will be kept and adjusted to the new release
during the Upgrade process. Most of the required processing steps can be
performed during system uptime.
Downtime is necessary, whenever live running transactions have to be replaced by new functionality, and a potential risk of data inconsistancy is given, i.e. changing the processing logic, or changing the data model / structure.
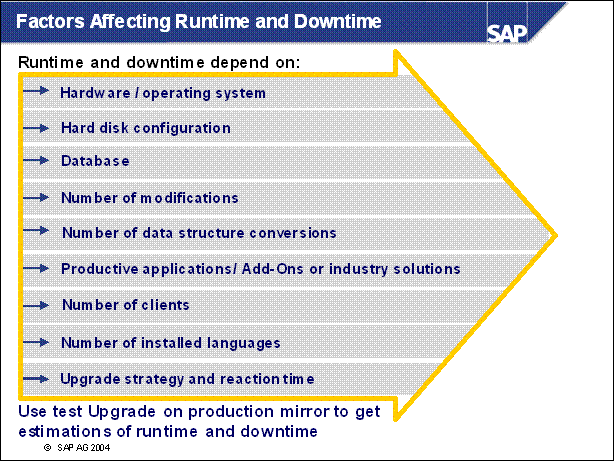
n A test Upgrade on a production system mirror and thorough analysis of the Upgrade log files can highlight many possibilities for effective manual tuning activities.
n Runtime and downtime depend on:
Hardware and operating system: The whole Upgrade runtime is very
different dependent on the hardware and operating system you use.
Hard disk configuration: Input / output throughput, backup speed
Database: Size of tables, database configuration, parameter tuning
Number of Modifications: SPDD and activation time
Number of data structure conversions: Phase PCON
Productive applications: More productive applications mean more data
conversions
Number of clients: Client cascade in phase TABIMP
Number of installed languages: More data import
Upgrade strategy: More or less down- and runtime
n An excellent preparation for achieving an optimal reduction of the production system downtime is to perform multiple Upgrade tests including manual tuning measures.
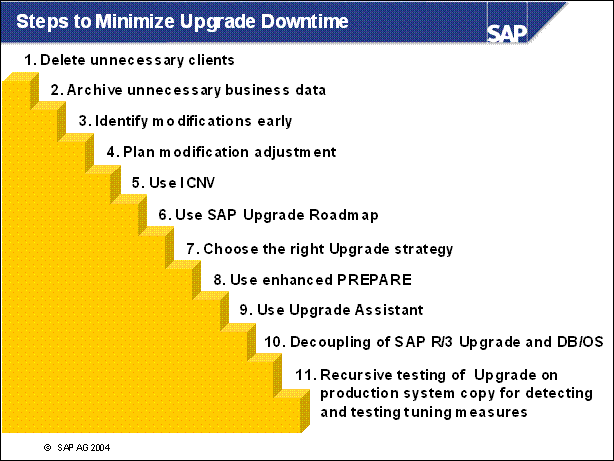
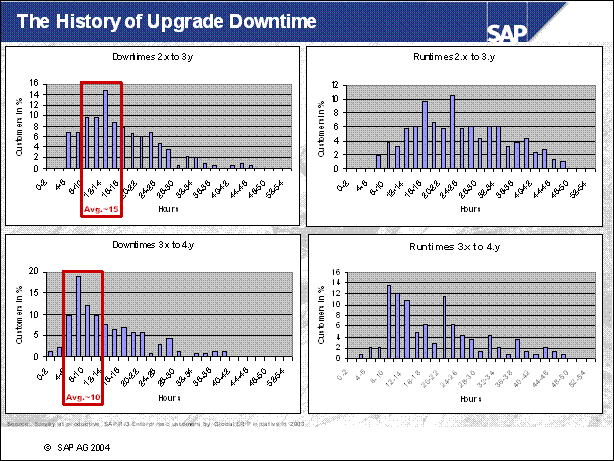
n These figures here, show the evolution of the downtime and runtime behavior in the past releases.
n If you compare the release change statistics from "2.x to 3.y" with "3.x to 4.y", you can see that downtime got reduced by around 30%. Even the whole Upgrade runtime got reduced.

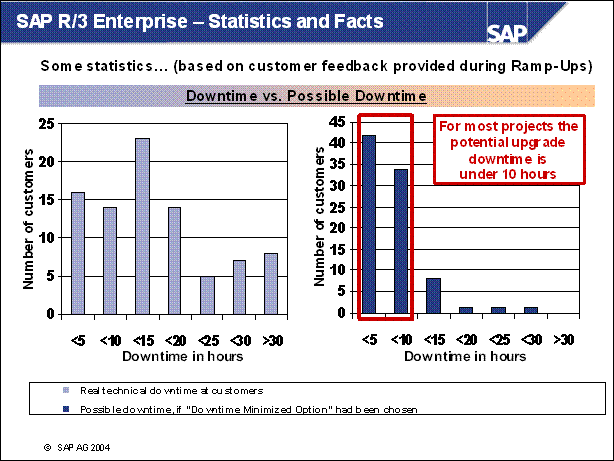
n New upgrade technology was introduced with the SAP Web Application Server - the "System Switch Upgrade" technology.
n This new technology offers the possibility of performing most of the upgrade steps in parallel with the production operation by using a parallel SAP Web Application Server Instance for upgrade processing. To activate this technique the customer must choose the "downtime minimized" option. As a result downtime is considerably reduced.
n However, the statistics have shown that many of our customers are currently not using this technology and in so doing are not benefitting from a short period of downtime.
n To achieve the shortest downtime during the upgrade, the customer should use the "downtime minimized" method which is part of the System Switch Upgrade
n NOTE: The downtimes mentioned in this slide are the time for the purely technical upgrade. In addition to that, database backup, and post-upgrade activities like final testing, final import of languages, and so on have to be considered. These additional times are customer dependent and have potential for different kinds of fine-tuning!
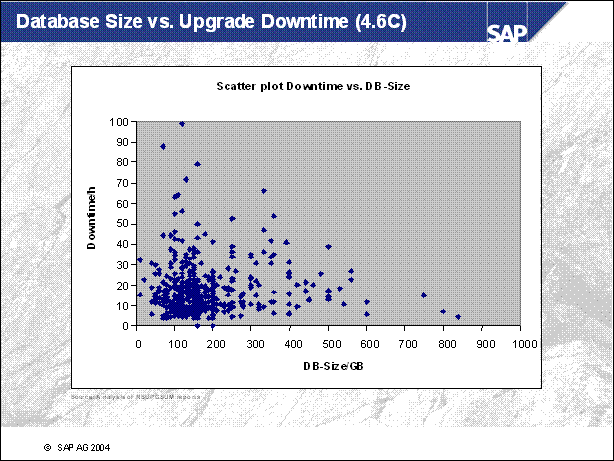
n Another point which often comes up in discussions with customers is an estimation on the length of "production downtime" resulting of the Upgrade itself. Many customer are afraid that especially the a larger size of the database is an indicator for a long downtime.
n The chart on this slide shows that the database size in deed has no direct impact to the downtime.
n Downtime is mainly influenced by the size of single tables and the number of clients in the system. The reason for this is the so called XPRA-Phase during the Upgrade, where a data model conversion in some area has to take place. This has to be done for each client which multiplies the processing time. Furthermore a conversion on larger tables takes more time than on short tables.
n To get a good estimation on the downtime, an Upgrade in a test environment has to be done. Normally this is the case by performing an Upgrade to the quality insurance system which is mostly a system copy of the productive system.
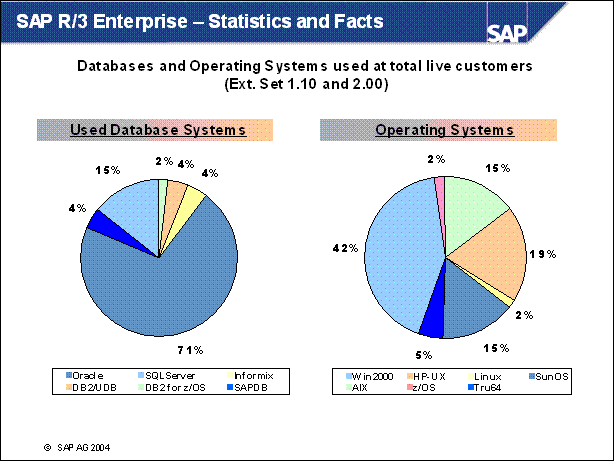
n This slide gives you an idea of the different databases and operating systems used by our "live" customers.
n Please note: These statistics are based on figures from the customers who supported us here.
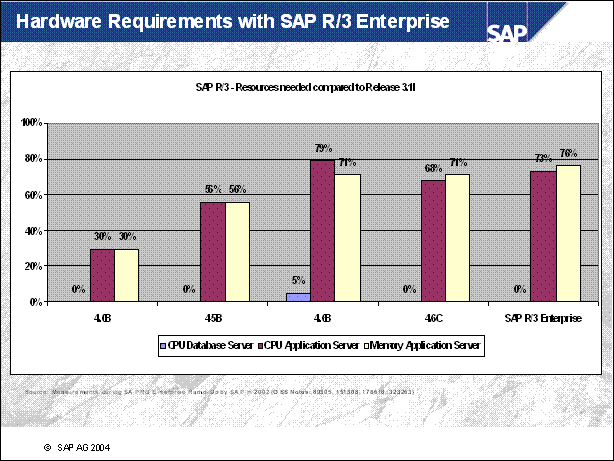
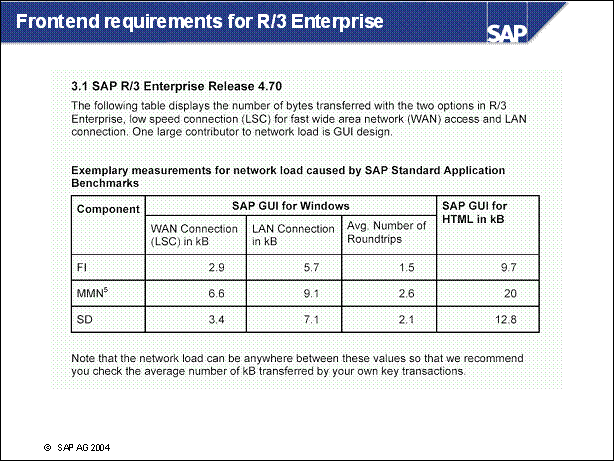
n This whitepaper can be found at https: / / service.sap.com / sizing -> Media Library -> Frontend Network requirements for SAP Solutions
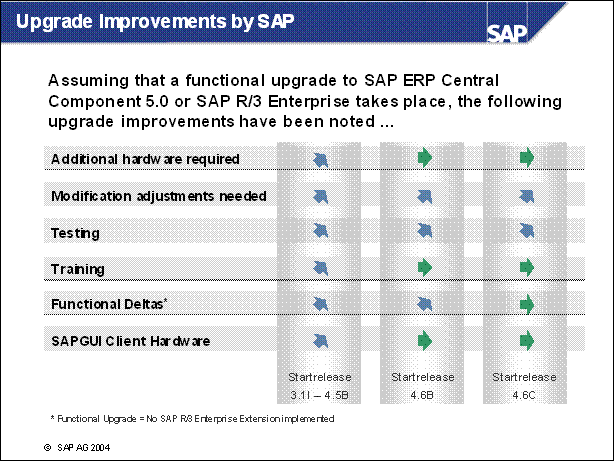
n For years, SAP has enhanced its upgrade technologies and the associated tools to reduce upgrade costs.
n This picture shows the results in certain areas. The green arrows signal that little effort is required, whereas the blue arrows indicate that greater effort is required.
n As you can see, the higher the start release, the more costs are reduced.
n To help understand this, here are some examples:
With the start releases SAP R / 3 3.1I up to SAP R / 3 4.5B the additional requirements on hardware for an upgrade to SAP R / 3 Enterprise or SAP ERP Central Component are between 15% and 70%. Starting from SAP R / 3 Release 4.6B the hardware requirements are between 0% and 15%. An upgrade from SAP R / 3 Release 4.6C requires more hardware resources around 5%.
Another example is in the area of functionality. Introduced with SAP R / 3 Enterprise, SAP offers new functionality as often as possible through the so-called extension set layer. As a result, the so-called core includes only a few changes. The application of SAP R / 3 4.6C, in particular, is very similar to this core. The customer can in many cases decide whether he wants to activate new functionality in the Extension Set layer by activating an Extension within this layer. As a consequence, the customer can limit the scope of functionality and with this the scope of the upgrade project. Finally this is also a benefit in the training area, where end users ideally need to be trained for the specific, activated area. In comparison, in previous releases of SAP R / 3, this was not possible. The upgrade influenced the whole functional scope of the system, creating training requirements in all areas.
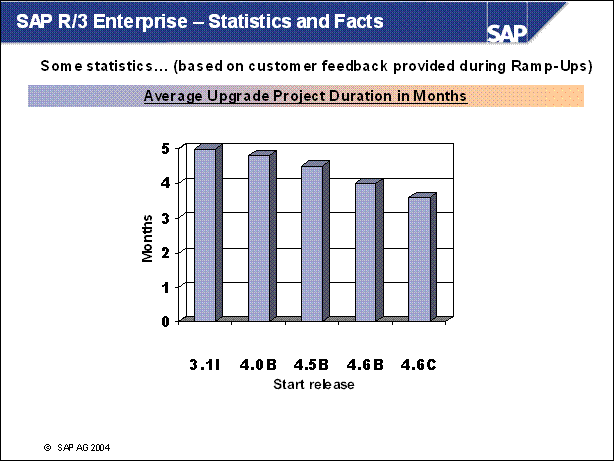
n An important question is: how long will my project take to upgrade to SAP R / 3 Enterprise? Here you can see the average project duration in months, broken down to the individual start releases. If you want to compare this with other data such as what were the modules used or the connected SAP systems, please refer to the "Upgrade Aspects with SAP R / 3 Enterprise - Statistics" document. See the appendix of this presentation.
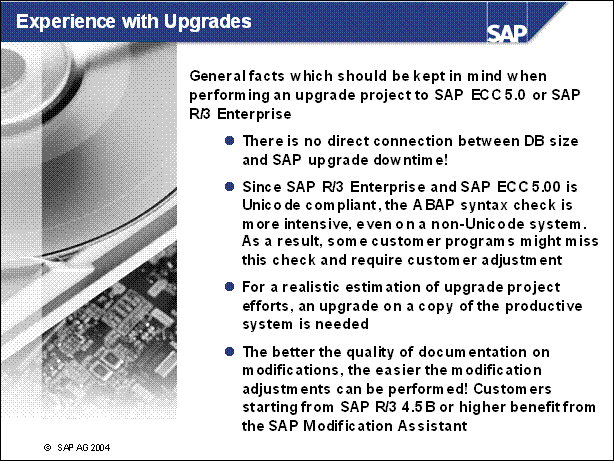
n This slide shows some general facts on upgrading to SAP ERP Central Component or SAP R / 3 Enterprise.
n One point which is often misinterpreted is the correlation between the
database size and the technical runtime of an upgrade.
There is no connection between DB size and the runtime, but there is a
correlation between the technical runtime and single tables in the database. As
a result, a customer A with a database size of >1Terra Byte may have a
shorter runtime than customer B with a 100 Giga Byte database, since customer B
might have some very large tables which unfortunately get converted during the
upgrade process.
n SAP R / 3 Enterprise as well as SAP ECC are Unicode compliant. Since coding runs differently in a Unicode environment (even in a system with Unicode switched off), SAP had to check and adjust nearly the complete coding in SAP R / 3 Enterprise (where Unicode was introduced for the first time). The same applies at the customer's site with custom programs. All customers' programs have to pass the much more intensive syntax check of the development environment. Some programs might fail the syntax check and will need adjustment.
n In all cases, an upgrade project is very customer individual due to the
customer-specific adjustments, customizing, and programs. SAP recommends two
ways of evaluating the efforts of an upgrade project.
1. Upgrade Assessment: In the next section you will see that SAP is offering special
"Upgrade Evaluation Services". This could be one option for you to evaluate
your upgrade efforts by using such a service. This is especially of interest
for customers with few upgrade skills and little experience. More details on
this can be found at: https: / / service.sap.com / upgradeservices
2. Project system: Another option, especially for customers with existing
upgrade skills, is the setup of a temporary projects system. This system should
be installed as a copy of the productive system. Here, the customer can perform
an upgrade to evaluate runtime / downtime, required modification adjustments,
adjustments on customer programs, and so on. And this is without interfering
with the current productive system landscape. Moreover, this allows the
customer to start the upgrade project already. All kind of adjustments can be
transported afterwards to the "real" productive system landscape.
n Finally, as already mentioned in a previous slide, the documentation is a key factor in an upgrade project. The better the existing documentation is, the quicker a customer can complete the upgrade project. All customers starting from SAP R / 3 4.5B and higher will benefit from the tool SAP Modification Assistant. This tool (introduced with SAP R / 3 4.5B) automatically does some documentation within the SAP R / 3 system to simplify the modification adjustments in particular within the upgrade.
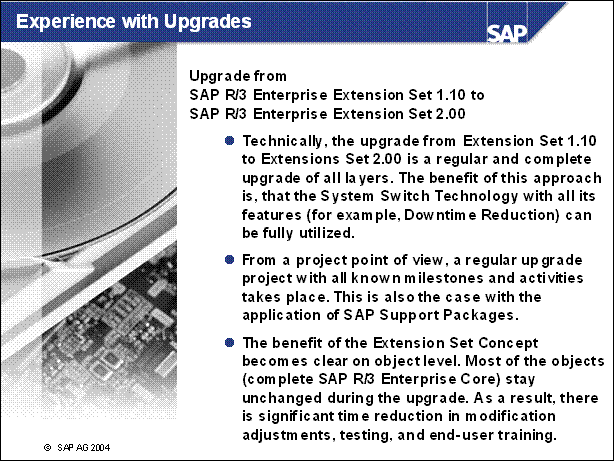
n Another important topic to touch upon at this point is the upgrade from SAP R / 3 Enterprise Extensions Set 1.10 to SAP R / 3 Enterprise Extension Set 2.00.
n Many customers expect that the SAP R / 3 Enterprise Extension Set layer can be upgraded without upgrading SAP R / 3 Enterprise Core or the SAP Web Application Server.
n Indeed, we are talking here technically about a full upgrade of the whole system, including SAP R / 3 Enterprise Core, SAP R / 3 Enterprise Extension Set, and the SAP Web AS.
n So the question is, why is a complete upgrade required and what is then the benefit of the SAP R / 3 Enterprise Extension Set?
n Well, this becomes clear if we look in detail. The reason for doing a complete upgrade is simply to leverage the SAP System Switch Upgrade technology which was introduced first with SAP R / 3 Enterprise. This technology in particular was designed to reduce the downtime of production systems during the upgrade. However, it also includes a lot of other technical benefits to make the technical upgrade process much smoother than in the past. The SAP System Switch Upgrade technology is designed to work with nearly all SAP components with time optimization in exchanging the full number of objects within a component. As a result, the technology is much quicker than it would be if an upgrade of a single layer were processed.
n The reason why a single layer upgrade would be more time consuming is, that even if the layers are encapsulated, they are technically stored in the SAP Repository. It would be more time consuming to select the specific objects instead of exchanging the whole SAP Repository. The secret comes with a technique, which has been in use for many years. The objects coming from SAP (with the upgrade CDs) get checked with the objects in the SAP Repository of the customer system. The SAP object will only be used if it has changed from the current release (start release) to the upgrading release (target release), otherwise it will be ignored and the existing object (which might include customer modifications) stays in the system. As we know, the SAP R / 3 Enterprise Core hasn't changed from SAP R / 3 Enterprise Extensions Set 1.10 to SAP R / 3 Enterprise Extension Set 2.00. As a result, all the Core objects will be ignored during the upgrade.
n So, there is indeed a benefit of the Extension Set layer, even if it technically looks like a full upgrade. Customers who already did the upgrade reported less efforts during modification adjustments. Furthermore, customers saw less problem situations while testing which as a result reduced time of testing.
n Furthermore, customers who have just one or a view Extensions activated in the Extension Set benefit from the fact, that they are facing less objects (just the ones from the activated Extension(s)) in the modification adjustments phase.
n One important point for customers during the upgrade, which should not be overlooked, is the downtime of their productive system. An upgrade from SAP R / 3 Enterprise Extension Set 1.10 to SAP R / 3 Enterprise Extension Set 2.00 provides, due to the facts above, in most cases a shorter downtime than all previous upgrades.
n If you are interested in more information regarding the upgrade technology and the steps taken within the technical upgrade, please consult the reference material at: https: / / service.sap.com / upgrade
n SAP recommends as a first step an upgrade project without the implementation of new functionality. This doesn't mean, that a customer shouldn't benefit from the so called "low hanging fruits". Especially customers with very low start releases (for example, SAP R / 3 3.1I) will see a lot of enhancement, which might replace existing customer programs or modifications. In these cases, customers should take the chance to reduce customer programs and modifications by implementing the SAP functions. Again, large implementations should be done in a subsequent implementation project. However, depending on the customer experience with upgrade projects, large implementations within an upgrade project aren't completely unrealistic. It must be said, that this would require much tighter project planning with a very good project team.
n One of the services offered by SAP is the "SAP GoingLive - Functional Upgrade Check". This service is already part of the customer's maintenance agreement. SAP recommends you make use of this service.
n Due to the fact that SAPGUI is downward compatible, customers can start distribution of the SAPGUI prior to the upgrade project. Experience has shown, that the SAPGUI distribution is sometimes an issue from a time perspective.
n As you will see later on in the section "SAP ECC 5.00 and SAP R / 3 Enterprise - Current Status", it is proven that the "Downtime Minimized" method of the SAP System Switch Upgrade technology is beneficial to all customers. SAP recommends performing upgrades with the "Downtime Minimized" method.
n SAP always recommends evaluating the change to return customers modifications and programs to SAP Standard. Customer modifications and programs are more expensive since the customer needs to maintain his changes by himself. SAP Standard, that is objects from SAP, are maintained through SAP Support and the existing maintenance agreement with SAP.
n Finally, customers should consult existing SAP Guides early on. At this point, customers with SAP Add-Ons (for example, SAP for Oil & Gas) in particular should read the Add-On specific guides. All guides can be found at: https: / / service.sap.com / instguides.
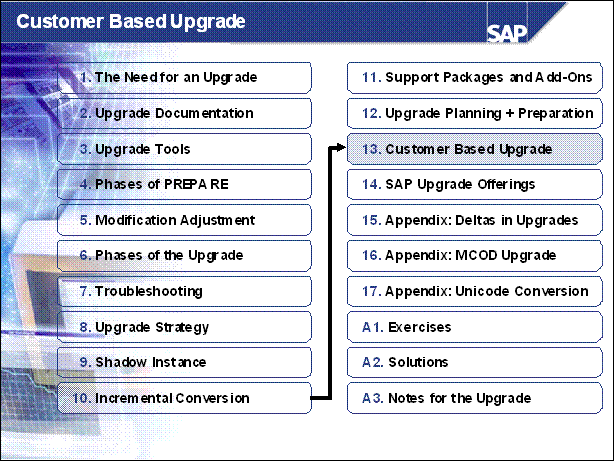
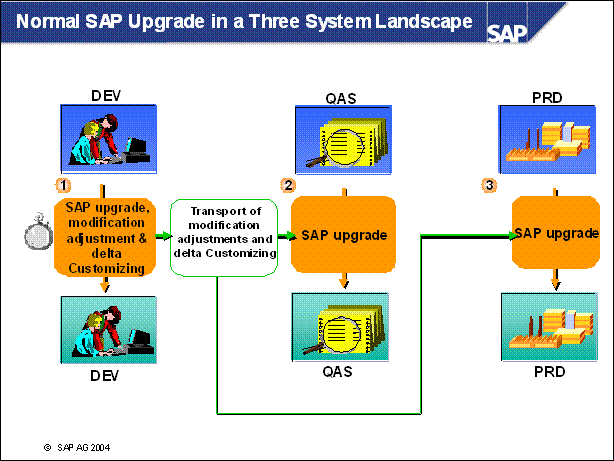
n In a three system landscape, the single upgrades are performed according to the transport routes.
n The tasks are performed in the following order:
Upgrade DEV and modification adjustment of DEV
Upgrade QAS (or upgrade of a copy of QAS), import of the modification adjustment of DEV into QAS and test functionality
Upgrade PRD, import of modification adjustment of DEV into PRD
n A great number of and complex modifications significantly lengthen the upgrade time for DEV
n The modification adjustment should be done by a developer and not by the system administrator or a consultant. All affected persons should be involved in the upgrade. Each modification should be documented.
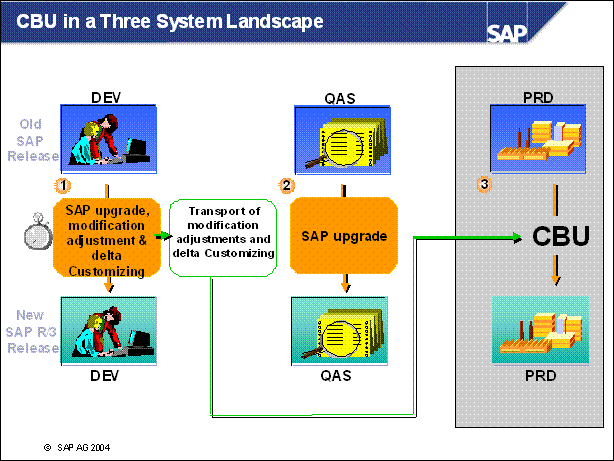

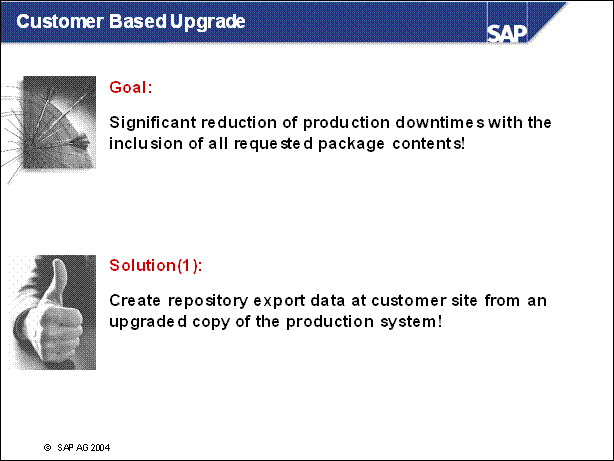
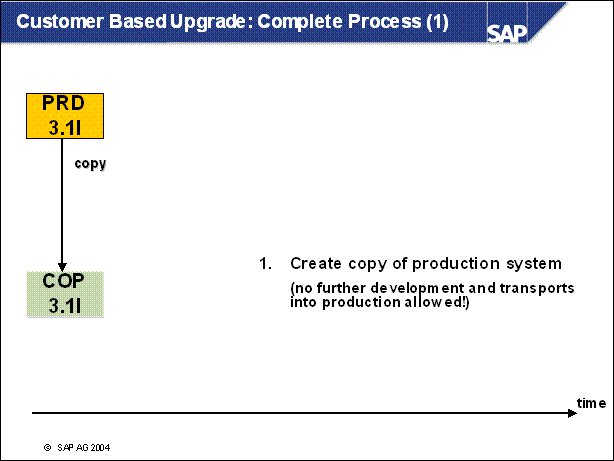
n CBU means that you import a customer specific repository into the system as opposed to the standard upgrade in which you import the target repository of the standard target release from SAP.
n For the CBU you create this customer specific repository in a Copy of the system you want to upgrade. Mostly the production system. So the first step ist the creation of this copy.
n At this point no further development will be transported into the production system! From now till to the finish of the CBU it is not allowed to change the repository of the production system. So you have to be sure that all your developments work fine and you do not have any bugs that force you to transport fixes in your production system.
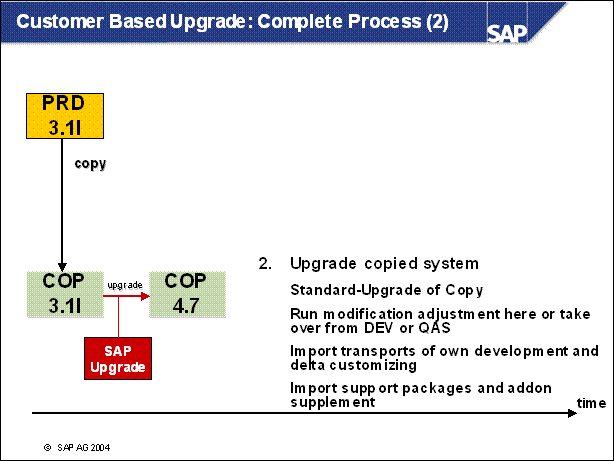
n Now you upgrade your Copy to the new target release. This is done by a normal standard upgrade. Here you adjust your modification or take over the adjustments from the DEV or QAS system.
n After the upgrade you do the delta customizing in the copied system and import transports of your own development.
n Here you got the chance to import the latest support packages. You can also execute SGEN, because you will import the generated objects during the CBU.
n After this phase there exists exactly the target repository you want for your production system. Here it is in your copied system.
n Now it is wise to make a backup of the system which you do not overwrite with backups in other phases.
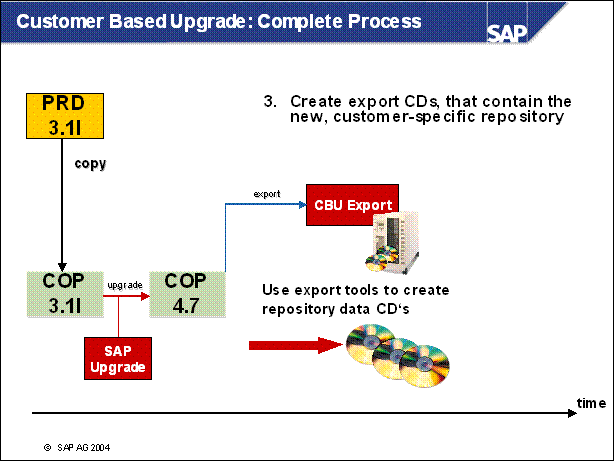
n To get the new repository into the production system you have to export it from your copy. This is done in this phase.
n With export tools you can find all the changes of the repository which were made during the upgrade and export them into a directory structure that looks like the export CDs 4 and 5 of a standard upgrade cd set.
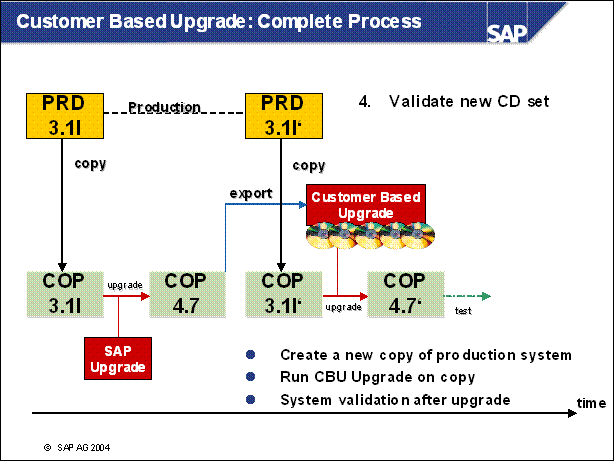
n To ensure that the cd set is created correctly you have to validate it.
n For this validatation you have to create another copy of your production system.
n This time you upgrade this system to the new target release with a customer based upgrade. Here the Repository will be switched to the new customer specific repository which is imported from the export CD set you made in the previous step.
n Here you get the first experience with the CBU. On a similar hardware you will find out the runtime of the CBU and the downtime saving.
n After the upgrade it is recommended to test the system very well. Because this is what you get when you upgrade the production system.
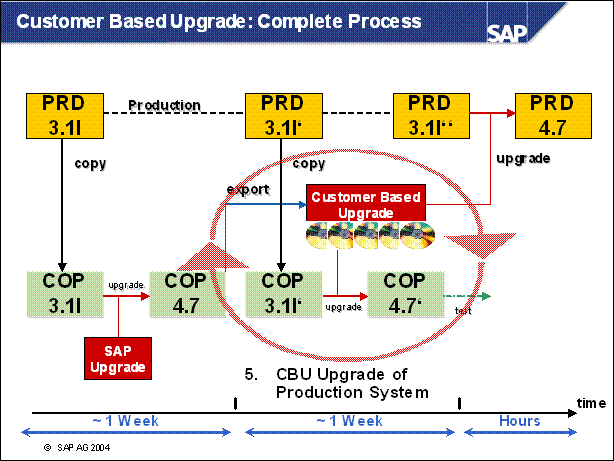
n Finally the last step is the upgrade of the production system. You already know this procedure because you did this already with the copied system. Here shouldn't come up errors you didn't have in the upgrade of the copy. If there still come up new errors, your production system has been changed for example by a transport you imported after the creation of the system copy.
n What you see here is the minimum of time you need for a CBU. At least you should take you time to test extensively the copied system which you brought to the new release with the CBU.
n On the other hand, when the test fails you have to repeat the export and the cd validation. Here you see the necessity of a backup of the upgraded copy. Remember step 2.
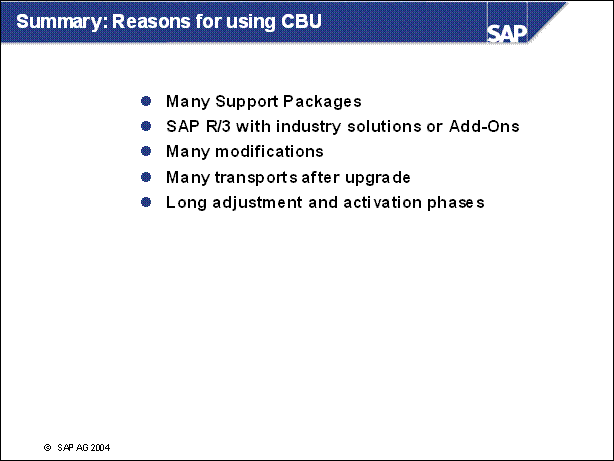

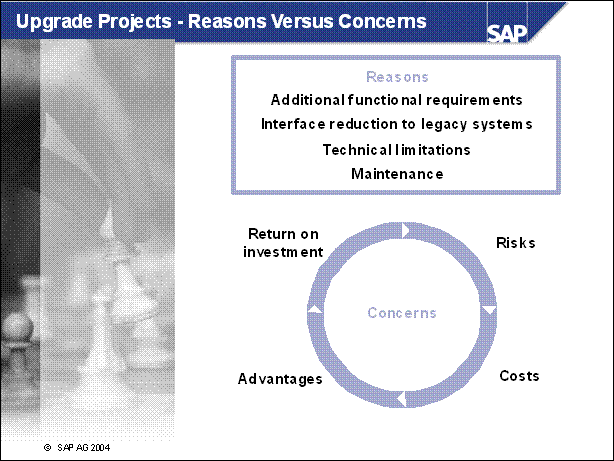
n There are a lot of reasons to upgrade, which can result in direct business benefits. Here we can mention not only cost reduction benefits in the system operation area, but also benefits from a functional delta point of view. New functionalities in higher releases can potentially replace lots of your modifications, which cost a lot of money to maintain. Furthermore, new functionalities can make your business more efficient.
n Additional functions: In the past, this was the key argument for an upgrade project. It is still a good argument and SAP R / 3 Enterprise as well as SAP ERP Central Component provide a lot of new functionalities in the application area. Keep in mind that the lower the start release is the larger the delta between start and target release and also the additional functionality.
n Technical limitations: The technology is becoming increasingly important in discussions about TCO. But besides this there are other things to consider. An old SAP R / 3 Release with older technologies has limitations like addressing bandwidth of memory, performance in general, and so on. So technical limitations are another point which could indeed be a reason for an upgrade.
n Reduction of interfaces: Staying with TCO, one of the biggest cost drivers is the number of interfaces used. Non-standard interfaces in particular cost a lot to maintain. With an upgrade to a higher release, many customers see potential in reducing their non-standard interfaces by replacing existing non-SAP systems with the functionality provided. Furthermore, SAP Exchange Infrastructure, which also comes with SAP NetWeaver can help customers to significantly reduce the TCO on the interfacing area. Also this important enhancement could be used without an upgrade to your existing SAP R / 3 system.
n Maintenance: Finally, the maintenance might also be a driver for some customers. SAP certainly does a lot to ensure that customers are aware of a lot of the reasons already mentioned. But even if the other areas currently offer no benefit to the individual customer, the customer might not need to do an upgrade if the mainstream maintenance has ended. There is also the option to extend the maintenance for a specific timeframe. Customers should consult https: / / service.sap.com / maintenance for more details.
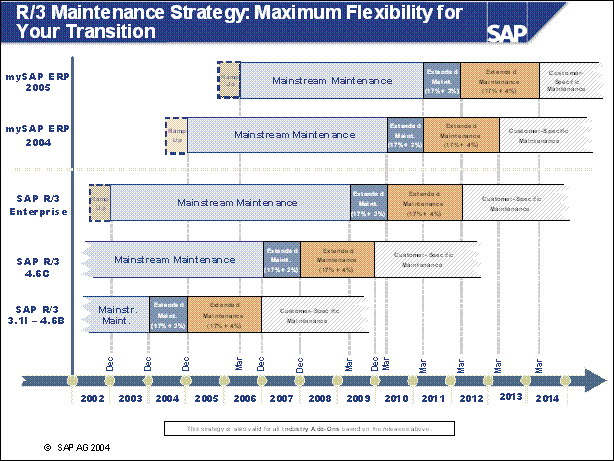
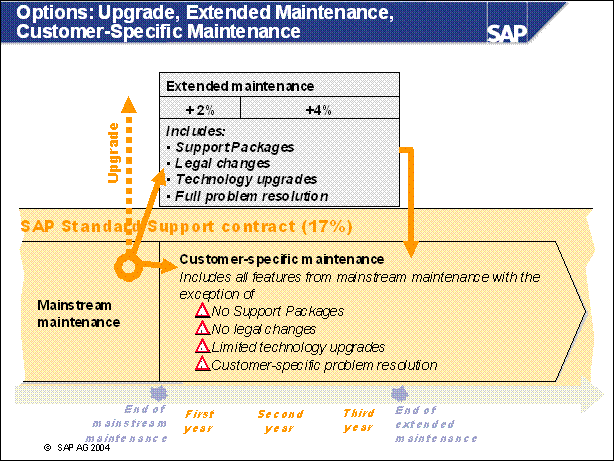
n As of June 2004, for all solutions based on SAP NetWeaver 2004, SAP offers eight years of mainstream and extended maintenance in total:
Five years of mainstream maintenance; at the standard maintenance fee
One year of extended maintenance; at an additional fee of 2%
Two years of extended maintenance; at an additional fee of 4% per year
Thereafter, the solution edition enters customer-specific maintenance.
n So, towards the end of the mainstream maintenance phase, customers have three options:
n They can upgrade to a higher release in mainstream maintenance
n They can go directly into customer-specific maintenance
n They can opt for extended maintenance. After the end of extended maintenance (maximum three years), customer-specific maintenance begins.
n Mainstream and extended maintenance offer the same scope.
n During customer-specific maintenance, the scope of SAP's Standard Support is slighly reduced.
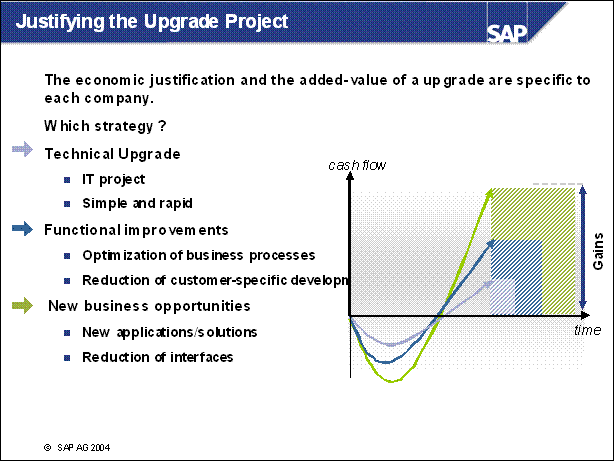
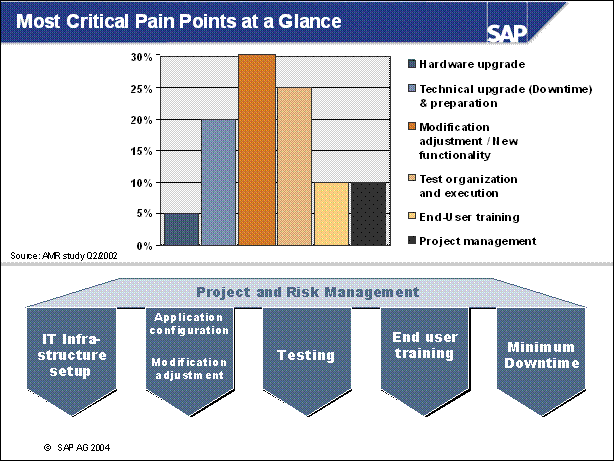
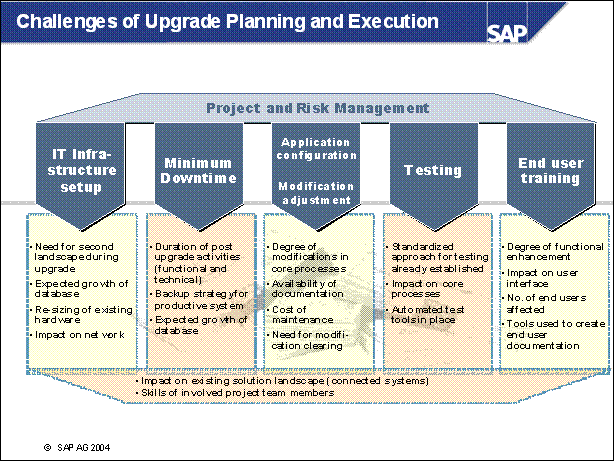
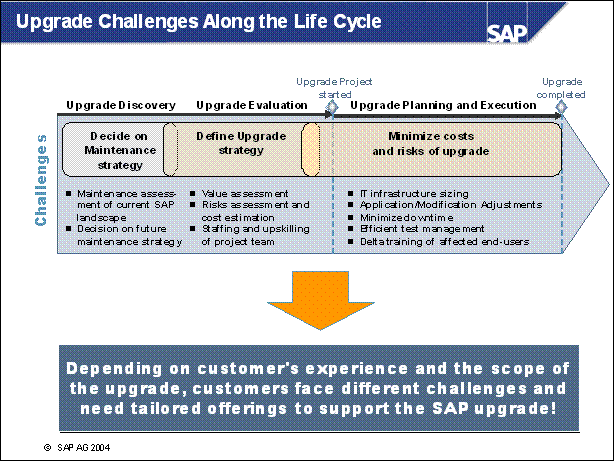
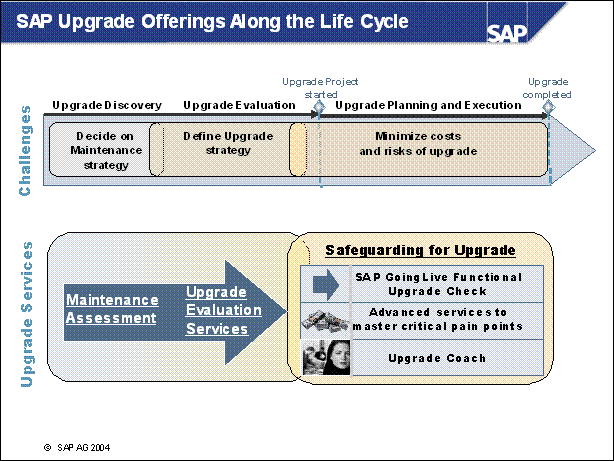
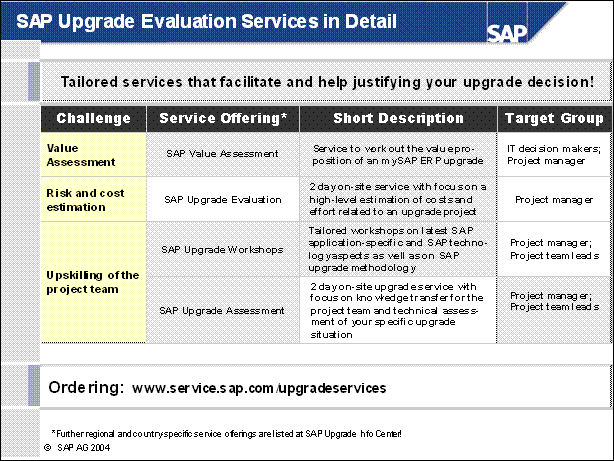
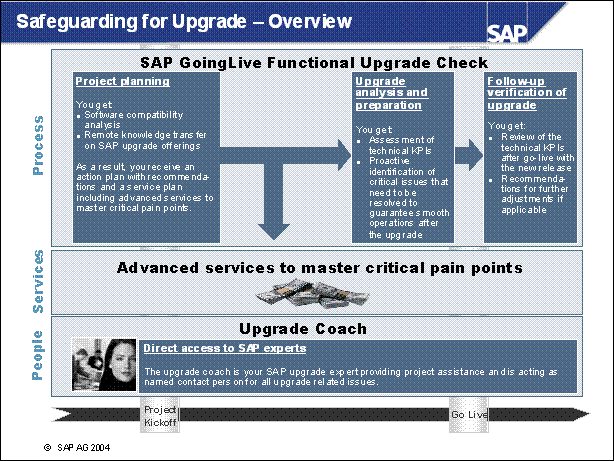
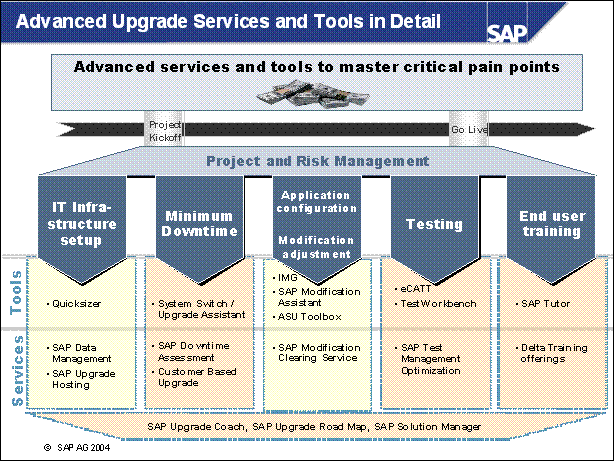
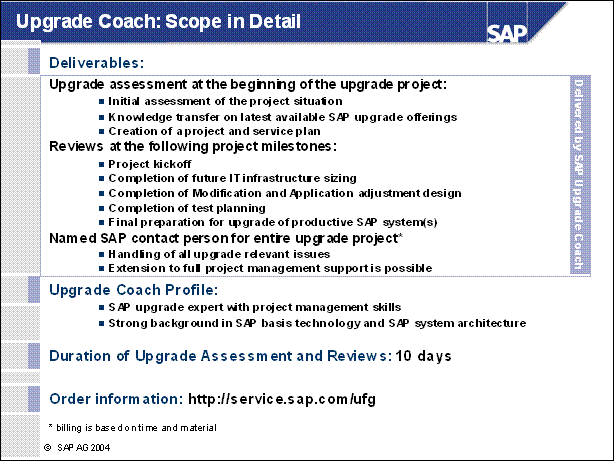
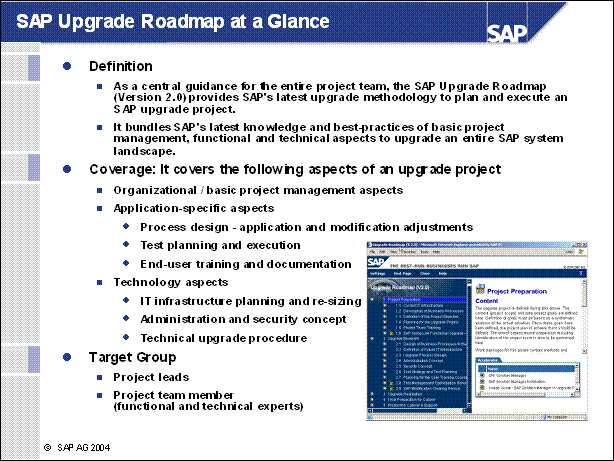
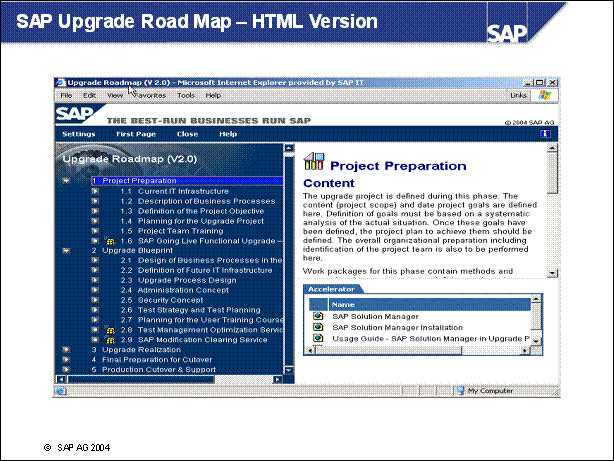
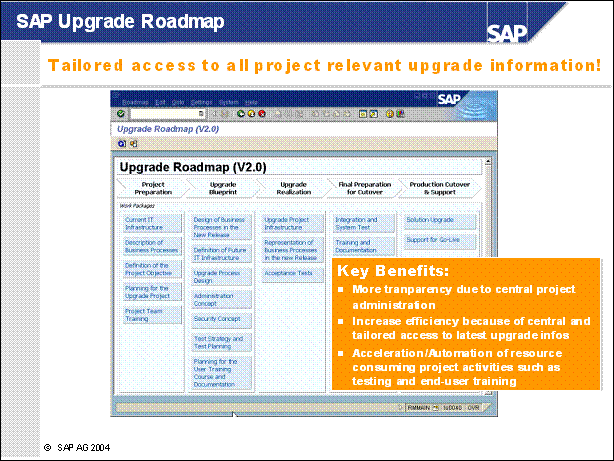
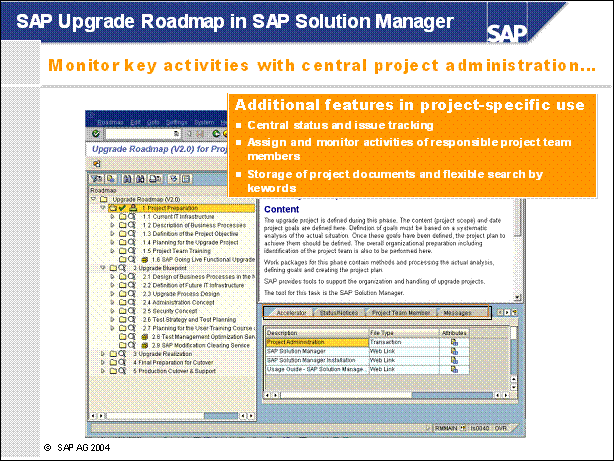
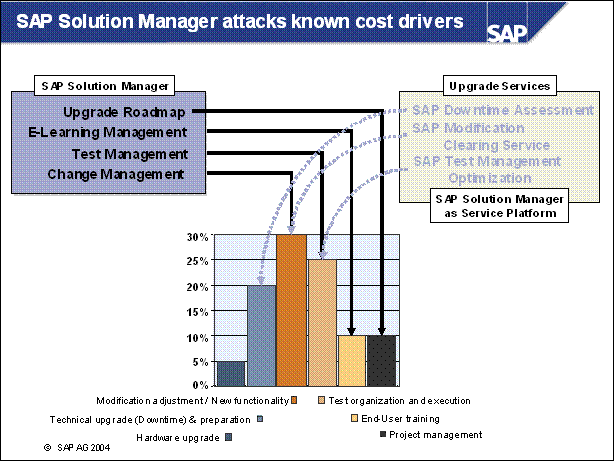
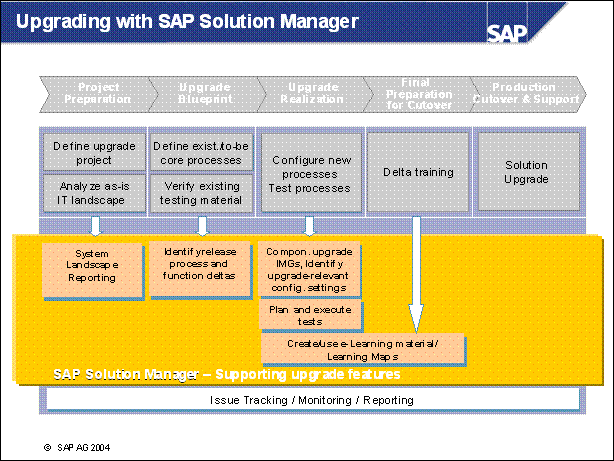
n Solution Manager for Implementation
n Procedure Model (Roadmaps)
Focus: product-specific information; no project management
Knowledge transfer to project team and technical implementation aspects are key elements
Available services aligned with the Procedure Model
n Implementation Content
Business process repository as initial input for a process-driven design of a customer solution
Intial focus: mySAP CRM and mySAP SCM implementations
n Tools
Basic ASAP tools (Blueprint and Master List functionality)
Integrated use of customizing and test tools
Focus: scoping, process-oriented configuration and testing, status and issue tracking
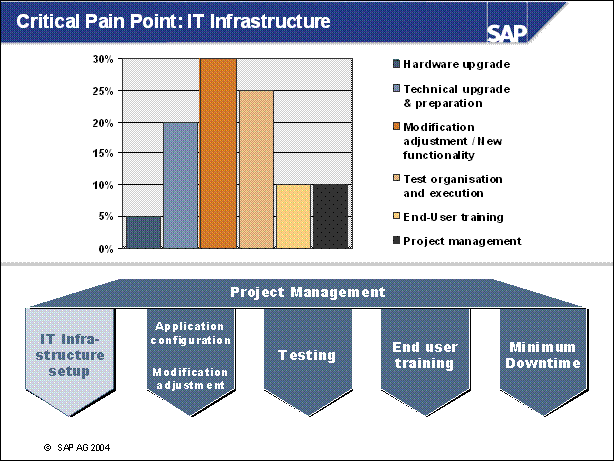
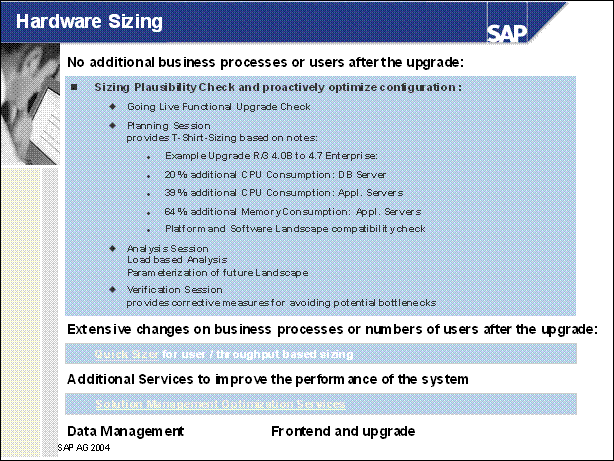
n Quicksizer to be found at https: / / service.sap.com / quicksizer
n Solution Management Optimization Services to be found at https: / / service.sap.com / smo
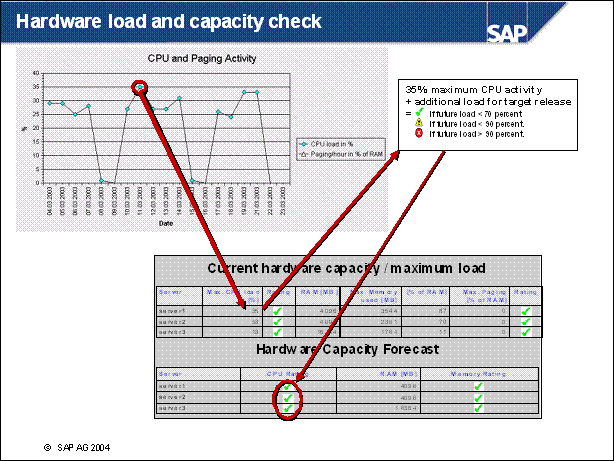
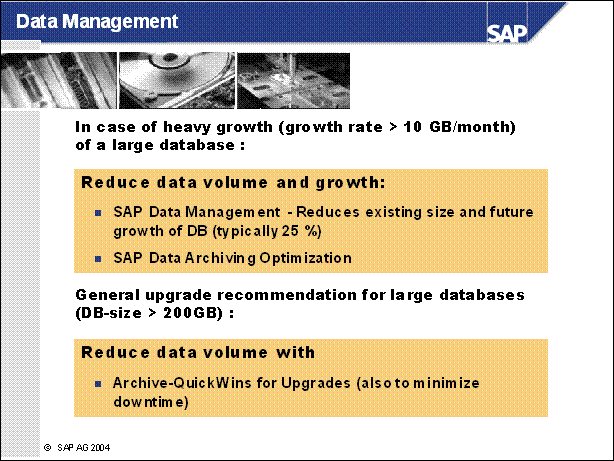
Improve system performance and response times because your DB stays small
Benefit from more efficient use of your resources such as hard drives, memory, and CPU
Reduction of IT related costs (Human resources, administration, .) as well as data storage costs
Increase system availability because administration tasks like software upgrade, database reorganization, data backups or recovery can be done in less time
Reduce the downtime for upgrades as well as diminish the runtime for migration and conversion projects
n Analyze your database and develop recommendations for potential disk space savings. Train your staff to optimally archive your data. The methodologies used to do this are prioritized in the following order:
n https: / / service.sap.com / dma
Data Avoidance
Data Summarization
Data Deletion
n https: / / service.sap.com / dao
Data Archiving
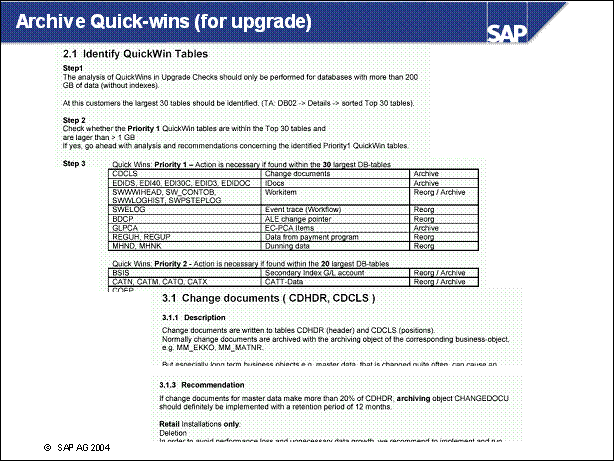
n The Best Practise "Archive Quick-wins" can be found at https: / / service.sap.com / dao -> Media Library
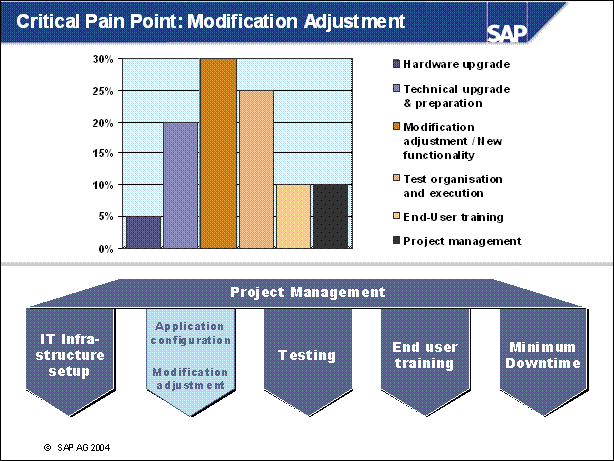
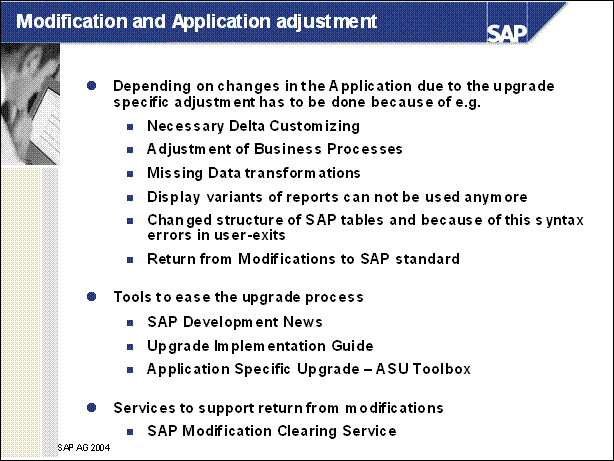
Development News serve as a key source to identify potential adjustments in existing customizing or possibilities to return existing modifications into SAP standard
The SAP Development News Browser allows dynamically to select by start and target release (e.g. R / 3 Enterprise Ext.Set 2.00) relevant Development News
Access the Development News Browser at https: / / service.sap.com / developmentnews -> Development News Browser for Upgrades or at https: / / service.sap.com / upgrade-erp
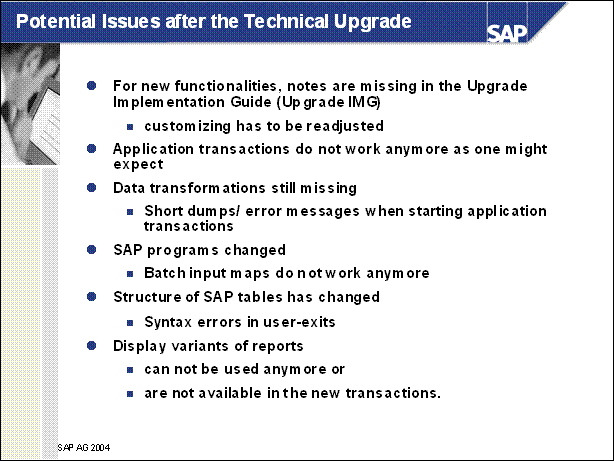
n In some cases, after the technical part of the upgrade has been finished, the tests in the upgraded system show a number of problems:
n Application transactions do not work anymore as one might expect (or in a different way than before the upgrade)
n You observe short dumps or error messages when starting application transactions because, for instance, data transformations are still missing.
n Background variants of programs possibly cannot be used anymore (see SAP notes 153865, 65343, 114675, 626408(variants!))
n Display variants of reports can not be used anymore or are not available in the new transactions.
n Batch input maps do not work anymore because the corresponding SAP programs have changed.
n Customer-specific user-exits have syntax errors because the structure of SAP tables has changed.
n For new functionalities, notes are missing in the Uprade Implementation Guide (Upgrade IMG). Therefore, the corresponding customizing has to be readjusted.
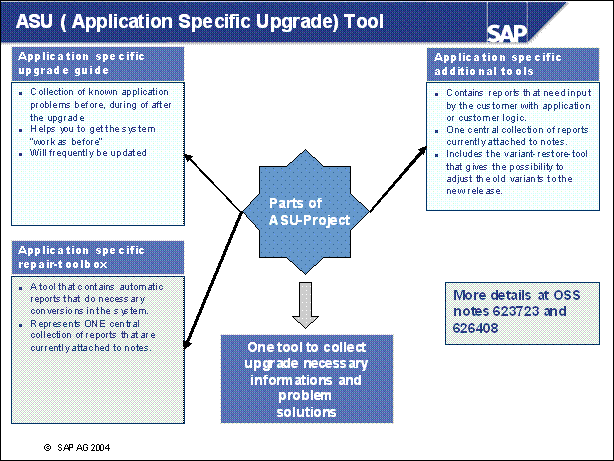
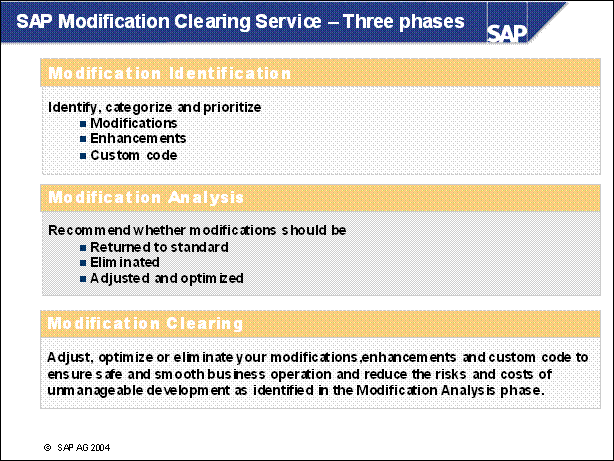
n The Modification Clearing Service is divided into three different phases build up on each other: the Modification Identification, Modification Analysis and Modification Clearing. Each of these phases are endowed with an own task and each phase's summary report will be the input for the succeeding phase. During all these three phases the customer's business experts and business owners are intimately involved in the process of this service. Their specific input is required to proceed from one phase to the next one and to esteem your business requirements.
n (1) Modification Identification: During the Modification Identification, the modifications of the customer's most beneficial core business processes will be identified in alliance with the customer. Having identified these modifications they will be categorized into the different business areas and prioritized with the customer for further investigation during the following phases.
n (2) Modification Analysis: In the Modification Analysis phase, the customer's modifications, enhancements and custom codes identified during Modification Identification will be analyzed in more detail with the objective to return them to the standard functionality, to eliminate or to adjust and optimize them, e.g. new BADI-definitions can be used on a higher release level.
n (3) Modification Clearing: Based on the Modification Analysis recommendations all necessary issues will be executed during the third phase, the Modification Clearing phase.
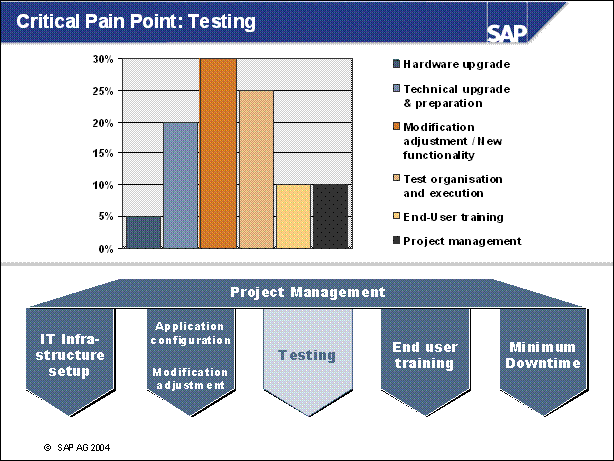
n Testing is the longest phase of an upgrade project and therefore it's one of the biggest cost drivers. If you don't organize testing in the right way, it can produce more costs and can take more time - Don't run out of budget and don't run out of time.
n Manual testing is a potential cost driver. It is important that the testing you perform is automated wherever possible. You can save a lot of time and money, because you need less personal- and workplace resources. In addition, human testers need training or experience. Automatic test cases are reusable, e.g. for redo tests or after applying support packages. Errors are easily reproducible. Automatic test cases reduce your costs of testing. The test automation should be up to 90%.
n The second typical problem concerning testing, is that different functional departments administrate their test cases in different ways and with different tools. E.g. one department stores the test case description in excel files and the other department stores it in word files. Additional are these files often are stored on different servers, in different versions and not all project members know where the files can be found and if there has to be added new test cases, several files has to be updated. It's difficult to keep an overview across this shared files. To prevent this, use a system, where you have a central administration.
n If you need an overview about the status of the test progress you need to have access to all the test process relevant data, e.g. test case description and the corresponding user documentation to the test case where you can see, if the test case has finished successfully or not. To avoid that, you should administrate all central.
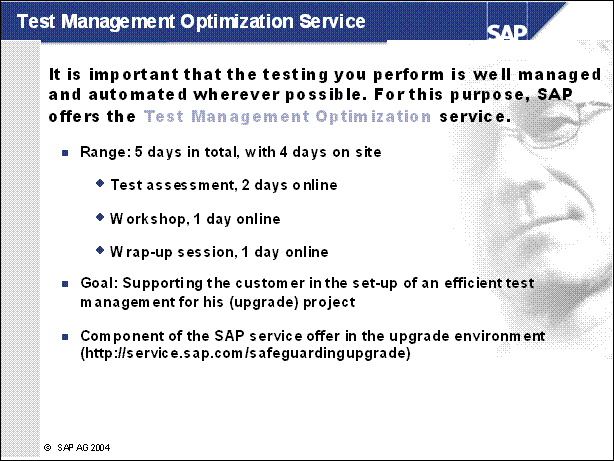
n SAP experts compare your testing process with the SAP Best Practices and based on the comparison, they are able to point out where you can optimize your current testing procedures, what tools you should use, where you can automate testing and in general, where you can reduce costs.
n Assessment: The Test Management Optimization service begins with a two-day, on-site assessment of your current test procedures. The assessment looks at the following areas to determine where there is a potential to optimize:
Established test organization, Test standards, roles, tools and approach to test automation
The assessment is done on-site with your upgrade project team. The result of the assessment is a report containing recommendations to improve the areas mentioned.
n Workshop: Following the assessment, there is a one-day workshop. The members of your upgrade project staff who attend the workshop learn what testing tools SAP has available and how to use them efficiently. Your project team receives practical experience with the SAP Test Workbench which contains the tools CATT / eCATT and Test Organizer; all of which are included in the SAP Solution Manager 2.2 and higher. No extra license fees apply.
n Wrap Up: On the final day of on-site delivery, a wrap up session will be performed. During this session, the results of the analysis are reiterated and the recommendations presented and reviewed. A first draft of an action plan to implement the recommendations is created at the end of the wrap up session.
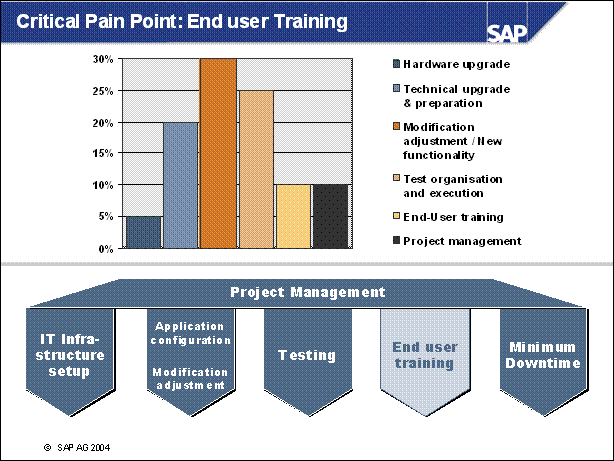
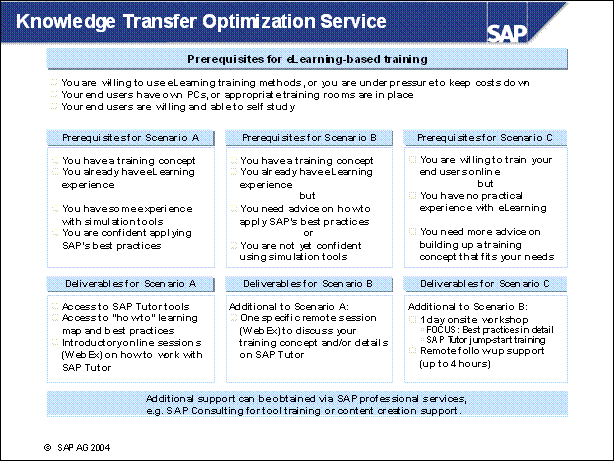
n Typical questions concerning training are e.g.
Where are the Users located?
Are Trainings systems available?
Is the Infrastructure for distribution already set up?
n Fitting to your needs we have defined three major scenarios of eLearning-based training:
n you are already experienced in eLearning and need only some how-to information as well as a tool
n you are experienced in eLearning but would like to have more advice
n you want to reduce costs by using eLearing but you have no proctical experience
n For a special remote or onsite workshop please ask your SAP contact about details. The deliverables for scenario A are accessible in the SAP Servicemarketplace. Also the recommended tool - the SAP Tutor - can be found here.
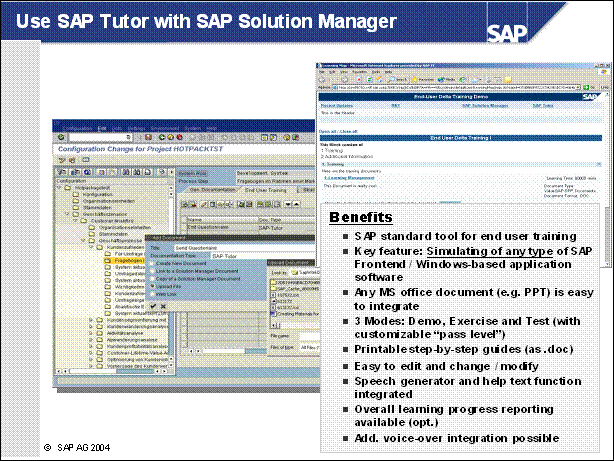
n The SAP Tutor allows you to record any windows based application software and create tutorials out of it. There exist three different types of sessions you can create with this tool - a demo mode, a (guided) exercise mode and a test mode. More information about the SAP Tutor including tutorials and more to be found at https: / / service.sap.com / saptutor
n With the Solution Manager 3.1 (with Support Package 13 and higher), it provides the following enhanced features:
Assign your learning materials to end user roles, processes and projects
Organize learning materials to role / task-specific "learning maps" for end users
Distribute "learning maps" to end users as a web transaction
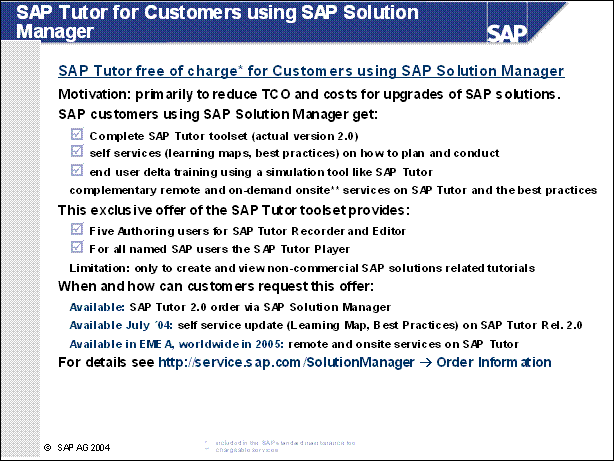
n In general the SAP Tutor is chargable depending on the number of licensed users as described in the pricelist. But when you use the SAP Solution Manager you will get 5 authoring users and for every licensensed SAP user the player free of charge if you create non-commercial SAP solution related tools.
n Details about this can be found at https: / / service.sap.com / SolutionManager Order Information
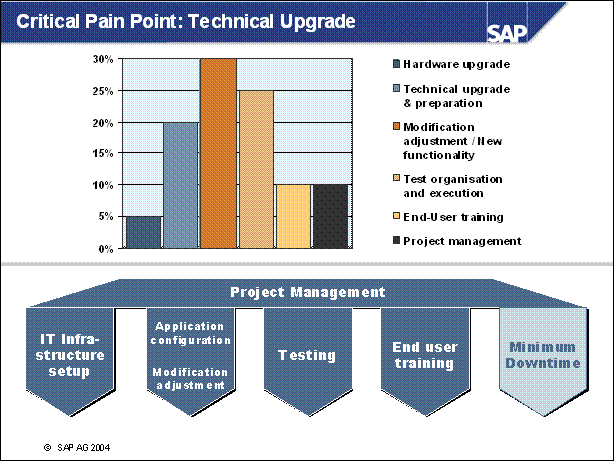
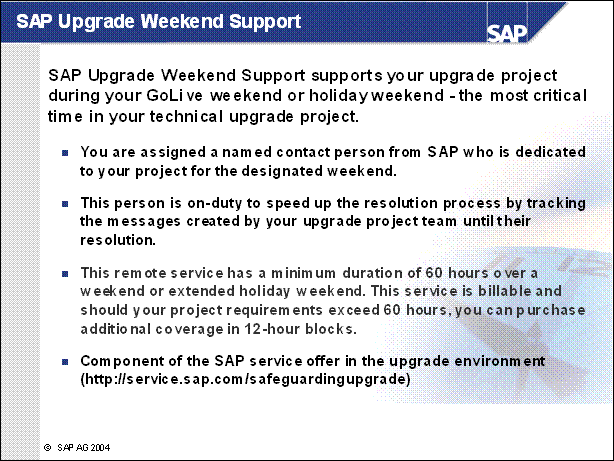
n A service that can support you in the critical time of the upgrade itself is the UWS.
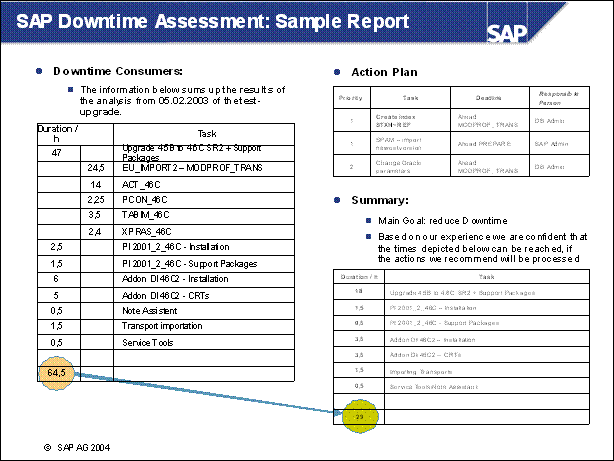
n SAP Downtime Assessment: By reorganizing the sequence of some actions of the upgrade procedure or by additional manual actions SAP often can reduce the technical upgrade-downtime by 30%.
n This service can be ordered when in Safeguarding for Upgrades program. A general factsheet for this service van be found at https: / / service.sap.com / safeguardingupgrade -> Affordable Downtime -> SAP Downtime Assessment
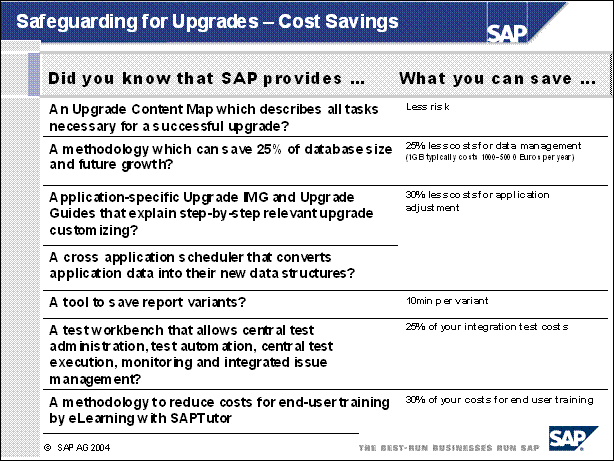
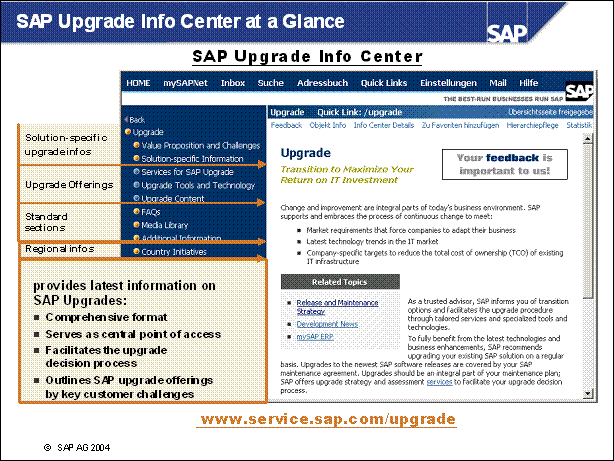
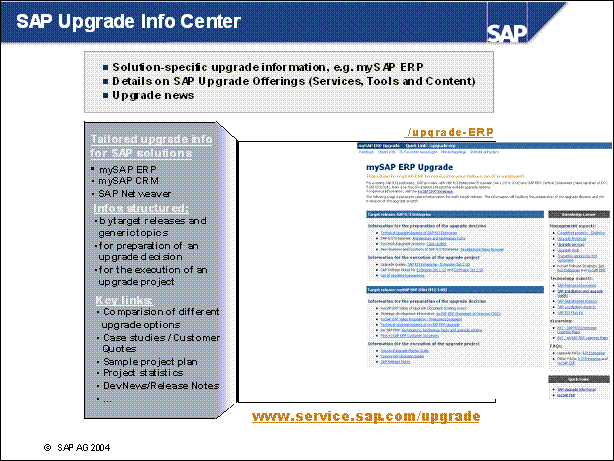

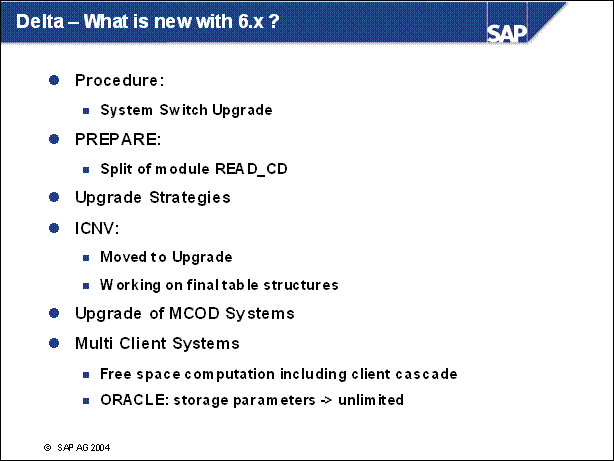
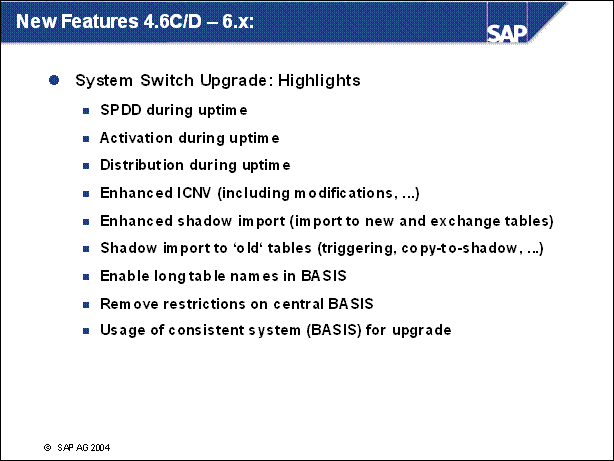
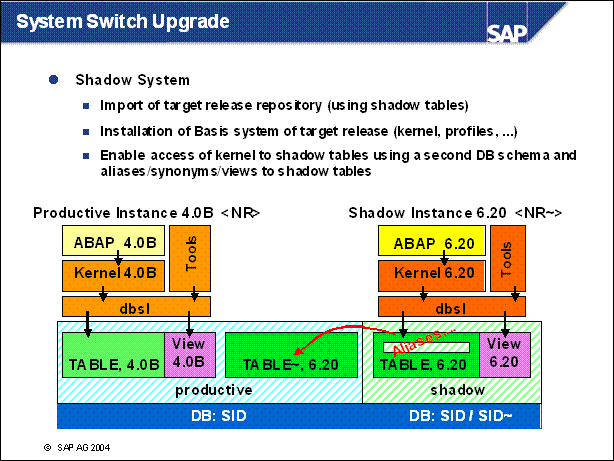
n Legend: of symbols used in the slide:
Productive system:
TABLE, 4.0B = original table of release 4.0B
TABLE~, 6.20 = shadow table of release 6.20 (needs additional disk space)
Shadow system
TABLE, 6.20 = alias / synonym / view which only points to the "shadow table" TABLE~, 6.20
n The Productive System DB was originally created by a "CREATE DATABASE"
command.
This DB contains own data files, transaction logs and so on.
n The Shadow System DB is created by a 'CREATE DATABASE SCHEME' command.
This DB does NOT contain own data files, transaction logs and so on. It also
does not contain own application tables (MARA, LFA1, ...). It only contains
synonyms and aliases which point to the application table DEFINITIONS, which
are stored in the SAP Dictionary shadow tables (DDNTT~, DDNTF~, DDXTT~, DDXTF~,
D0*~, ...) in the productive system. The shadow DB has its own sapr3 <SID>
user, who is granted to access the SAP Dictionary shadow tables in the
productive system. Using this technical workaround, the SAP instance connected
to the shadow database has access rights to read and modify the SAP Dictionary
shadow tables in the productive system.
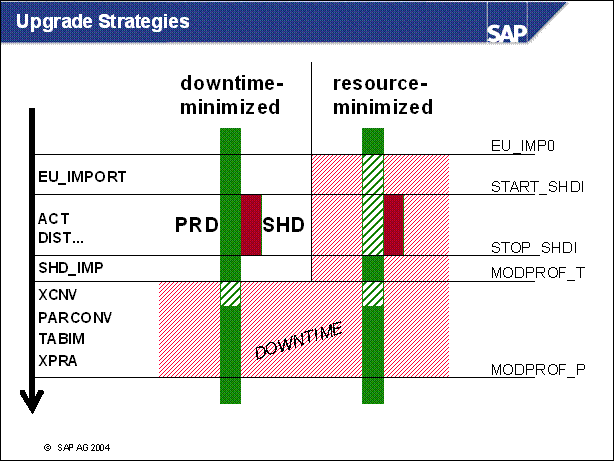
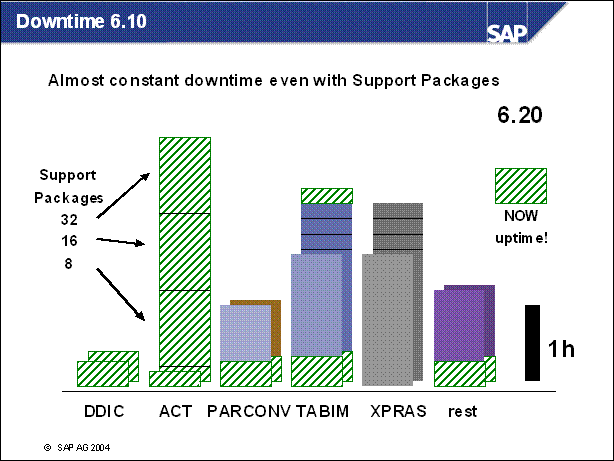
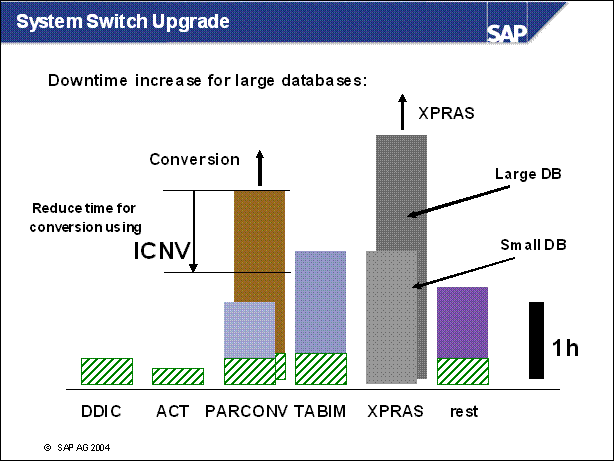
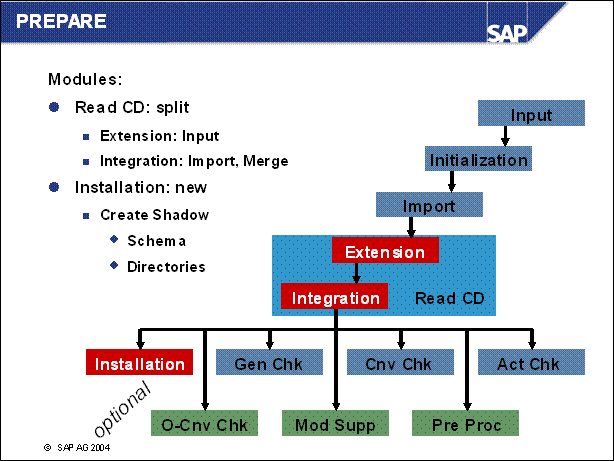
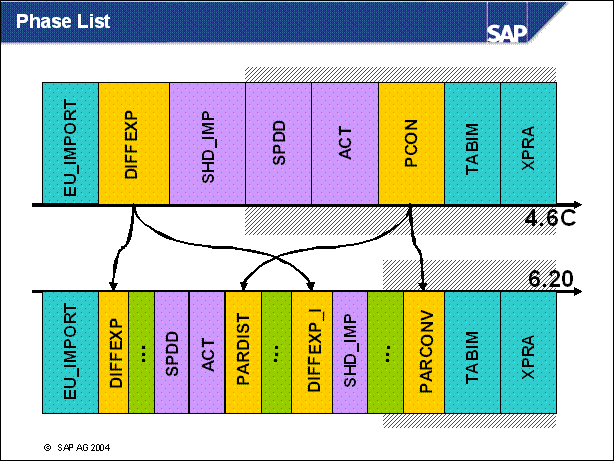
n DIFFEXP:
DIFFEXP* phases copy only DDIC to shadow
DIFFEXP*I phases copy only non-DDIC (ABAP) to shadow
This way, the shadow
instance remains consistent
DB nametab ABAP
n PCON:
PARDIST: distribution during uptime (special upgrade distributor)
PARCONV: conversion during downtime
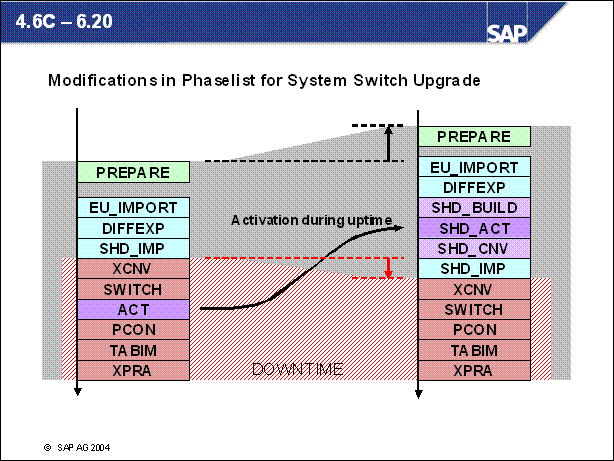
n For the system switch upgrade, the activation phase has been moved to the uptime.
n Additional phases are needed to build and remove the shadow tables
n Several conversion can be done during uptime: SHD _ CNV
n Additional phases to built up / remove the shadow instance
SQLSCREXE _ *, PSCRGEN _ *, EXEC _ *
SQLSCREXE _ *, SCRGEN _ *, SQLSCREXE _ *
PSCRGEN / SCRGEN: Script generation (+ execution)
EXEC _ * / SQLSCREXE _ *: Script execution
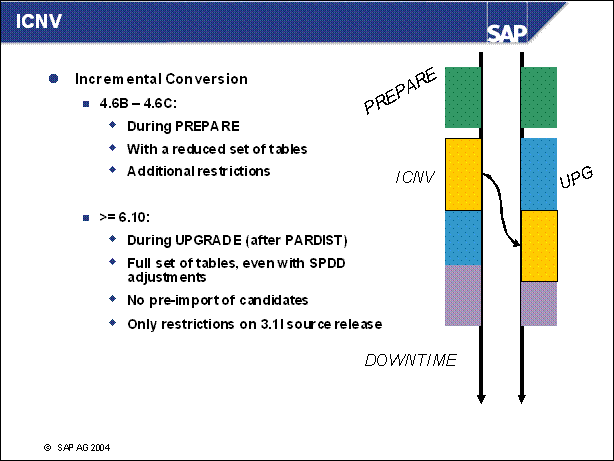
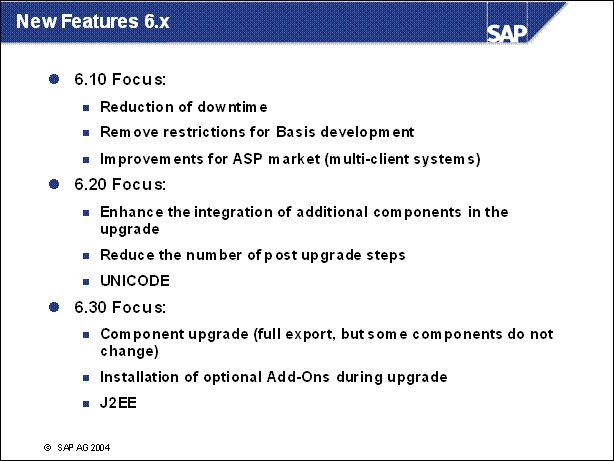
n The component upgrade will be necessary, for example, to handle an 'Extension-only' upgrade
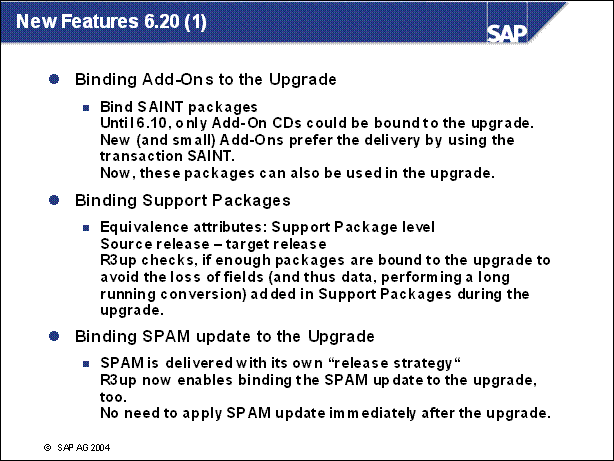
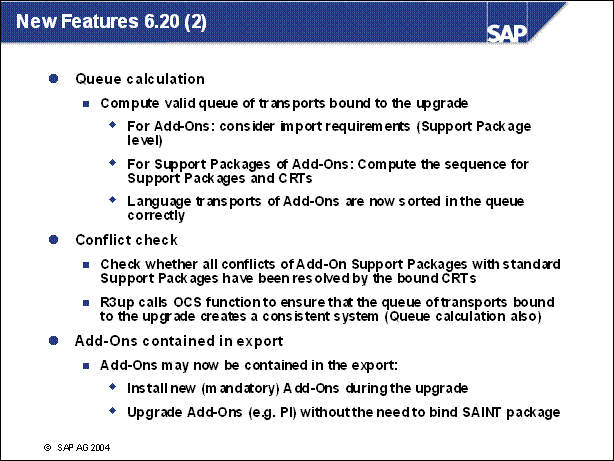
n The queue calculator scans through all specified Support Packages, Add-Ons, CRTs and Language Transports. It detects the dependencies between these objects and calculates an appropriate queue for the installation via transaction SPAM.
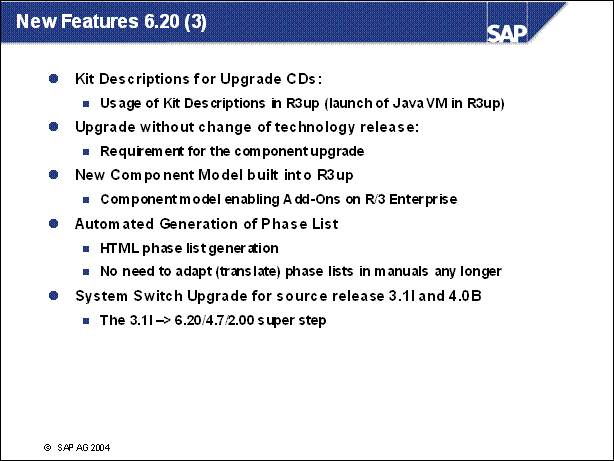
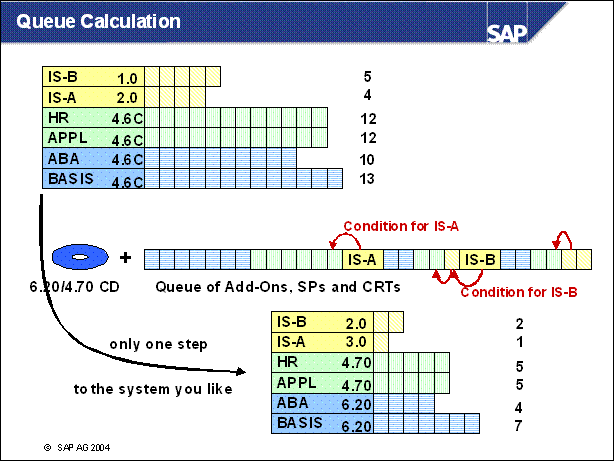
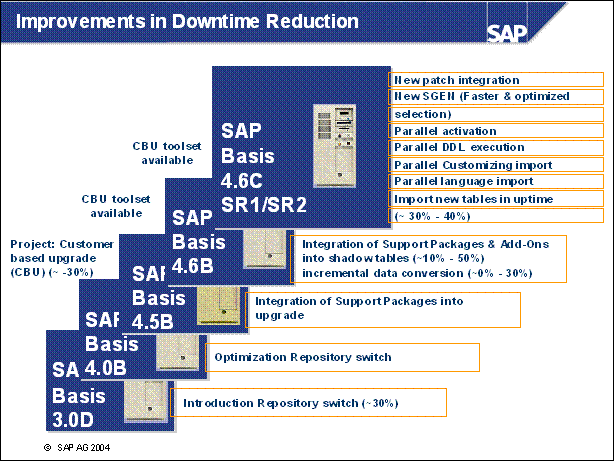
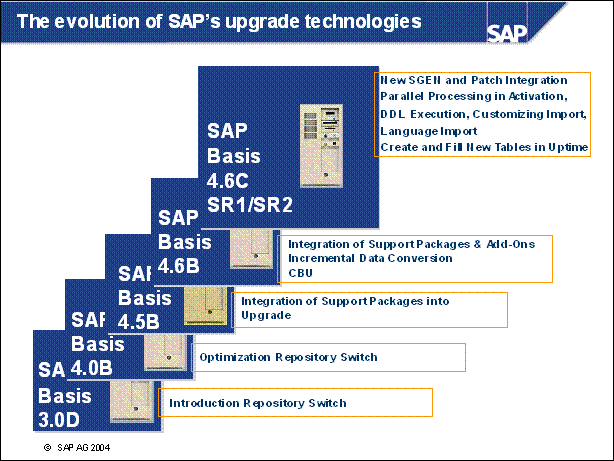
n Whith release 3.0D of SAP R / 3 we introduced the upgrade technology Repository Switch. This technology got its optimizations with the release of new R / 3 versions. All this optimizations had the main goal to reduce the downtime of the system during the upgrade.
n For the upgrade to the target releases 4.6B and 4.6C SAP offers the Customer Based Upgrade. A technology which reduces the downtime of the repository switch upgrade by importing a customer specific repository in stead of the SAP standard repository.
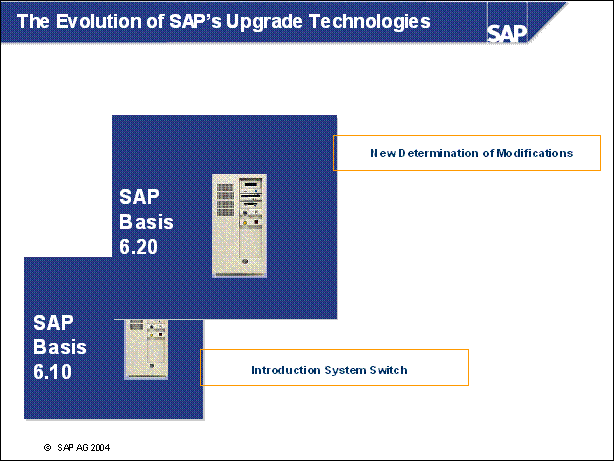
n With the release of SAP systems with SAP Web Application Server technology the repository switch upgrade got another big improvement. This new kind of upgrade is called System Switch Upgrade.

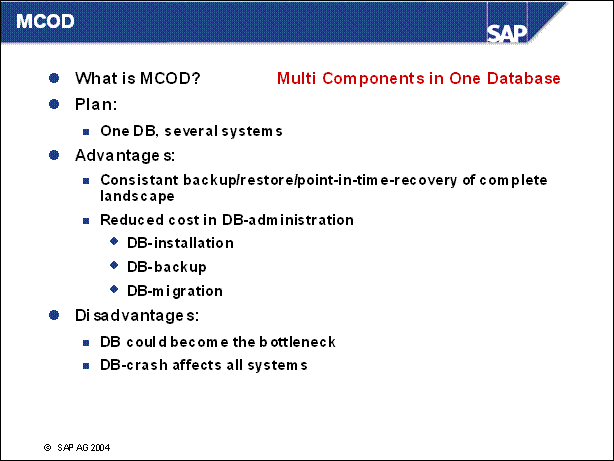
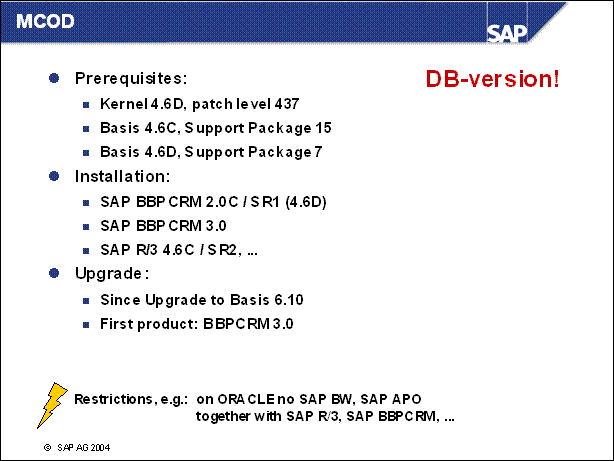
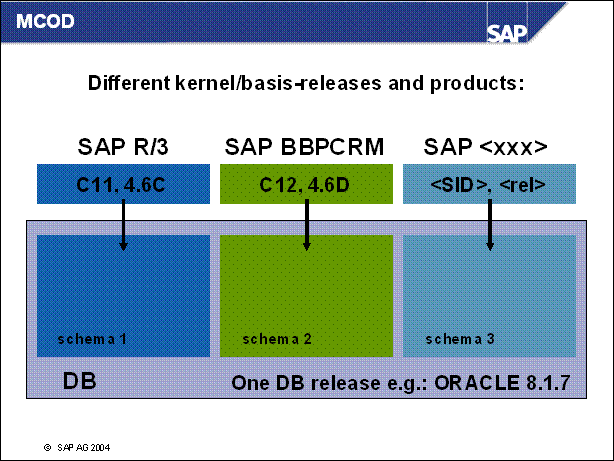
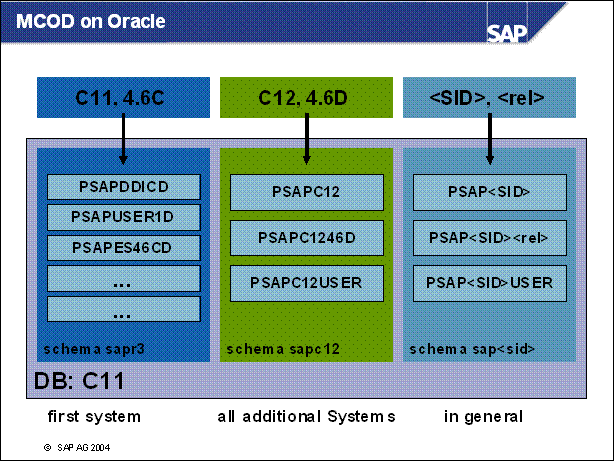
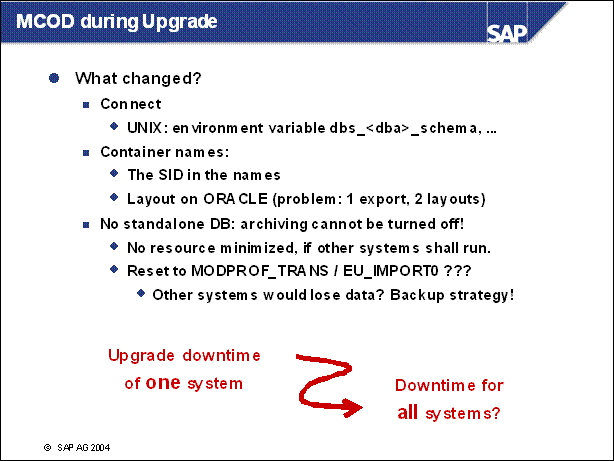
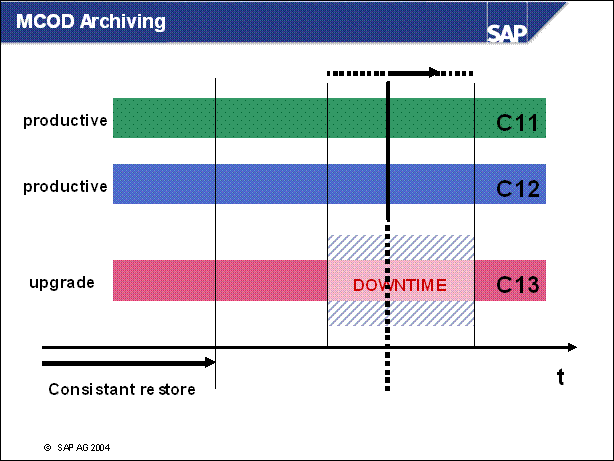
n As of SAP Web Application Server 6.10, you can upgrade systems in an Multiple Components on One Database (MCOD) system landscape. Note the following when you upgrade an MCOD system:
The database user, tablespaces, dbspaces,
(Waltraud) or devspaces, and for MS SQL Server also the database name of an
MCOD system may have different names to those of an MCOD system without MCOD
layout or of a non-MCOD system.
The names you need to enter for systems with normal or MCOD layouts are listed
at the appropriate place in the text.
Do not switch off archiving when upgrading in an MCOD
system landscape.
All SAP systems in the database are affected if you need to reset the upgrade.
PREPARE asks you at the start of the upgrade whether there is more than one SAP
system installed in the database. If there is more than one SAP system installed
in the database, do not switch off archiving during the upgrade.
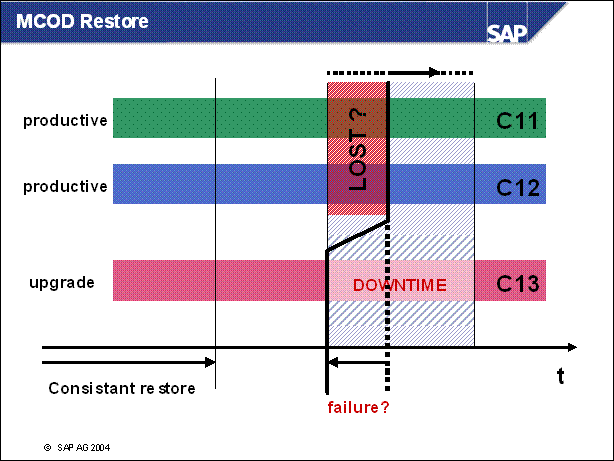
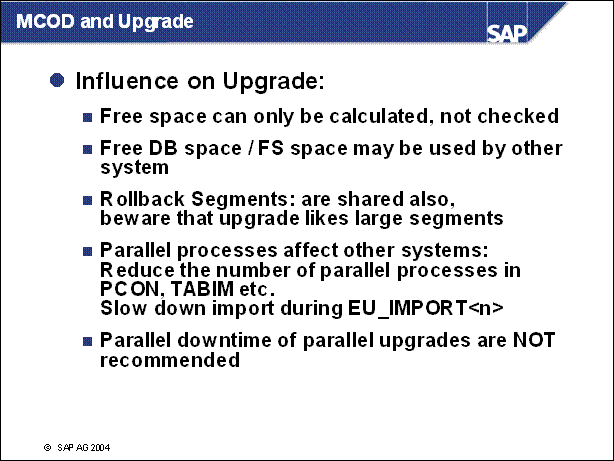
n What changed in upgrade:
Scripts with create table:
Create statements of all tables are in ntabsql / <dba>.TAB
Container names like entries in TA <dba>, IA <dba> on export system
Table create statements in bin / <name>. <dba>
Container names like entries in TA <dba>, IA <dba> on export system
R3load-templates:
Container names in exchange / tplpack / DDL <dba>.TPL
Free space requests:
With standard container names
Container requests
Single table and index requests
-> DB6, INF, ORA: Replace container names
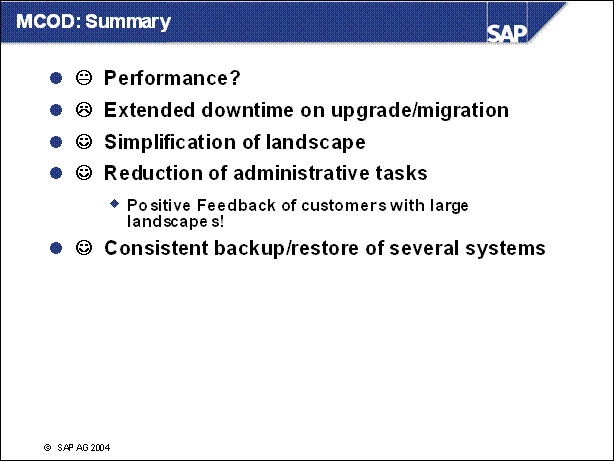
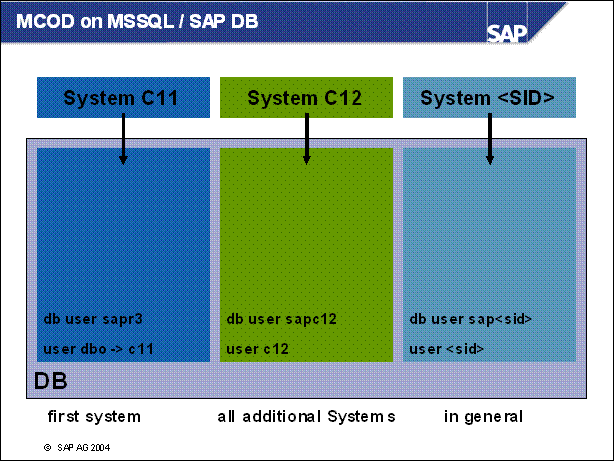
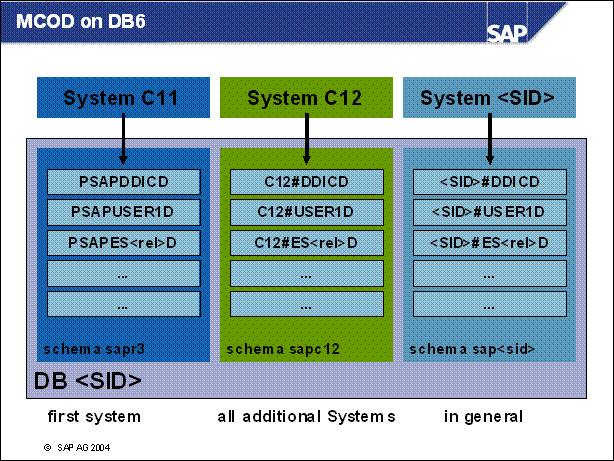
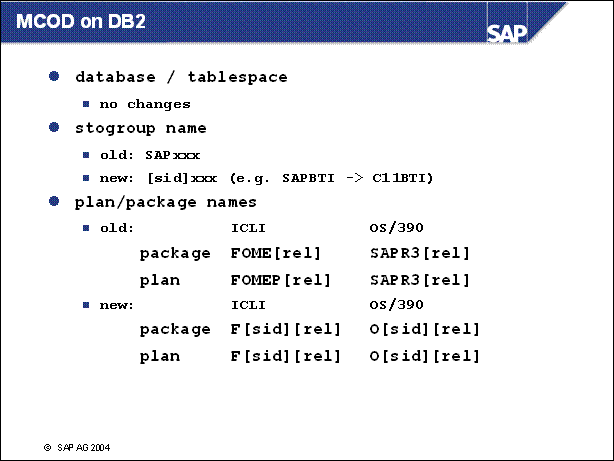
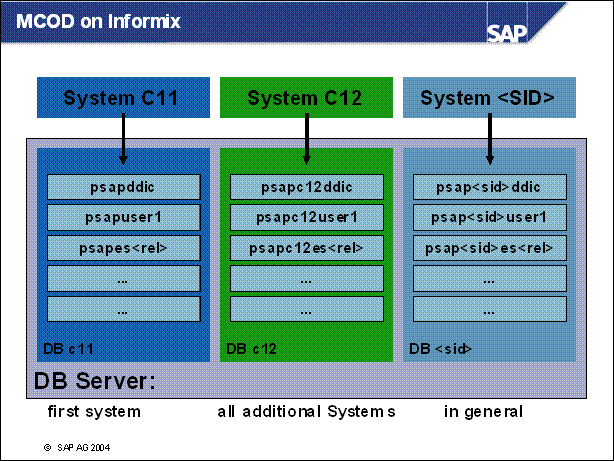


n For R / 3 language combination check Note: 736060
n SAP supports over 30 languages on Non-Unicode systems, but due to the technical limitations of code pages, only certain combinations of languages to be used without restrictions. The following options are available:
n Single standard code pages, which can support specific sets of languages. The number and combination of languages that are supported cannot be altered, but there are no restrictions on users.
n Unambiguous Blended Code Pages, which are SAP proprietary code pages that contain characters from one or more standard code pages. This increases the combinations of languages that can be used. Functionally, a Blended Code Page system uses a single code page.
n Multi-Display / Multi- Processing _ (MDMP) _ _ _ which allows dynamic code page switching on the application server by using a Workprocess (using the "set locale" command. Prerequisite: codepage must be known / configured on the OS , and therefore permits any combination of standard code pages on one system. The log-on language determines the code page that is active for each user. Some restrictions must be followed.
n For R / 3 language combinations check Note: 736060
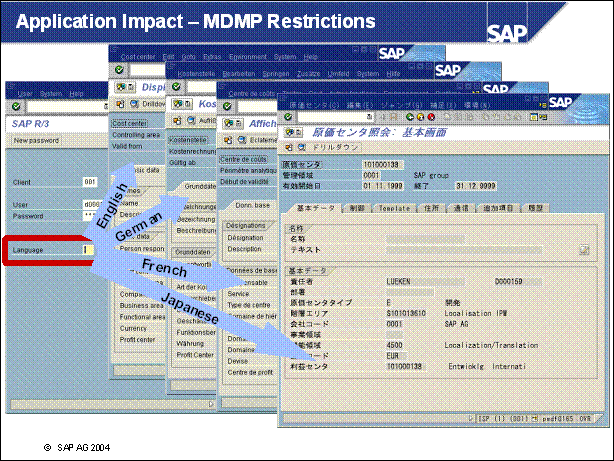
n The log-on language determines the code page that is active for each user and within the data which is visible.
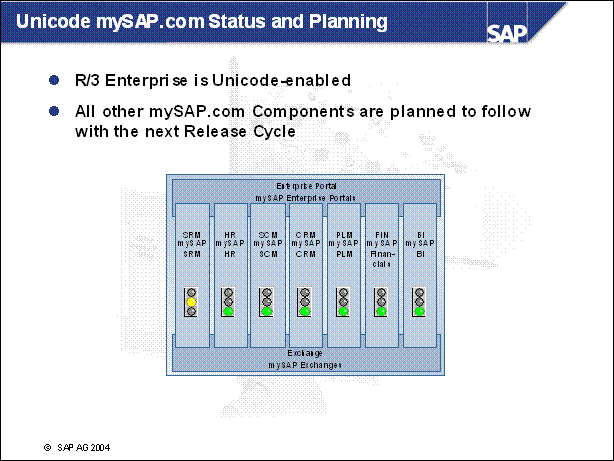
n Check Note: 379940 for detailed information concerning Unicode based mysap.com components availibility.
n If the source system is a MDMP system perform additional steps that are described SAP Note 551344.
n If you are using HR functionality within R / 3 Enterprise, additional steps are mandatory, which are described in SAP Note 573044.
n Currently SAP does not support an upgrade with simultaneous Unicode conversion. Therefore you must first upgrade a non-Unicode system with a basis release less than release 6.20 to release 6.20 (or higher). Once the non-Unicode system uses basis release 6.20 or later you can convert to Unicode.
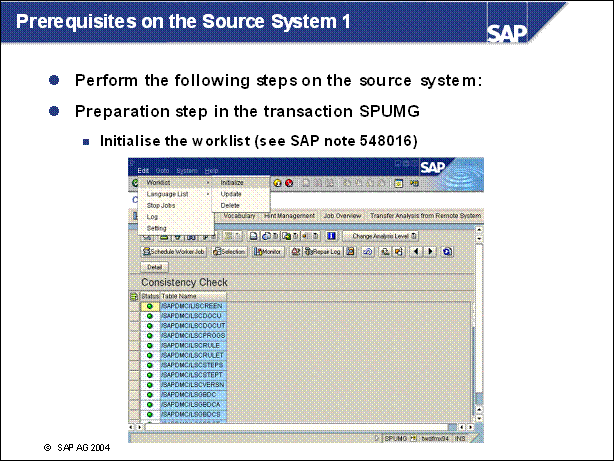
n To be able to perform the conversion from non-Unicode to Unicode, you require a non-Unicode Kernel CD for the export and a Unicode Kernel CD for the import. Therefore you need both, the Non-Unicode and the Unicode Installation Package.
n In the transaction SPUMG select Edit -> Worklist -> Initialise worklist. The analysis level should be Level 1 Consistency check, and this should appear directly above the worklist. All tables in the database's nametab will appear in the worklist. The Status indicator shows whether the initialisation was completed or shows an error; select ICON from the toolbar to see the error message for a selected entry; to view all errors, select ICON from the toolbar. The error log indicates what steps are needed to repair the table.
n Changes to the database (Transports, Support Packages, etc.) are not automatically updated in the worklist. Update the worklist periodically. Select Edit -> Worklist -> Update worklist
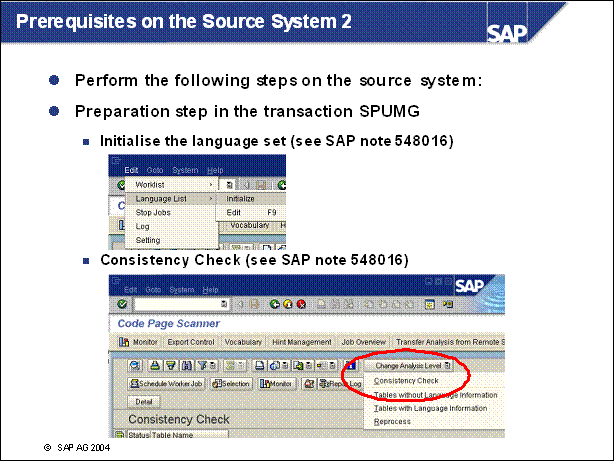
n Initialise the language set: Select Edit -> Language set -> Initialize. The language set is used in conjunction with language keys to determine the correct code page to use for converting data. It is also possible to exclude languages or include additional ones: Edit --> Language set --> edit. You may want to exclude languages that are installed on the system, but not used, for example. If you have used an improper front end code page setting (see SAP Note 73606) it is possible to add languages to the language set in order to save this data;
n Consistency Check: The analysis level should be Level 1 Consistency check, and this should appear directly above the worklist. To change the analysis level select Change Analysis Level from the toolbar.
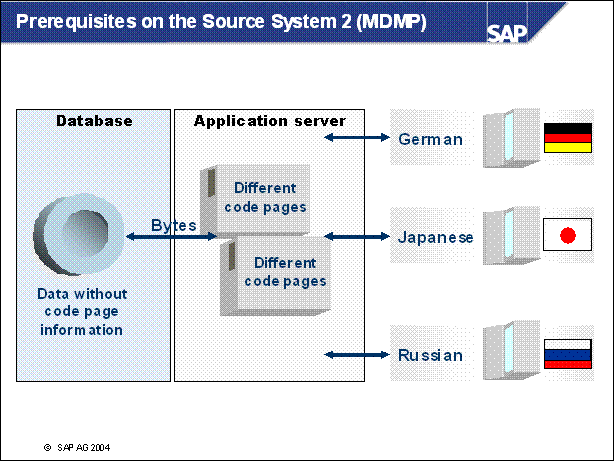
n In an MDMP system the conversion must use language
field information to correctly convert character data. If the restrictions on
global data were followed in the MDMP system (see Note 73606), then tables
without a language field should only contain 7-bit ASCII characters. It is
however possible that other characters were entered into tables without a
language field or that some tables may not have a language field. Converting
such tables is problematic, but the Conversion Preperation and Postprocessing
phases are designed to prevent any data loss in these problematic cases.
In the transaction SPUMG, collect language information from the MDMP database
(see online documentation for SPUMG). For each table in the database, this
information is placed in a Conversion Description, which is stored in the
Conversion Control Table. The conversion tools read from Conversion Control
Table during database export and use it to correctly convert character data to
Unicode. In addition, this data is needed in for post-conversion processing.
This step is required for MDMP systems only and must be done before converting
the database to Unicode.
n For code page dependent text (non 7-bit ASCII characters) without a language key there are two possibilities to determine the correct language key:
n Code page guess function: heuristic approach to determine the corresponding language, depending on the amount of the different characters in the text
n System vocabulary: try to find words from this text in other data with language information
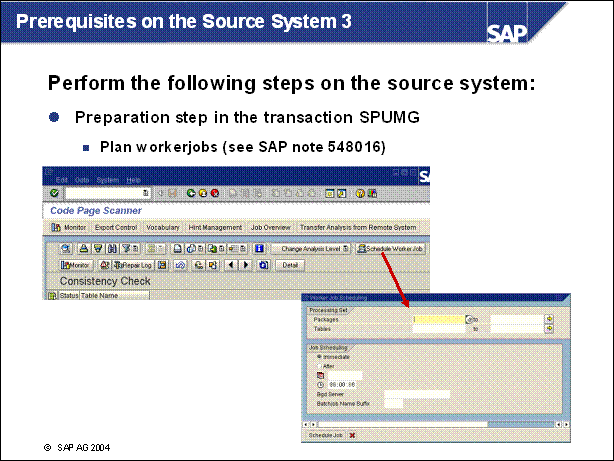
n Plan Workerjobs
Select Schedule Worker Job, and then set the time and date for the worker job. Select Monitor from the toolbar to view table statistics, including the number of transparent, cluster and pool tables. The statistics also show the number of inconsistent tables, which must be repaired before the migration. To get the list of all bad tables, select Select entries from the toolbar and in selection screen enter E in the field Status. For information about each table, select DETAIL from the toolbar and to see all errors, select ICON.
To see the running Workerjobs, select Job Overview from the toolbar. In the job overview there is one master job, UMG _ PMIG _ MASTER _ JOB, for the planned Workerjobs UMG _ PMIG _ WORKER _ JOB. If the Workerjob is cancelled due to an error, the master job will then restart a new worker job. This is only true for the consistency check.
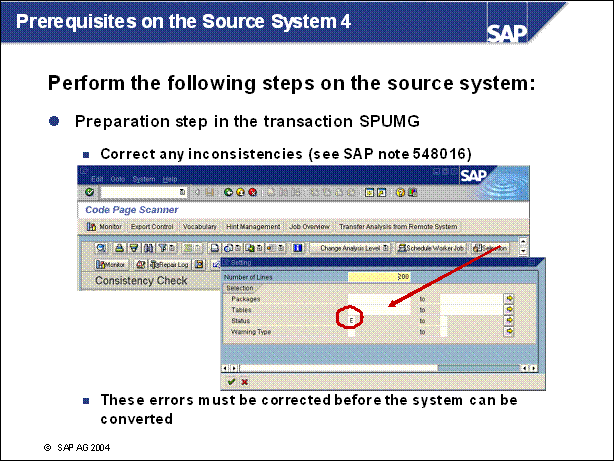
n There are several types of inconsistencies. These errors must be corrected before the system can be converted. Or the tables can be manually deleted from the R3Load control file, and these tables will not be exported.
n To see the tables with inconsistencies, select Selection from the toolbar and then Status E. To see a detailed description of the inconsistency and how to handle the error select DETAIL from the toolbar. One of the following error categories are displayed:
Error Categories: Database consistency
1 = Incorrect Table definition (solution see SAP note 548016)
2 = Table cannot be read
3 = Conversion error with interrupt
4 = Language key is not type LANG (solution see SAP note 548016)
5 = Guessing function failed (Only for MDMP systems: see SAP Note 551334)
6 = Invalid language key
7 = Illegal initial values (solution see SAP note 548016)
8 = Illegal pool table values (solution see SAP note 548016)
9 = Multiple language keys
A = Pool Table: language key not in table key (Such tables will have be repaired manually after conversion: see SAP note 548016)
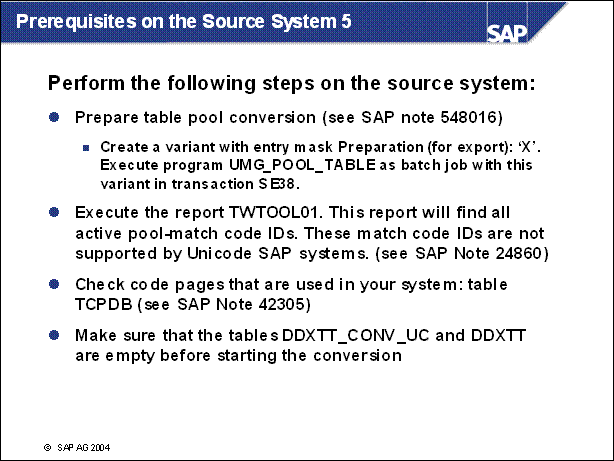
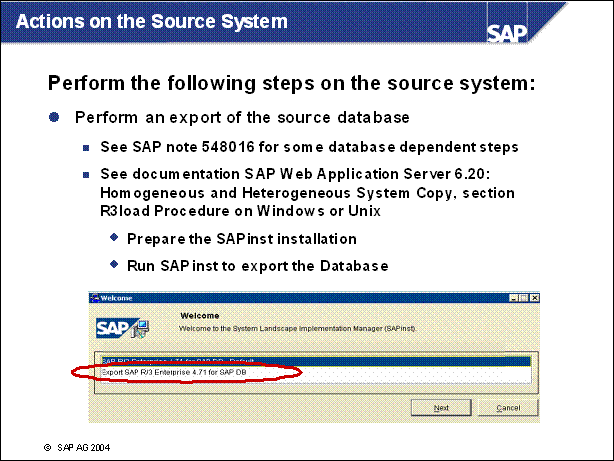

n Big Endian: the most significant byte is stored in memory at the lowest
address and the least significant byte at the highest address. (The big end
comes first.)
As an analogy, we say 'twenty-four' in English; the more significant number,
twenty, comes first.
n Little Endian: the least significant byte of the number is stored in
memory at the lowest address, and the most significant byte at the highest
address. (The little end comes first.)
As an analogy, we say 'fourteen' in English; the less significant number, four,
comes first.
n For example, 0xAABBCCDD would be stored as follows:
Address Big-Endian Little-Endian
3 DD AA
2 CC BB
1 BB CC
0 AA DD
n When converting to Unicode, the export code page should correspond to
the endianness of the target system.
4103 Little Endian Alpha, Intel X86 (and clones)
4102 Big Endian HP PaRISC, IBM 390, AS / 400, PowerPC (AIX), Sun
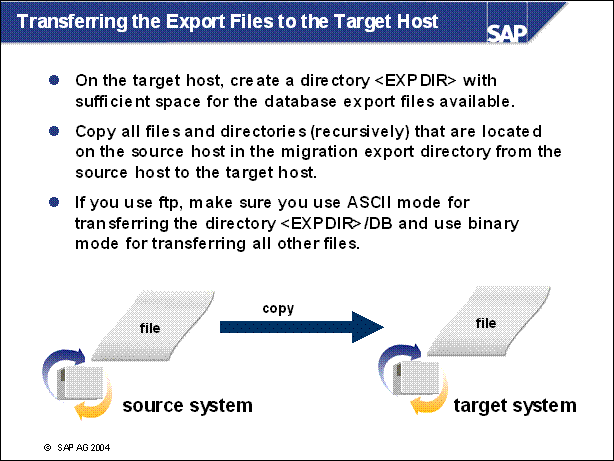
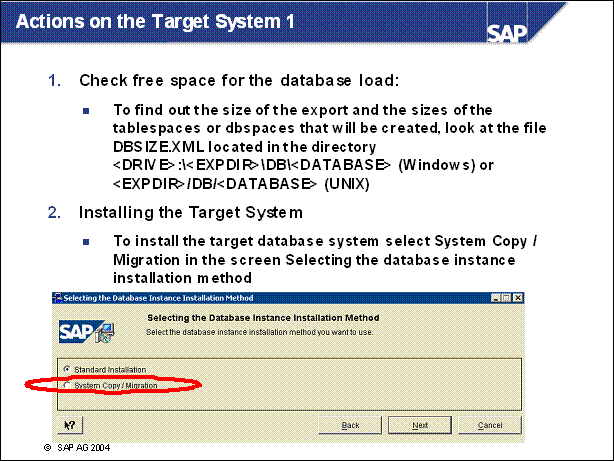
n To install the target database system, see documentation Installation Guide SAP Web Application Server on <Platform>: <Database>, section Input for the Installation.
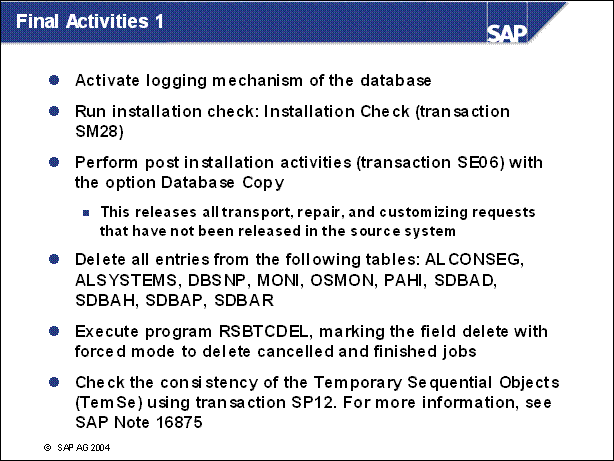
n See installation guide SAP Web Application Server 6.20: Homogeneous and Heterogeneous System Copy section Final Activities
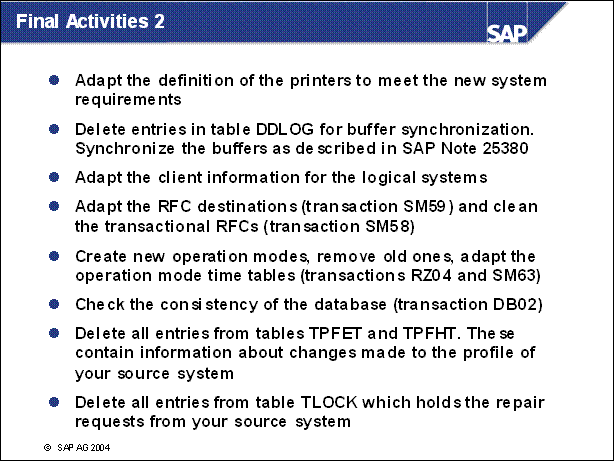
n See installation guide SAP Web Application Server 6.20: Homogeneous and Heterogeneous System Copy section Final Activities
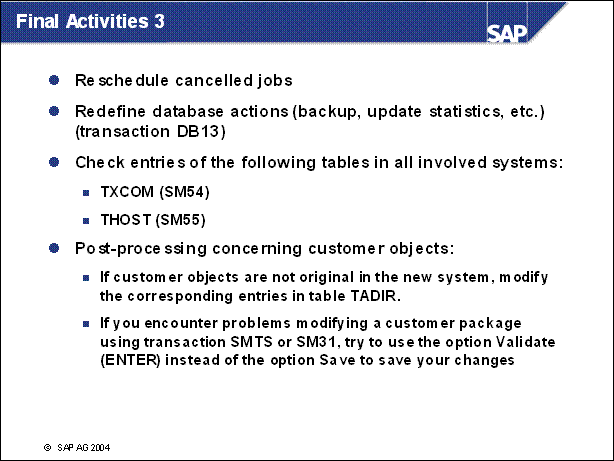
n See installation guide SAP Web Application Server 6.20: Homogeneous and Heterogeneous System Copy section Final Activities


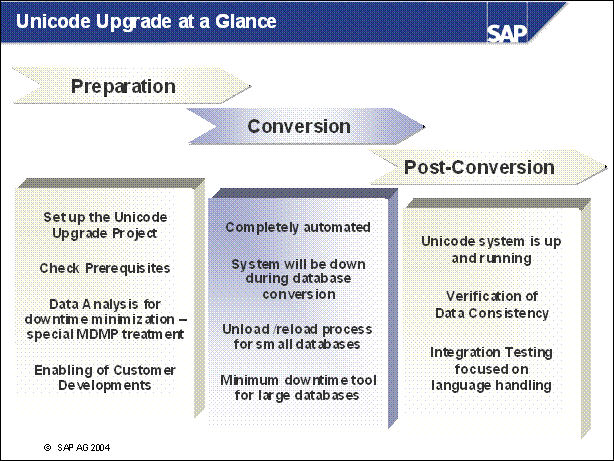
n Note: the data analysis (Unicode Syntax check) can be done as part of the preparation phase!
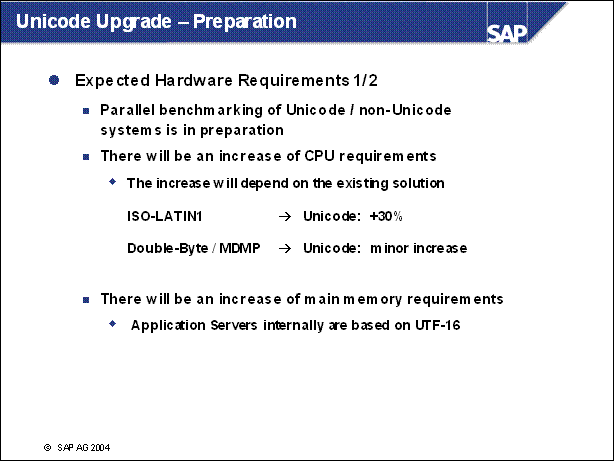
n The "SET LOCALE" command is expensive in terms of CPU usage on an MDMP system (codepage switch).
n The "SET LOCALE" command is not CPU expensive on a Unicode system - though it is exclusively used for sorting etc.
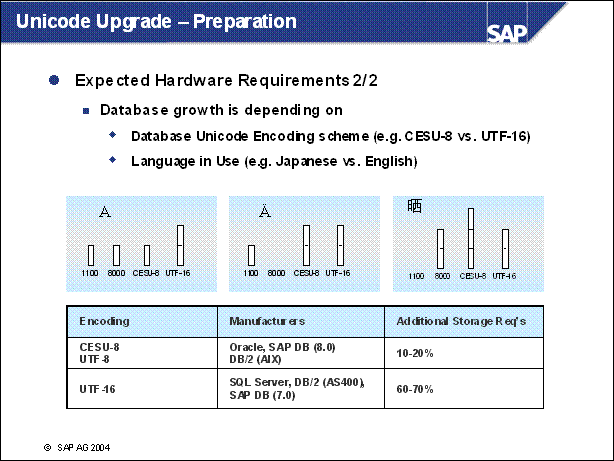
n Increase to UTF-16 for e.g. "A" on Application Server.
n Concerning the growth of the database there are differences between UTF-8 and UTF-16. If the database is using a 16 bit encoding scheme already the database will grow much more than within a 8 bit encoding scheme.
n As well the growth depends very much on the kind of the application data of the customer (a lot of characters ?). Therefore exact forecasts cant be given.

n Check Locales: Note 0158774 contains a list of bad locales, e.g. DEC English (Case Mapping).
n Check Database consistency.
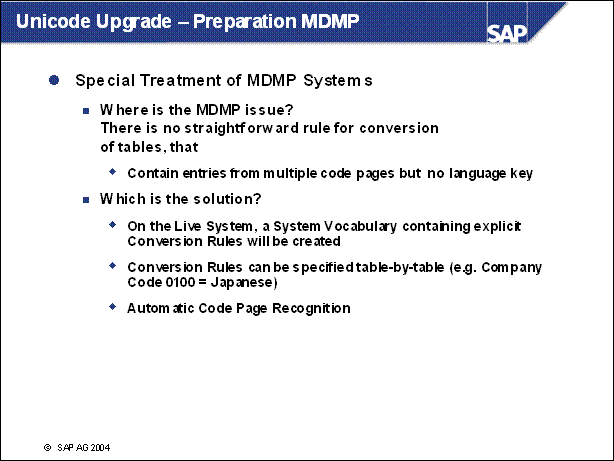
n In an MDMP system, multiple code pages are used simultaneously on the application server. The log-in language determines which code page is active for a user. Because the active code page changes, tables that contain non-ASCII character data must have a language key to insure that all data is processed with the correct language.
n The Unicode Conversion of an R / 3 database converts text data from the code page(s) of the original system to Unicode. In an MDMP system, the conversion must use the language key information to prevent data corruption.
n It is possible that non-ASCII characters were entered into tables without a language key or that the language keys are not present, for example in tables created by customers; converting such tables is problematic. The Preparation and Post processing phases are designed to prevent any data loss in these problematic cases.
n Conversion Preparation: collect information about the database (language keys, tables, etc). For each table in the database, this information is placed in a Conversion Description, which is stored in the Conversion Control Table. The migration tools read from Conversion Control Table during import and export and this information is used in Post-Conversion Processing.
n Post-Conversion Processing: use the information gathered in the Conversion Preparation to repair data that was not converted correctly.
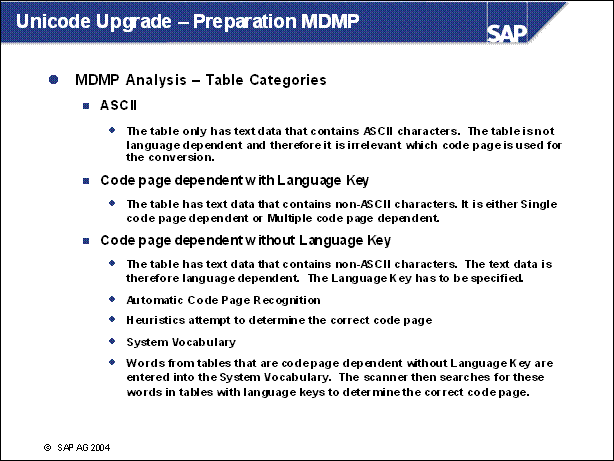
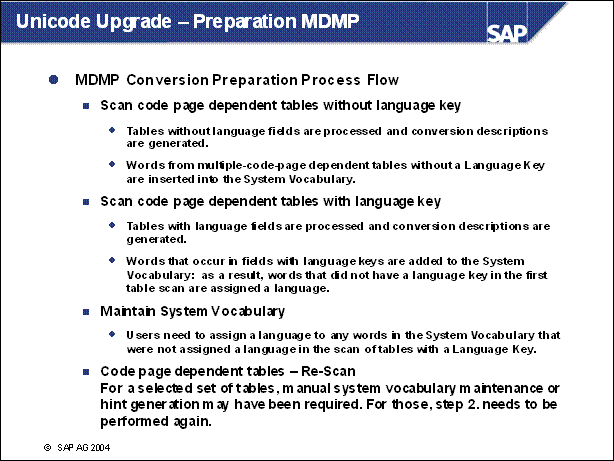
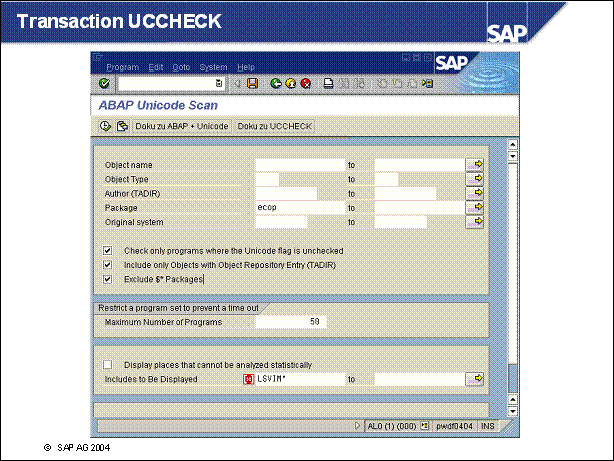
Start transaction UCCHECK
Analyze your application
Remove errors
Tip: inspect extended text of error messages (if available)
(optional) Show untyped not statically analyzable places
Try to insert types for parameters and field symbols wherever possible (also improves performance
Tip: New generic types CLIKE, CSEQUENCE, XSEQUENCE, NUMERIC, SIMPLE available
Set unicode program attribute
Using UCCHECK or SE38 / SE37 / SE24
Do runtime tests
Tip: Use coverage analyzer (transaction SCOV) to find out which parts of your programs did run
n Define the programs for which the extended unicode check should be performed.
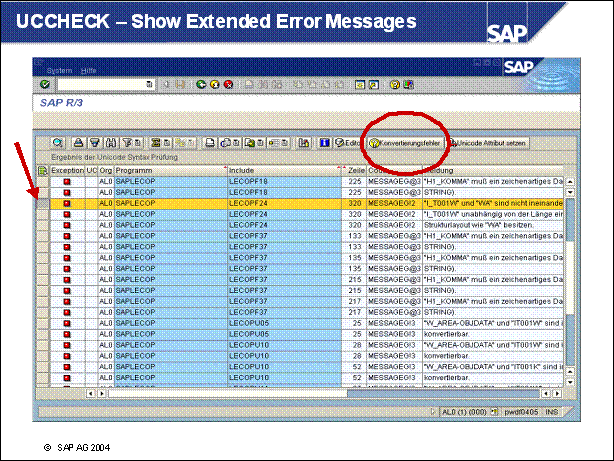
n Mark programs which contain conversion errors and get more information about the problem (double click).
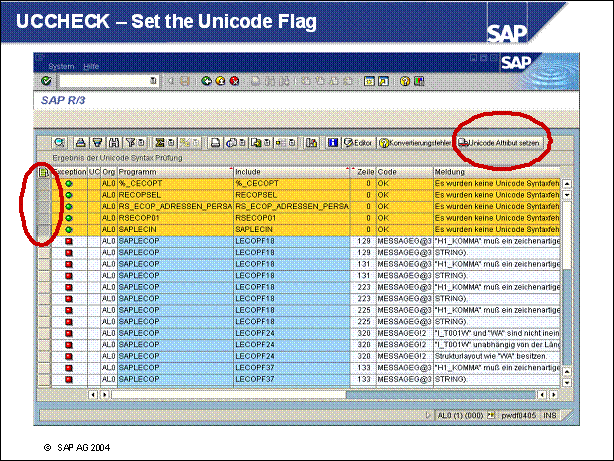
n Programs which do not contain any Unicode syntax errors can get the unicode flag.
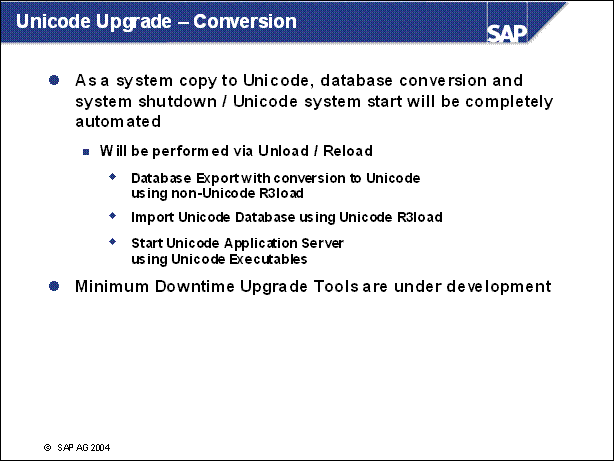

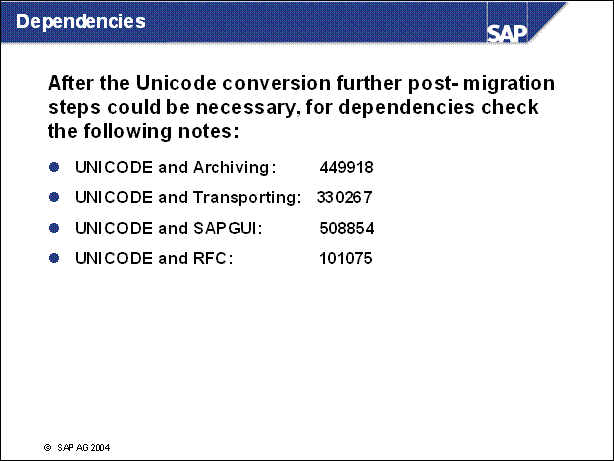
|
|
Unit: R / 3 Topic: 1. SAP Notes |
Get the relevant SAP Notes for upgrading SAP R / 3, as
described in the upgrade guide Component Upgrade Guide, SAP R / 3
Hint: Component EA _ GLTRADE is not being used in this
system.
The plan version is 01
Evaluate the SAP Notes. What actions are required?:
Perform the steps from exercise 1-2, as far as this is currently possible:
2. Upgrade Planning - Exercises
|
|
Unit: R / 3 Topic: 2. Upgrade Planning |
5-1 Perform the upgrade planning as described in chapter 4.1 Product-Specific Information: Upgrade Planning and chapter 5.1 Upgrade Planning of the upgrade guide and make the necessary adjustments. Consider the following points:
Do NOT perform a database backup.
Perform the ICNV during the upgrade for all suggested tables.
Do NOT use the SAP Internet Solution.
Do NOT import additional languages during the upgrade.
3. PREPARE - Exercises
|
|
Unit: R / 3 Topic: 3. PREPARE |
5-2 Perform the upgrade preparations and start PREPARE as described in chapter 4.2 Product-Specific Information: Upgrade Preparations and chapter 5.2 Upgrade Preparations of the upgrade guide and make the necessary adjustments. Consider the following points.
Phase BIND _ PATCH: Include following Support Packages located on
the server: BASIS(B): 20,
Direct Input is not used in the system.
4. R3up - Exercises
|
|
Unit: R / 3 Topic: 4. R3up |
Perform the upgrade as described in chapter 5.3 The Upgrade of the upgrade guide. Consider the following points:
Provide the following input:
- the upgrade key from SAP note 587896 is 83478
- choose downtime minimized
- import time: 1 hour
- confirm that the archiving is switched on
- confirm early locking of the ABAP workbench (development)
Perform the transaction SPDD at the begin of upgrade phase ACT _ 620. The upgrade stops for SPDD.
Stop in the ICNVREQ phase to perform the ICNV.
Solution: perform the ICNV for all suggested tables with transaction ICNV.
5. Post Upgrade Activities - 5. Post Upgrade Activities - Exercises
|
|
Unit: R / 3 Topic: 5. Post Upgrade Activities |
Perform the post upgrade activities as described in chapter 4.4 Product-Specific Information: Post Upgrade Activities and chapter 5.4 Post-Upgrade Activities of the upgrade guide.
|
|
Unit: R / 3 Topic: 1. SAP Notes |
Get the relevant SAP Notes for upgrading SAP R / 3, as
described in the upgrade guide Component Upgrade Guide, SAP R / 3
Hint: Component EA _ GLTRADE is not being used in this
system.
The
plan version is 01
The most important SAP Notes, according to the upgrade guide are:
SAP Notes 587896, 575280 and 156387 (Pages 18 and 29-34)
Evaluate the SAP Notes. What actions are required?:
According to SAP Note 587896, the following actions are required:
I / R3up key word -> used later, when starting the upgrade
II / Important general remarks:
- Integrate Fix-Pack 22 as soon as possible -> before starting
PREPARE
- Patch
R3up
- Check tp version -> patch the
whole 3.1I Kernel now with the
3.1I Kernel patch and the 4.0B tp patch
III / Correction of the upgrade guide:
Several corrections of the upgrade guide
According to SAP Note 575280, the following actions are required:
I / Important remarks
Version of R3up
Delete database objects -> see note 410963
Adjust several storage parameters
Check init <SID>.ora parameters
According to SAP Note 156387 the following actions are required:
SAP Note 317722:
The contents of table T77S0 must be
saved before the upgrade and checked after the upgrade.
Perform the steps from
exercise 1-2, as far as this is currently possible:
Perform the actions described in SAP Notes 587896, 575280 and 156387.
If tp hangs during the import of a transport request, check the
job RDDIMPDP in the Job Overview
(transction SM37), and look for the
following error message in the tp log files in directory usr\sap\trans\log:
ERROR: Background job RDDIMPDP could not be
started or terminated abnormally.
Solution: Find the cause in SAP R / 3 using transaction SM37 and, if necessary, schedule the job RDDIMPDP correctly (client 000,
user DDIC, using report RDDNEWPP).
You can correct this error now or later during PREPARE.
2. Upgrade Planning - Solutions
|
|
Unit: R / 3 Topic: 2. Upgrade Planning |
Perform the upgrade planning as described in chapter 4.1 Product-Specific Information: Upgrade Planning and chapter 5.1 Upgrade Planning of the upgrade guide and make the necessary adjustments. Consider the following points:
Do NOT perform a database backup.
Perform the ICNV during the upgrade for all suggested tables.
Do NOT use the SAP Internet Solution.
Do NOT import additional languages during the upgrade.
3. PREPARE - Solutions
|
|
Unit: R / 3 Topic: 3. PREPARE |
Perform the upgrade preparations and start PREPARE as described in chapter 4.2 Product-Specific Information: Upgrade Preparations and chapter 5.2 Upgrade Preparations of the upgrade guide and make the necessary adjustments. Consider the following points.
Set the environment variable USE _ KIT = OFF.
Log off and log on so that the environment variable is read.
Create a directory called put under \usr\sap.
5-2 Switching the SAP Kernel
The system already uses a 3.1I COM Kernel.
Apply the Kernel patches which are located on the server.
Important: you need the 4.0B tp version during the productive time of the
upgrade (until phase MODPROF _ TRANS) because of the combination of an SAP R / 3
3.1I and an Oracle 9.20 database.
After PREPARE has started it extracts some files and prompts you for the
upgrade directory.
When PREPARE prompts you for Scroll / Server / Exit, choose Exit. Now patch the
executable R3up. As soon as possible patch the executables tp and R3trans. and
install the Fix-Pack 22.These patches are located on the server.
If PREPARE reports an error concerning the SAP profile parameter DIR _ PUT,
correct this parameter using transaction RZ10.
The password for the user SAPserviseUPG is the same as the password of upgadm.
Confirm any 3.1I Support Packages with transaction SPAM, client
000, user DDIC if neccessary.
Phase BIND _ PATCH: Include following Support Packages located on
the server: BASIS(B): 20, ABA(A): 20, APPL(H): 10, HR(E): 15.
Therefore the Support Packages have to be copied to directory G:\usr\sap\trans
and extracted from there. Then they are located in the directory G:\usr\sap\trans\EPS\in
where PREPARE can find them..
Perform all necessary steps listed in the log file CHECKS.LOG.
These could be for example:
- release open transports
- extend and create tablespaces
- address data conversion errors
Perform a backup of the Kernel directory.
Perform the described steps.
Perform the described steps.
Set the operation mode.
Direct Input is not used in the system.
4. R3up - Solutions
|
|
Unit: R / 3 Topic: 4. R3up |
Perform the upgrade as described in chapter 5.3 The Upgrade of the upgrade guide (Page 134-156). Consider the following points:
Provide the following input:
- the upgrade key from SAP note 587896 is 83478
- choose 4 parallel batch processes
- choose 4 parallel R3trans processes
- choose downtime minimized
- import time: 1 hour
- confirm that the archiving is switched on
- confirm early locking of the ABAP workbench (development)
Perform the transaction SPDD
at the begin of upgrade phase ACT _ 620. The upgrade stops for SPDD.
To unlock the system for logons, respond to the corresponding input request
from the Upgrade Assistant with unlock.
Log on to the shadow instance of the SAP system with user DDIC, client 000 and
create a new user to perform the modification adjustment. Now log on to the
shadow instance with this new user and call transaction SPDD.
When making the first adjustment, create a new transport request for the entire
SPDD modification adjustment.
a) Table TADIR:
Although the contents of table TADIR
were not changed (compare versions 1
and 2 with transaction SE11
-> Utilities -> Versions -> Version management), it is regarded as
modified because it is included in a transport request.
Action: Return to the standard by choosing Reset
to original.
b) Technical Properties of the table TADIR:
Action: Return to the standard by choosing Reset
to original.
c) Table ACCTIT:
Action: Accept the proposal. This places the customer fields in an append.
c) Table BKPF:
The field ZCURR, added by a
modification, and its contents are no longer required.
Action: Return to the standard by choosing Reset
to original.
d) Data element KZBWS
This is the same as under a), that is, there are no changes.
Action: Return to the standard by choosing Reset
to original.
Call transaction SE09 and
release the task for your SPDD request. Do not release the request yourself. In
this way, it is possible to use the request for an automatic adjustment of the
next system.
To do this, choose Select for transport
in transaction SPDD and
select your SPDD request.
Respond to the input request in the Upgrade Assistant with Repository ok.
Termination
in the ACT _ 620 phase.
Unlock SAP R / 3 as described in chapter 6.1.11 Correcting Errors in the ACT
Phase (Page 202).
Log on to the shadow instance with the newly created user, client 000.
Change the system change option in transaction SE06 by setting System
change option to Modifiable.
Check the corresponding log files in the \usr\sap\put\log
for the errors.
a) Table ZCUSTOMER (Log file SAPACCC46C)
Problem: The field ZZTEL refers to
the SAP data element ABAVERN, which
was automatically deleted during the upgrade.
Solution: Determine the definition of the deleted data element ABAVERN using transaction SE14, and choosing Extras -> Database object -> Display
(for example NUMC 6).
Change the ZCUSTOMER table using
transaction SE11 and
enter an appropriate, valid data element for field ZZTEL (such as NUM06).
Save the ZCUSTOMER table, but do not
activate it! Create a new transport request to do this.
b) Table LIKP
Problem: A previous correction created a new SAP field, FOLAR, in an append structure in SAP R / 3 3.1I. The upgrade has
brought this field also and added it to the table itself. This means that the
field exists twice.
Solution: Delete the append ZALIKP
using transaction SE11,
by entering ZALIKP in the Database
table field and choosing the delete button. You can ignore any warnings and
errors that appear.
c) Table LIPS
Problem: As with table LIKP (in this
case field KZUML). The customer field
ZADDR was additionally placed in the
append. This means that it is not possible to delete the append, as the ZADDR field would be deleted also, along
with its contents.
Solution: Delete the field KZUML from
the append ZALIPS. (Transaction SE11 -> enter LIPS in the database table field -> Display
-> Append structure -> Continue -> Display <-> Change ->
Select line KZUML -> Delete line -> Save)
After correcting the error, respond to the input request in the Upgrade
Assistant with repeat.
Stop in the ICNVREQ phase to perform the ICNV.
Solution: perform the ICNV for all suggested tables with transaction ICNV.
Stop in the MODPROF _ TRANS phase for Isolating the Central Instance.
Solution: Isolate the system as described in the Isolating the Central Instance (Page 217).
Don't forget to shut down the second instance (instance 01)!
Stop in the REQGENLD phase with the message '...
Start transaction SGEN and select the load generation after an
upgrade...'
Solution: Confirm the information.
Stop in the CHK _ POSTUP with the message '...
Errors occurred during the upgrade that require revision ... for detailed
information ... LONGPOST.LOG...'
Solution: Evaluate the LONGPOST.LOG
file in the \usr\sap\put\log
directory:
a) 4PEIU022 Necessary to reprocess using
Transaction ICNV
=> See Exercise 4-3 Post Upgrade
Activities
b) 2PE56692 Feature TRVCT must be
activated in all clients
=> No action required, as Travel Management is not in use.
c) 2PE6C817 Incompatible source release
for posting applicn conversion in TR-LO Cust:
=> No action is required, as the start release is SAP R / 3 3.1I, and Treasury Loans is not in use.
Stop in the SPAUINFO phase
Adjust the following two repository objects using transaction SPAU:
RSBTCDEL: Reset to original
RSPFPAR: Keep the modification
To do this, create a transport request of your own, and, after the adjustment,
mark it for the next system using transaction SPAU.
Note: R3up only performs the automatic export of this transport request if you
have not yet terminated R3up - that is, for example, during this SPAUINFO phase, or if you ended the SPAUINFO with exit and
are now restarting it.
5. Post Upgrade Activities - Solutions
|
|
Unit: R / 3 Topic: 5. Post Upgrade Activities |
Perform the post upgrade activities as described in chapter 4.4 Product-Specific Information: Post Upgrade Activities and chapter 5.4 Post-Upgrade Activities of the upgrade guide. Consider the following topics:
Switch the database to CBO and generate the update statistics
once and schedule them on a weekly basis.
In transaction SGEN choose Regenerate After an SAP System
Upgrade
Perform the Late ICNV for the tables CDCLS and EDIDOC.
With transaction STMS create a three system landscape consisting
of this system UPG as the development system, a virtual system QAS
as the quality assurance system and a virtual PRD as the productive
system.
Note: Remember to restore the HR data according to note 317722
SAP-Hinweis Nr. 587896
Nummer 587896
Version 24 vom 30.07.2003
Status Für Kunden freigegeben
Gesetzt am 30.07.2003
Sprache EN
Mastersprache DE
Kurztext Add. info on upgrade to SAP R / 3 Enterprise Core 4.70
SR1
Verantwortlich SAP
Komponente BC-UPG-RDM
README: Upgrade-Ergänzungen
Langtext
Symptom
An error occurs in the upgrade procedure or in the upgrade guide;
preparation for the upgrade.
Additional key words
Update, migration, release upgrade, release, maintenance level, R3up,
PREPARE
Cause and prerequisites
Solution
CAUTION: This note is updated on a regular basis.
You should therefore read it again immediately before implementing the
upgrade.
CAUTION: This note only applies to R / 3 Enterprise Core 4.70 Support
Release 1.
What can you expect from this note?
It specifies problems that may occur when upgrading the system and
describes appropriate solutions. It usually refers to other notes.
The main purpose of this note is to prevent data loss, upgrade shutdown
and long runtimes.
It only deals with database-independent problems.
What can you not expect from this note?
Problems after the upgrade are only dealt with if they are caused
directly by the upgrade tools.
Which notes do you also need for preparing the upgrade?
This depends on the functions you use.You need one or more of the
following notes:
Short text .....Number
Additional information on upgrade to SAP Web AS 6.20 SAP..490325
Additions upgrade SAP Web AS 6.20 iSeries.................597256
Additions upgrade to SAP Web AS 6.20 DB6..................490095
Additions upgrade to SAP Web AS 6.20 DB2 UDB for OS / 390...517267 517267
Additions upgrade to Web SAP AS 6.20 MS SQL Server........517070
Additions upgrade to SAP Web AS 6.20 Oracle 9.2.0.........575280
Add. information on upgrading to Basis 6.20 Informix......486274
Current note on the language import 6.20 ................482462
Language import and Support Packages 352941
Corrections for upgrading to systems with Basis 620......517731
Corrections for upgrading to Basis 620...................522711
OCS: with Supp. Packages in Basis Rel. 6.20 .............447925
Contents
I / ...R3up keyword
II / ..Important general remarks
III / .Corrections to the guides
IV / ..Errors on the CD ROM
V / ...Avoiding loss of data, upgrade shutdown and long runtimes
VI / ..Preparing for the upgrade
VII / .Problems in the PREPARE and upgrade phases
VIII / Problems after the upgrade
IX / ..Chronological summary
I / R3up keyword
The R3up keyword is: 83478
It is to be entered for the first call of R3up.
II / Important general remarks
----- ----- ---------- < Changed D025323
----- ----- ------------- < D025323
Source Release 3.1: Integrate Fix Pack 22
For source release 3.1, you must integrate at least Fix Pack Version 22
into PREPARE. Otherwise, you risk data loss.
If you have already started PREPARE with an older Fix Pack, repeat the
PREPARE module IMPORT and all subsequent modules.
For more information, see note 522711.
----- ----- ------------- < D025323
Corrections and repairs for the upgrade
Before the upgrade, check whether the following applies for your
specific upgrade:
o Is there a new version of R3up? For more information, see note
517731.
o Have corections been made to the upgrade's ABAP program?For more
information, see note 522711.
It is imperative that you use these two notes.
----- ----- ------------- < D028310
Problems with the shadow instance
The following notes contain information on problems with the shadow
instance:
o 525677: Problems starting the shadow instance
o 430318: Remote shadow instance on another operating system
----- ----- ------------- < D022030
Support Package statuses in Enterprise SAP R / 3 4.70 SR1
SAP R / 3 Enterprise 4.70 Support Release 1 is based on the following
Support Package statuses:
Main components:
o SAP _ BASIS 620 Support Package 17
o SAP _ ABA 620 Support Package 17
o SAP _ HR 470 Support Package 10
o SAP _ APPL 470 Support Package 6
Add-ons
o EA-HR 110 Support Package 10
o EA-APPL 110 Support Package 6
o EA-PS 110 Support Package 6
o EA-IPPE 110 Support Package 6
o EA-FINSERV 110 Support Package 6
o EA-RETAIL 110 Support Package 6
o EA-GLTRADE 110 Support Package 6
Plug-ins
o PI _ BASIS 2002 _ 1 _ 620 Support Package 6
o PI 2002 _ 1 _ 470 Support Package 3
Installation of the SAP J2EE Engine
The SAP J2EE Engine is not required for SAP R / 3 Enterprise 4.70.
To ensure that you make optimal use of your live environment's system
resources, the SAP J2EE Engine is not installed automatically with R / 3
If you would like to install the SAP J2EE Engine, you can install it as
described in note 545422.
----- ----- ----- ----- ----- < D029035
Upgrade and unicode conversion
At present, SAP does not support an upgrade with simultaneous Unicode
conversion.To obtain a unicode system, you must first carry out an
upgrade of the non-unicode system of release versions earlier than 4.70
(SAP
perform the Unicode conversion.
For more information, see note 548016.
Retrofit add-ons
For more information on dealing with add-ons that underwent a retrofit
for R / 3 Enterprise 4.70, see note 533348.
----- ----- ----- ----- ---- < D033327 JUL / 23 / 02 >----- ----- ---------
Only Windows: No Windows XP
Windows XP is not supported.
----- ----- ------------- < D025323 SEP / 20 / 02 >----- ----- ----------
Only Windows NT: Check tp version
Ensure that the directory \usr\sap\ <sid>\sys\exe\run does not contain a
tp with version 305.12.58 (tp for the source release, for source release
4.6x).
Use either a more current version or the previous one, as otherwise
errors will occur during the upgrade.
For more information, see note 537347.
III / Corrections to the guides
----- ----- ----- ----- ---- < D033327
Windows only: Wrong Note no. in postprocessing work for MSCS
Sections "Upgrade - Step by Step" and "Post-Upgrade Activities for the
Microsoft Cluster Server" refer to Note 144031 during the postprocessing
work for MSCS. This is incorrect. The correct reference is Note 544988.
----- ----- ----- ----- ----- < D000706
Date of the R3trans required for the source release
Section "Checking SAP Programs"
asks for an R3trans of
for the source release.
This date refers to the file date. R3trans itself reports back with the
later date
----- ----- ----- ----- ----- < D022030 JUN / 23 / 03 >----- ----- ----- ----- ----
Error in parameter rdisp
The parameters rdisp / mshost and rdisp / wp _ no _ vb have been written
incorrectly in some guides. They should read "rdisp", not "rsdisp".
----- ----- ----- ----- ----- < D022030 SEP / 09 / 02 >----- ----- --------
HR composite SAP Note
The HR composite SAP Note 156387 specified in the guide does not apply
to R / 3 Enterprise 4.70 until further notice.
IV / Errors on the CD ROM
V / Avoiding loss of data, upgrade shutdown and long runtimes
----- ----- -------- < changed D035061 09 / MAY / 03 >----- ----- ------------
----- ----- ------------- < D035061 08 / MAY / 03 >----- ----- ----- ----- ------
Inclusion of certain Support Package statuses
If you include the following Support Packages in the upgrade, include to
at least the following level:
SAP _ APPL 470 ... Support Package 0010*
EA-APPL 110 .... Support Package 0004
* Until this Support Package is released, proceed as follows:
o Customers without EA _ GLTRADE:
Include SAP _ APPL to at least Support Package 0008. The error
message in phase ACT _ 620 for views h _ tmfk, v _ tb2bt and v _ tb2bu
can be ignored in this case. You will find more information in
note 610295.
o Customers with EA _ GLTRADE:
During the upgrade, include the EA _ GLTRADE Support Packages to at
least Support Package 0007. You will find more information in
note 615187.
----- ----- ----- ----- ---- <I023086 APR / 08 / 03 >----- ----- ----------
Archiving of work items to shorten the conversion time
During the transfer to 46A, corrections were made in table SWWWIHEAD to
improve performance.These corrections require an (automatic) table
conversion on the database.
To minimize the conversion time, we urgently recommend that you archive
and / or delete entries in these tables that are no longer required (work
items in an end status) before the actual upgrade.
To archive / delete the data, see notes: 49545, 145291, 153205, 159065.
----- ----- ------------- < D030326 MAR / 28 / 03 >----- ----- ----------
Missing contents for proxy generation of the Exchange Infrastructure
As of Basis Release 6.20, extended information on DDIC objects, classes
and interfaces is delivered that is required when you use the product
SAP Exchange Infrastructure (SAP XI).The information for DDIC objects is
not imported in the upgrade.
The error is eliminated with the correction for the upgrade procedure
from note 522711.
If you have already performed the upgrade to Basis Release 6.20, you
will find information on the subsequent importing of the missing data in
note 439915 on the add-on "Exchange Infrastructure - Integration Server"
(APPINT).
----- ----- ------------- < D030326 SEP / 17 / 02 >----- ----- ----------
DDIC password
After the upgrade is started, the DDIC password may not be changed
either in the original or in the shadow system.Otherwise, it is not
possible to log in to the system during the upgrade.
VI / Preparing for the upgrade
----- ----- ----- ----- ------ < D025323 APR / 24 / 03 >----- ----- -------
Upgrading with AIX: saposcol
See notes 526694 and 569015 before the upgrade.
----- ----- ----- ----- ------ < D030326 AUG / 08 / 02 >----- ----- -------
Adjusting profile parameters
Check whether the profile parameter "rsts / ccc / cachesize" is set.
If it is, remove it or extend it to 6, 000, 000 bytes, as described in
note 5470.
Otherwise, the following errors appear in different phases (for example,
PARCONV _ UPG, XPRAS _ UPG) of the upgrade:
Runtime error "IMPORT _ INIT _ CONVERSATION _ FAILED"
The following message appears in the syslog:
"E 14 Reorganized Buffer RSCPCCC with Length xxxxx (Overflow)"
----- ----- ----- ----- ----- < D032986 JUL / 09 / 02 >----- ----- --------
Upgrade with reintegrated add-ons
For R / 3 Enterprise 4.70, the following add-ons were reintegrated into
R / 3 Enterprise Core or the extension set:
BANKING, BANK / CFM, CA-ACB, HR-PS, IS-PS, HR-IN, HR-KR+CN, EHS, LTRM,
SDP _ SABRE, LAM-ACC, TR-TM-BOTTOM, FAS133.
For more information on processing these add-ons, see note 533348.
----- ----- ----- ----- ----- < D025323 08 / JUL / 02 >----- ----- --------
Upgrade with 32-bit operating systems
Your source release system is on the operating system version AIX
32-bit, HP-UX 32-bit or SUN-OS 32-bit, switch to a 64-bit version before
the PREPARE, ideally directly to the 64-bit version required for the
target release.
If you are using a 64-bit AIX 4.3, additional steps must be taken before
the upgrade.
For more information, see notes 496963 and 499708.
----- ----- ------------- < D021371 OCT / 12 / 01 >----- ----- ----------
Only for AIX: Application Runtime
For an upgrade under AIX, you need at least the AIX application runtime
version 5.0.2.0.
Using the command
lslpp -l xlC.rte
check whether the C set ++ is installed.
If it is not installed, or if the incorrect version is installed,
download it from your country version of the Internet IBM AIX Fix
Distribution, or from the US Web page
Install it using smit (-> software) as the user root.
If you also require the "Base Level Fileset" (xlC.rte.5.0.0.0), download
the vacpp5 _ runtime.tar.Z file from:
----- ----- ---------- < added D032986 JUL / 05 / 02 >----------
----- ----- ----- ----- ----- < D028310 JUL / 02 / 02 >----- ----- --------
Upgrade with add-on PI, PI-A or their predecessors BW-BCT, APO-CIF,
B2B-PRO-PI and CRM-R3A
PI Release 2002 _ 1 _ 470 is part of the R / 3 Enterprise delivery (R / 3
Enterprise Core 4.70, R / 3 Enterprise Extension 1.10).
If you have already installed PI, PI-A or their predecessors in your R / 3
source release, proceed as follows:
o Source releases higher than 3.1I:
If the add-on PI with a release up to or including 2002 _ 1 _ 31I is
installed in your 3.1I system, select "Passive deletion" in the
phase IS _ READ (that is, neither "Supplement CD" nor
"Received").As the add-on PI is part of the export when upgrading
to R / 3 Enterprise 4.70, you automatically receive the current
version with the upgrade.
If the version in your 3.1I system is higher than 2002 _ 1 _ 31I, you
must include a supplement CD in the phase IS _ READ, to avoid data
loss.
o Source release 3.1I:
Before you start with PREPARE, you must have installed at least
the PI- / PI-A Release 2001.2 (technically, for example,
2001 _ 2 _ 40B).
For more information, see notes 533568 and 214503. Detailed
information on the R / 3 plug-in (Contents, releases, dates,
installation and upgrade strategy, maintenance) is provided on
the SAP Service Marketplace under the alias R3-PLUG-IN
If you have not installed PI or PI-A or their predecessors in your R / 3
source release, you can carry out the upgrade to R / 3 Enterprise without
installing PI or PI-A in the R / 3 source release.
----- ----- ----- ----- ----- < D022030 JUN / 24 / 02 >----- ----- --------
Database archives
The archives used during the upgrade help you select an upgrade or
archiving strategy.The first of the two digits specifies the size of the
archives up to phase MODPROF _ TRANS, the second specifies the size of the
archives up to the end of the upgrade.
DB2 UDB for UNIX / Windows: 26 GB / 31 GB
Informix: 22 GB / 27 GB
MS SQL Server: 24 GB / 30 GB
Oracle: 26 GB / 31 GB
SAP DB: 15 GB / 20 GB
The sizes are based on sample data.
----- ----- ----- ----- ----- < D022030 JUN / 24 / 02 >----- ----- --------
Storage requirement in the database
The database must be enhanced during and through the upgrade.The first
of the two digits specifies the maximum anticipated enhancement during
the upgrade, the second specifies the permanent enhancement of the
database.
DB2 UDB for UNIX / Windows: 18 GB / 15 GB
Informix: 15 GB / -- GB
iSeries: 25 GB / 16 GB*
MS SQL Server: 15 GB / -- GB
Oracle: 18 GB / 15 GB
SAP DB: 14 GB / 8 GB
The sizes are based on sample data.
* depends predominately on the upgrade and archiving strategy as a
number of journal receivers may arise during archiving.
VII / Problems in the PREPARE- and upgrade phases
This section describes problems that you cannot eliminate using
preventative measures.These problems can only occur under specific
conditions or if particular prerequisites apply.
Problems in the PREPARE phases
----- ----- ------------- < D038245 30 / JUL / 03 >----- ----- ----- ----- -------
Replacement of the target release kernel
After running module "General Checks", you may get the following error
message in log file CHECKS.LOG:
There are dependencies between Basis Support Packages included in phase
BIND _ PATCH and the patch level of the target release kernel in directory
/ usr / sap / put / exe.
In this case, a support package included in the upgrade needs another
kernel patch level.
Proceed as described in Note 211077.
----- ----- ------------- < D022256 SEP / 04 / 00 >----- ----- ----------
For Windows NT 4.0 only
If, during the PREPARE, a dialog box with the following error message
appears:
'The procedure entry point ... could not be located in the dynamic link
library ...'.
implement the latest DLLs using the program R3DLLINS.EXE.The program is
available on the SAP kernels CD in the directory \NT\ <processor
type>\NTPATCH.
Boot your machine and restart PREPARE with 'PREPARE repeat'.
As of source release 4.0A:
Termination in the phases TOOLIMPD1 or TOOLIMPD2.For more information,
see note 98198.
Problems in the upgrade phases
Phase: PARDIST _ SHD
Note: 73999
Description: Upgrade phase PCON _ 620 or PARDIST _ SHD: TG450 to TG453
Phase: STARTR3 _ NBAS
Description: For MS SQL and MSCS termination only
A termination may occur when you combine MS SQL Servers and MSCS Cluster
if
disp / sna _ gw _ service = sapgw <System-ID> is not set in the profile of the
parameter.
Set the parameter and repeat the phase.
Phase: PARCONV _ UPG ***
Note: 339126
Description: SQL error in the database when accessing a table.Call
report RADUTMST for the tables involved and then continue with Repeat.
Phase: STARTR3 _ IMP
Note: 525006
Description: Only if you are using AIX and the Upgrade Assistant
The program R3up cannot start the system and terminates.
----- ----- ----- ----- ----- < D038245 MAR / 06 / 03 >----- ----- --------
Phase: XPRAS _ UPG
Description:If a database error occurs in this phase (for example,
overflowing tablespace), R3up automatically repeats the phase.In some
cases, R3up may continue to run, but the task is still deactivated in
the system.The following entry appears in the system log:
The update task was deactivated.
In this case, solve the database problem (for example, by extending the
tablespace), call transaction SM14 and activate the update.
----- ----- ----- ----- ----- < D022030 JUL / 09 / 02 >----- ----- --------
Phase: XPRAS _ UPG
Note: 534826
Description: LONGPOST.LOG:XPRA RMCSXP03 reports the error M2392, M2108
or M2685.In addition to the solution, the above-mentioned note contains
more information on problems with update programs.
----- ----- --------- < changed D030326 JUN / 21 / 02 >----- ----- ------
Phase: XPRAS _ UPG
Description: LONGPOST.LOG:The following entries from XPRA RMCSXP04
(SAPK46AXP5) can be ignored:
3PEM2579 client "xxx":
Problem adapting " " / " "
to updating IS "S216" (TMC2F)
where xxx is a client in your system. The same applies for "S217" and
"S218".
----- ----- --------- < changed D030326 21 / JUN / 02 >----- ----- ------
Phase: JOB _ RSTLANUPG
Note: If necessary 196113
Description:Under certain circumstances, the report RSTLAN _ UPGRADE
called in this phase may terminate with an ABAP dump message
ABAP / 4 runtime error (short dump) in SAPLSBAL _ DB _ INTERNAL
SAPLSBAL _ DB _ INTERNAL
LSBAL _ DB _ INTERNALU02
IF NOT i _ s _ db _ tables-balhdr _ i IS INITIAL.
INSERT balhdr CLIENT SPECIFIED FROM TABLE
terminated. If this happens, repeat the phase again.If the error
persists, implement note 196113.
Phase: JOB _ RDDNTPUR
Description:For source release 4.6B, the following error message may
appear in the log LONGPOST.LOG:
Table and runtime object "TSTCCLASS" exist without DDIC reference
You can ignore this error message.
Phase CHK _ POSTUP
Note: 197886
Description:If you have imported notes 178631, 116095 or 69455 in your
system before the upgrade, LONGPOST.LOG error messages appear in the log
for objects without a DDIC reference.
Follow the instructions provided in the note.
Phase: CHK _ POSTUP
Description:For source release 4.6, the tables SPRTL1, SPRTL3 and SPRTL9
may appear with the following error message in the log LONGPOST.LOG:
Table and runtime object "SPRTL1" exist without DDIC reference
You can ignore this error message.
VIII / Problems after the upgrade
This section describes problems that you cannot prevent using preventive
measures.These problems only occur under very specific conditions or if
certain prerequisites apply.
----- ----- ----- ----- ----- < I019889 21 / JUL / 03 >----- ----- ------------
Payroll Great Britain: Syntax error in Report RPCALCG0
When you get syntax error 'The FORM "FUXDEC" does not exist' in Report
RPCALCG0, proceed as described in Note 642937.
The problem has been solved with HR Support Package 18.
----- ----- ----- ----- ----- < D020815 MAR / 25 / 03 >----- ----- --------
User exits in the SPAU
Due to the changed procedure for the modification adjustment during the
upgrade, users exits that were delivered with earlier releases and used
by customers, are now displayed as modifications and must be adjusted.
For more information, see note 607893.
----- ----- ---------- < supplemented D027999 OCT / 07 / 02 >----------
----- ----- ----- ----- ----- < D027999 SEP / 27 / 02 >----- ----- --------
Problems with user exits and customer enhancements
New and intensified rules for (unicode-enabled) ABAP sytax and runtime
have been introduced with the SAP Web Application Server, and these
apply for unicode and non-unicode installations.Due to the stricter
checks, syntax errors may occur for exits and customer enhancements.
o For information on eliminating possible errors for userexits, see
note 553110.
o For information on eliminating possible errors for customer
enhancements, see note 493387.
----- ----- ----- ----- ---- < D020815 AUG / 23 / 02 >----- ----- ---------
SPAU: Names of interface methods are truncated
In transaction SPAU, some methods modified and overwritten by the
upgrade (ABAP Objects) may be displayed in a truncated form (30
characters).As a result, methods in SPAU may be incorrectly sorted under
"Deleted objects".
Caution:Deleted objects are not displayed in SPAU in the standard
selection.It is possible that these may be overlooked.
For more information on the correction, see note 547773.
----- ----- ---------- < changed D032781 06 / MAY / 03 >----- ----- -----------
----- ----- ----- ----- ----- < D020847 13 / AUG / 02 >----- ----- ----- ----- -----
Windows / Microsoft Cluster Server (MSCS)
If you perform an upgrade under MSCS, you must carry out the
post-upgrade activities described in note 544988. To do this, you
require a special installation CD which you must order separately.
----- ----- ----- ----- ---- < D022860 JAN / 09 / 01 >----- ----- ---------
Incomplete path in .sapenv _ <hostname>.sh
Only for UNIX:If you use the bourne or corn shell as a login shell for
<sapsid>adm, and you can no longer start / stop the system, this may be
caused by an incomplete path specification in
$HOME / .sapenv _ <hostname>.sh.In the file $HOME / .sapenv _ <hostname>.sh,
change the line:
for d in / usr / sap / <SAPSID> / SYS / exe / run; do
in
for d in / usr / sap / <SAPSID> / SYS / exe / run $HOME .; do
Linux: Importing new saposcol version
For more information, see note 19227
Solaris: saposcol version 32 or 64 bit
For more information, see note 162980
IX / Chronological Summary
Date........Topic....Short description
30 / JUL / 03...VII........Replacement of the target release kernel
21 / JUL / 03..VIII........Payroll GB: Syntax error in Report RPCALCG0
02 / JUL / 03...III........Windows only: Wrong note for MSCS postprocessing
27 / JUN / 03....II........Source release 3.1: Integrate Fix Pack 22
26 / JUN / 03...III........Date of R3trans required for source release
23 / JUN / 03...III........Error in parameter rdisp
08 / MAY / 03....II........Support Package statuses in SAP R / 3 Enterprise
4.70 Support Release 1
08 / MAY / 03.....V........Including certain Support Package statuses
02 / MAY / 03.....V........Loss of customer matchode IDs
24 / APR / 03....VI........Upgrading with AIX: saposcol
08 / APR / 03.....V........Archiving of work items
28 / MAR / 03.....V........Missing contents for proxy generation of the XI
Mar 25 2003...VIII.....User exits in SPAU
Mar 06 2003...VII......Phase: XPRAS _ UPG - Update
Feb 25 2003...VII......Phase: JOB _ RDDNTPUR - TSTCCLASS
Feb 24 2003...VII......Phase: CHK _ POSTUP - Tables SPRTL1, SPRTL3, SPRTL9
Sep 27 2002...VIII.....Problems with user exits
Sep 20 2002...II.......Only Windows NT : Check tp version
Sep 17 2002...V........DDIC password
Sep 13 2002...VII......Only MS SQL with MSCS: STARTR3 _ NBAS - Termination
Sep 09 2002...III......Invalid HR composite SAP note
Sep 05 2002...II.......Upgrade and Unicode conversion
Sep 02 2002...II.......SAP J2EE Engine is not needed
Aug 23 2002...VIII.....SPAU: Names of interface methods are truncated
Aug 13 2002...VIII.....Windows / MSCS: Postprocessing
Aug 09 2002...VII......Phase PARCONV _ UPG: SQL error
Aug 08 2002...VI.......Profile parameters
Aug 07 2002...VII......Phase SHADOW _ IMPORT _ ALL: Duplicate key error
Aug 07 2002...II.......Retrofit add-ons
Jul 23 2002...II.......Windows: Windows XP is not supported
Jul 19 2002...II.......Problems with the shadow instance
Jul 09 2002...VI.......Upgrade with reintegrated add-ons
Jul 09 2002...VII......Phase XPRAS _ UPG: LONGPOST.LOG: XPRA RMCSXP03
Jul 08 2002...VI.......Upgrade with 32-bit operating systems
Jul 02 2002...VI.......Upgrade with add-on PI
Jun 24 2002...VI.......Database archive used
Jun 24 2002...VI.......Storage requirements in the database
June 21 2002..VII......Phase JOB _ RSTLANUPG - termination
23 / MAY / 02 ..VII.. XPRAS _ UPG: LONGPOST.LOG: XPRA RMCSXP04 (SAPK46AXP5)
June 04, 2002.VII.....Phase STARTR3 _ IMP with AIX - system does not start
May 24 2002...II.......Corrections and repairs for the upgrade
May 23, 2002..VII .....Phase CHK _ POSTUP - objects without DDIC reference
Oct 12 2001...VI.......AIX Application Runtime Version 5.0.2.0.
Jan 09 2001...VIII.....Incomplete path in .sapenv _ <hostname>.sh
Feb 20 2002...I........R3up keyword
Oct 19 2000...VIII.....Linux: Importing new saposcol version
Sep 04 2000...VII......Windows NT: Error message in the PREPARE
Feb 16 2000...VIII.....saposcol version 32 or 64 bit on Solaris
Source code corrections
Gültige Releases
Software Komponente Release
von bis
SAP _ BASIS SAP Basiskomponente 620 - 620
Verweise auf verwandte Hinweise
Nummer Kurztext
486274 Additional information on upgrading to Basis 6.20 INFORMIX
490095 DB6: Add. info on upgrading to SAP Web AS 6.20
490325 Additional information on upgrade to SAP Web AS 6.20 SAP DB
493387 Potential effects of table- and structure - extensions
496963 32-bit source release in upgrades to 620
499708 Additional information on upgrading to Basis 620 with AIX
19227 Get the latest saposcol
5470 SysLog E14: Buffer RSCPCCC ... is being reorganized
49545 Deleting unnecessary work items
148926 saposcol version 32 or 64 bit on ReliantUNIX
145291 Performance of deletion from archive file
197886 Upgrade: messages in CHK _ POSTUP: BDL*, STSL*, BAM*, SQLR*
196113 SAPSQL _ ARRAY _ INSERT _ DUPREC, BALHDR
159065 Data selection for work item archiving
153205 Direct deletion of type C work items
214503 Release strategy for PI and PI-A add-ons
211077 Exchanging target release kernel during upgrade
430318 Shadow instance on other operating system
98198 Error in upgrade phase TOOLIMPD1, TOOLIMPD2
352941 Consultation: Languages and Support Packages
304809 SAPCAR does not start
73999 Phase PCON _ <REL> or PARDIST _ SHD: Messages TG450 to TG453
162980 saposcol for 64-bit Solaris
339126 Table conversion error
439915 Exchange Infrastructure Integration Server 2.00
307189 User exit MV45AFZB and others overwritten during upgrade
447925 OCS: Known problems with Supp. Packages in Basis Rel.6.20
482462 Current note on the language transport in Release 6.20
553110 User Exits: Behavior within non-Unicode R / 3 Enterprise
597256 Additions Upg.SAP R / 3 Enterprise 4.7 SR1 Ext.1.10: iSeries
517070 Add. info. on upgrading to SAP R / 3 Enterprise 4.70 MSSQL
517267 DB2 / 390: Additions upgrade to R / 3 Enterprise 4.7
517731 Corrections for the upgrade to systems with Basis 620
522711 Repairs for upgrade to Basis 620
525006 Startup problems during the upgrade on AIX
525677 Problems with starting the shadow instance
526694 saposcol based on AIX perfstat library
607893 User exits in transaction SPAU
610295 Error during upgrade to R / 3 Enterprise
615187 Activation error when importing Support Package 7
642937 Syntax error in RPCALCG0 after upgrade to R / 3 Enterprise
533348 Add-ons integrated into R / 3 Enterprise (Core 470 / Ext. 110)
533568 Upgr. R / 3 Enterprise 47x110 with PI / PI-A 2001.2 and 2002.1
534334 Composite SAP note Installation / Upgrade SAP R / 3 Enterprise
534826 LIS: Current update programs after upgrade
537347 tp writes corrupt buffer line to NT
540021 Add. information on migrating / updating to Oracle 9.2.0: UNIX
544988 Post-upgrade activities for MSCS using SAPinst
545422 INST: SAP J2EE Engine Inst. for SAP R / 3 Enterprise 4.70
547773 SPAU: interface method names are truncated
548016 Conversion to Unicode / Unicode System Copy
569015 64 bit saposcol on AIX terminates immediately on AIX 4.3.3
575280 Additional info on upgrade to SAP Web AS 6.20 ORACLE 9.2.0
578131 Releasing Oracle 9.2 for older SAP versions
SAP-Hinweis Nr. 575280
Nummer 575280
Version 9 vom 28.05.2003
Status Für Kunden freigegeben
Gesetzt am 28.05.2003
Sprache EN
Mastersprache DE
Kurztext Additional info on upgrade to SAP Web AS 6.20 ORACLE
Verantwortlich SAP
Komponente BC-UPG-RDM
README: Upgrade-Ergänzungen
Langtext
Symptom
There is an error in the upgrade procedure or in the guide.
Additional key words
Release, upgrade, migration, updates, maintenance level release
Cause and prerequisites
Solution
This note only deals with problems specific to Oracle!
CAUTION: This note is constantly updated. You must therefore read it
again immediately before the upgrade.
CAUTION: This note only applies to ORACLE database Version 9.2.0. Refer
to note 491598 if you are performing the upgrade with ORACLE database
version 8.1.x.
Contents
I / Important general remarks
II / Freespace requirement in the database
III / Correction to the guides
IV / Errors on the CD-ROM
V / Problems during Oracle migration / upgrade
VI / Problems with PREPARE
VII / Problems in the upgrade phases
VIII / Problems after the upgrade
I / Important general remarks
----- ----- ------------- < D025323 JAN / 17 / 03 >----- ----- ---------
Correct R3up version
To upgrade certain components under Oracle 9.2.0 as well, you need an
R3up of at least Version 620-2 11.127. This applies to the upgrade of
the following components:
o SAP R / 3 Enterprise 4.70 *
o SAP BW 3.0B
o SAP CRM 3.10
o SAP EBP 3.50 *
o Web SAP AS 6.20
* The Support Release for the component contains a high enough R3up
version.
----- ----- ------------- < D029037 OCT / 31 / 02 >----- ----- ----------
Installing Oracle client software
For UNIX:Before starting the PREPARE, you must install the Oracle client
software for the target release. The installation is described in note
----- ----- ------------- < D020847 JUL / 22 / 02 >----- ----- ----------
Windows NT: DB connect problems
If the database is not on the upgrade host, connect problems may occur
in the PREPARE phases SHDBINST _ SDB _ CHK or DBCHK _ PRE.For more
information, see section VI "Problems with PREPARE".
----- ----- ------------- < D032185 JUN / 12 / 01 >----- ----- ----------
Delete the objects SYS.USER _ IND _ COLUMNS _ RULE, SAPR3.USER _ IND _ COLUMNS and
SYSTEM.USER _ IND _ COLUMNS before the upgrade.
For more information, see note 410963.
----- ----- ------- < supplemented by D025323 JUN / 28 / 02 >----------
----- ----- ------------- < D022030 JUL / 21 / 00 >----- ----- ----------
The NEXT _ EXTENT storage parameter for the following tables and indexes
must contain the minimum values specified:
ATAB~0: ......... NEXT _ EXTENT 10240 KB
BRATEXT: ........ NEXT _ EXTENT 10240 KB
BRATEXT~0: ...... NEXT _ EXTENT 2560 KB
GLOSSARY: ....... NEXT _ EXTENT 10240 KB
GLOSSARY~0: ..... NEXT _ EXTENT 2560 KB
E071K: .......... NEXT _ EXTENT 10240 KB
E071K~0, ~ULI ... NEXT _ EXTENT 5120 KB
STERM _ REF: ...... NEXT _ EXTENT 10240 KB
STERM _ REF~0: .... NEXT _ EXTENT 2560 KB
USR13~0: ........ NEXT _ EXTENT 2560 KB
UST10S~0**: ..... NEXT _ EXTENT 2560 KB
UST10S~001**: ... NEXT _ EXTENT 2560 KB
UST12~0**: ...... NEXT _ EXTENT 2560 KB
UST12~VON**: .... NEXT _ EXTENT 2560 KB
* For source release 4.6x only.
** Enhancement may be required as of approximately 10 clients.
Note 11777 describes the procedure.
----- ----- --------- < changed by D030326 JAN / 10 / 03 >-------------
----- ----- --------- < changed by D028310 OCT / 06 / 02 >-------------
----- ----- --------- < changed by D025323 MAY / 13 / 02 >-------------
----- ----- ----- ----- ---- < C1399108 MAY / 15 / 00 >----- ----- --------
Parameters for Oracle:
Check the value for the following parameters in the file
$ORACLE _ HOME / dbs / init <SID>.ora (Unix) or
%ORACLE _ HOME%\database\init <SID <.ora (NT)
o Parameter shared _ pool _ size = 400000000
If the value of the parameter is lower than 400 MB, increase it
to at least 400 MB and restart the database.
For more information, see note 556764.
Caution:If you do not increase the value, errors may occur in the
phase ACT _ <REL> (ORA-4031).
o Parameter compatible = 9.2.0.0.0
II / Freespace requirement in the database
III / Correction to the guides
----- ----- ------------- < D029037 MAR / 12 / 03 >----- ----- ----------
Installation of Oracle client software: SAP note
Refer to the following notes, and not note 303238, which is specified in
some guides (including the upgrade to SAP Web AS 6.20 / R / 3 Enterprise
4.70 / BW 3.1 Content) for the procedure for installing the Oracle client
software:
o Note 539922 for R / 3 Enterprise on AIX 5.x or HPIA64
o Note 406140 for all other combinations
IV / Errors on the CD-ROM
V / Problems during Oracle migration / upgrade
VI / Problems with PREPARE
----- ----- ------------- < D025323 JUL / 31 / 02 >----- ----- ----------
Termination in phase INIT _ CNTRANS
You get the error message:
The following entries in table 'TAORA' do not represent existing DB
containers: [TABART, DBSPACE] USER2 PSAPROLD
You can find information on troubleshooting for
o Source Release 6.10 on Windows in note 407460, section IV
o Source Release 6.10 on UNIX in note 407110, section III
o All other source releases in note 541542.
----- ----- ------------- < D020847 JUL / 22 / 02 >----- ----- ----------
SHDBINST _ SDB _ CHK / DBCHK _ PRE phase: DB connect problems
If the database is not on the upgrade host, connect problems may occur
in the PREPARE phases SHDBINST _ SDB _ CHK or DBCHK _ PRE.For more
information, see note 525471.
----- ----- ------------- < D020904 MAR / 18 / 02 >----- ----- ----------
DBCHK _ PRE phase
If your central instance is not running on the same host as the database
instance, an error occurs in the DBCHK _ PRE phase because the script does
not take the configuration into account at this stage.
To avoid the error, you must edit the \usr\sap\put\bin\ORAGETNLS.SQL
script as follows:
Replace the 'Connect / as sysdba' row with 'connect / @ <DBSID>', for
example, connect / @PRD.
For <DBSID>, use the value of the environment variable dbs _ ora _ tnsname.
A working OPS$ configuration is a prerequisite here.If an error still
occurs after the change, check the OPS$ configuration in accordance with
note 50088.
VII / Problems in the upgrade phases
----- ----- ------------- < D038006 FEB / 24 / 03 >----- ----- ----------
Phase: PARCONV _ UPG, SHADOW _ IMPORT _ UPG2 and XPRAS _ UPG
Note: 558197
Description:The upgrade hangs during one of these phases because an
Oracle shadow process consumes a lot of CPU.To solve the problem,
proceed as described in the note mentioned above.
----- ----- ------------- < D030326 NOV / 04 / 02 >----- ----- ----------
Phase: JOB _ RSTODIRM
The following terminations may occur in the phase:
ORA-01555: snapshot too old, rollback seg. XX with name "..." too small
In this case, you must rerun the phase with "REPEAT" (several times, if
necessary).We recommend adapting the rollback tablespace PSAPROLL and
the rollback segments accordingly.
----- ----- ------------- < D025323 AUG / 30 / 02 >----- ----- ----------
Termination in the phase ALTEXT _ MAXALL
This may occur in rare cases. In the case of the error message:
ORA-00054: resource busy and acquire with NOWAIT specified
, you should repeat the phase. This should eliminate the error.
VIII / Problems after the upgrade
----- ----- ------------- < I000037 SEP / 13 / 02 >----- ----- ----------
Only AIX: Stopping / starting the database no longer possible
Following the upgrade, you can no longer start or stop the database with
the user <sid>adm.When you call svrmgrl, you get the following error:
ORA-03113: end-of-file on communication channel
Delete the environment variable EXTSHM=ON from
.sapenv _ <hostname>.csh / .sh
For more information on the EXTSHM variables, see note 203651.
IX / Chronological Summary
Date Topic Short description
MAR / 12 / 03 ... III . Installation of Oracle client software: SAP note
FEB / 24 / 03 ... I ....Importing scripts
FEB / 24 / 03 ... VII ..Phases PARCONV _ UPG, SHADOW _ IMPORT _ UPG2, XPRAS _ UPG
JAN / 17 / 03 ... I ... Correct R3up version
NOV / 04 / 02 ... VII.. Phase: JOB _ RSTODIRM
OCT / 31 / 02 ... I ... Installing Oracle client software
SEP / 24 / 02 ... I ... Oracle patches
SEP / 13 / 02 ... VIII. Only AIX: Stopping / starting not possible
SEP / 02 / 02 ... VII.. Termination in the phase ALTEXT _ MAXALL
JUL / 22 / 02 ... VI .. Termination in phase INIT _ CNTRANS
JUL / 22 / 02 ... VI .. SHDBINST _ SDB _ CHK / DBCHK _ PRE phase: DB-Connect
MAR / 27 / 02 ... VI .. DBCHK _ PRE phase: Adapting the script
JUL / 20 / 01 ... I ... Creating new tablespaces with autoallocate
JUN / 12 / 01 ... I ... Deleting objects before the upgrade
JUL / 20 / 00 ... I ... Adding storage parameters NEXT _ EXTENTS
MAY / 15 / 00 ... I ... Parameters for Oracle
Source code corrections
Gültige Releases
Software Komponente Release
von bis
SAP _ BASIS SAP Basiskomponente 620 - 620
Verweise auf verwandte Hinweise
Nummer Kurztext
484876 Additional information on upgrading to SAP Web AS 6.20
491598 Additional info on upgrading to SAP Web AS 6.20 ORACLE 8.1.x
407110 INST: SAP Web AS 6.10 Inst. on UNIX - Oracle
407314 Released operating systems SAP R / 3 kernel 6.x ORACLE
157755 Using R / 3 as SAP Retail (Releases 4.6A / B, 4.6C, 4.70)
410963 Removing private Oracle objects for 6.X0 kernels
50088 Creating OPS$ users on Windows NT / Oracle
407640 INST: SAP Web AS 6.10 on Windows - Oracle
587896 Add. info on upgrade to SAP R / 3 Enterprise Core 4.70 SR1
513536 Add. information on upgrade to SAP R / 3 Enterprise Core 4.70
603852 Additional information on upgrading to SAP SCM 4.0
525471 Shadow upgrade with remote database host NT / ORA
637683 Ergänzungen Upgrade auf SAP R / 3 Enterprise Core 4.70 Ext. 2
534208 Ramp-up 1: Upgrading to SAP R / 3 Enterprise Core 4.70
534334 Composite SAP note Installation / Upgrade SAP R / 3 Enterprise
539519 Ramp-up 2: Upgrading to SAP R / 3 Enterprise Core 4.70
541542 Upgrade phase INIT _ CNTRANS: Container inconsistency
556764 Upgrade hangs in ACT _ 620 / ACT _ 610 / ACT _ 46C phase
558197 upgrade hangs in PARCONV _ UPG, XPRAS _ UPG or SHADOW _ IMPORT _ UPG2
578131 Releasing Oracle 9.2 for older SAP versions
SAP-Hinweis Nr. 156387
Nummer 156387
Version 16 vom 03.08.2003
Status Für Kunden freigegeben
Gesetzt am 03.08.2003
Sprache EN
Mastersprache DE
Kurztext References to upgrade notes regarding HR
Verantwortlich SAP
Komponente PA-PA-XX-BS
Grundlagen
Langtext
Symptom
This note is a collective note on the HR upgrade.
It contains references to other notes on the upgrade to Release
4.6A / 4.6B / 4.6C and 4.70.
This note is updated continuously. Therefore, we recommend that you
check the note regularly to see whether any new notes have been added
that may be useful for your system. This note lists the most important
notes, but not all. Some of the notes specified may have been archived
in the meantime and others may have been re-edited. In this case, the
status of the note itself is valid.
Note the release for which the notes are valid. The notes are listed
under the target release of an upgrade.
In addition, you should also consult notes on the upgrade in application
area BC-UPG-RDM as these may also be useful for HR.
Additional key words
Cause and prerequisites
Solution
Contents:
General information / Please Note
I / Upgrade to 4.6A
II / Upgrade to 4.6B
III / Upgrade to 4.6C
IV / Upgrade to 4.70
0 / General information / Please Note
You can now access the HR Upgrade Information Site at
https: / / service.sap.com / hrupgrade on the SAP Service Marketplace. It is
available for both customers and partners. The HR Upgrade Information
Site is tasked with bundeling all information about XPRAs and other
upgrade-relevant Reports in the area of HR at an easily-accessible
location.
I / Upgrade to 4.6A
128454 No upgrade to functional release with HR LCPS
152578 XPRA RPU40ACD terminates
154492 PU12: Short dump importing "INTERFACE _ VER"
156956 Conversion of payroll results for Rel. 4.*
156568 Data loss of T5DB4 after upgrade to 4.*
160177 Upgrading FSAs 3.x / 4.0 -> 4.5 / 4.6A
160132 HR-DPF: no garnishment calculation with retroactive accounting
164197 Source code of customers functions and operations
164770 Functions SETCU and ADDCU in payroll schema
165934 CONNE _ IMPORT _ ILL _ OBJECT _ TYPE in RPU40Axx
165241 HR-GB: RPUABPG0 not converting SSP paid weeks
173440 Deductions of health or insurance plans different
174606 Parallel processing of report RPU40ACL
175525 Branch upgrade of incentive wage
176739 RPUQTA50: For REJECT, personnel numbers are mixed
178905 Upgrade to 4.5 for FSAs after adjustment run
181747 Incorrect benefits in retro after upgrade to 4.5 II
198755 XPRA RPUQTA50 does not convert data
201827 Dump in RPUPTEXDIR00
209476 RPUQTA00: Absence quotas w consumption > entitlement
211603 Endless loop in XPRA RPUQTA50
310852 Performance improvement with upgrade and service packages
315364 You cannot start the task catalog
326712 Cancelling work time events after release upgrade
329101 Upgrade to 4.6B or 4.6C: DBIF _ RSQL _ INVALID _ RSQL
329103 FF804: Variable KSCHL is empty..
358014 Problems with RPUQTA50
398557 Payroll: Short dump CONNE _ IMPORT _ WRONG _ COMP _ TYPE
II / Upgrade to 4.6B
128454 No upgrade to functional release with HR LCPS
152578 XPRA RPU40ACD terminates
154492 PU12: Short dump importing "INTERFACE _ VER"
156568 Data loss of T5DB4 after upgrade to 4.0
160132 HR-DPF: no garnishment calculation with retroactive accounting
164770 Functions SETCU and ADDCU in payroll schema
165934 CONNE _ IMPORT _ ILL _ OBJECT _ TYPE in RPU40Axx
165241 HR-GB: RPUABPG0 not converting SSP paid weeks
173440 Deductions of health or insurance plans different
174606 Parallel processing of report RPU40ACL
181747 Incorrect benefits in retro after upgrade to 4.5 II
198599 PU12: Upgrade to Rel. 4.5 - filling infotype 0415
198755 XPRA RPUQTA50 does not convert data
201827 Dump in RPUPTEXDIR00
209476 RPUQTA00: Absence quotas w consumption > entitlement
211603 Endless loop in XPRA RPUQTA50
304563 HR-OM: PPOM Authorization Missing
310852 Performance improvement with upgrade and service packages
315364 You cannot start the task catalog
317722 Table T77S0 delivered with errors
323979 Incorrect attributes in Release Note in HR
326712 Cancelling work time events after release upgrade
328396 HR-OM: Multiple selection in RHXSTEL0
329101 Upgrade to 4.6B or 4.6C: DBIF _ RSQL _ INVALID _ RSQL
329103 FF804: Variable KSCHL is empty.
358014 Problems with RPUQTA50
398557 Payroll: Short dump CONNE _ IMPORT _ WRONG _ COMP _ TYPE
373038 Organizational Management: data missing after upgrade
III / Upgrade to 4.6C
160132 HR-DPF: no garnishment calculation with retroactive accounting
201827 Dump in RPUPTEXDIR00
209476 RPUQTA00: Absence quotas w consumption > entitlement
211603 Endless loop in XPRA RPUQTA50
310852 Performance improvement with upgrade and service packages
315364 You cannot start the task catalog
317722 Table T77S0 delivered with errors
318380 Error in HR Support Package 01 (HR SP 01) in 4.6C
323979 Incorrect attributes in Release Note in HR
326712 Cancelling work time events after release upgrade
328396 HR-OM: Multiple selection in RHXSTEL0
329101 Upgrade to 4.6B or 4.6C: DBIF _ RSQL _ INVALID _ RSQL
329103 FF804: Variable KSCHL is empty.
353861 MR: Upgrade to 4.6C (or higher)
354418 Additions to the HR-PS 462A installation
354437 Additions to the R / 3 4.6C SRX upgrade with HR-PS 462A
358014 Problems with RPUQTA50
384888 Add-on upgrade to HR-PS 462A and IS-PS-CA 462
398557 payroll: Short dump CONNE _ IMPORT _ WRONG _ COMP _ TYPE
428300 PE01 / 02: Syntax error after upgrade to Release 4.6C
373038 Organizational Management: data missing after upgrade
IV / Upgrade to 4.70
317722 Upgrade information for table T77S0
353861 HR: Upgrade to 4.6C (or higher)
518591 Documents of Generic Object Services assigned incorrectly
537338 User exit for collective search help PREM and PAPM
542091 Migration from ZDATA to CI-include
543680 Upgrade to Unicode: Convert additional data f relationships
555018 Reduction of VDATA
373038 Organizational Management: data missing after upgrade
Source code corrections
Gültige Releases
Software Komponente Release
von bis
SAP _ APPL R / 3 Standard 470 - 470
46C - 46C
46A - 46B
Weitere Komponenten
BC-UPG
Upgrade allgemein
PA-PA
Personaladministration
Hinweisattribute
HIER
Transaktionscodes PPOM
PU12
Transaktionscodes XPRA
Verweise auf verwandte Hinweise
Nummer Kurztext
374172 Q&A: Master Note for
Conversions / Upgrades -
179373 Additional info for upgrade to Rel.4.6B
114792 HR upgrade, special feat. HR-PSG, Public Sector
358014 Problems with RPUQTA50
67921 References to upgrade notes concerning HR 3.1G-4.5*
372978 MSC2001: Converting payroll results in upgr. to 46C
318054 4.6B HR upgrade for
551688 Contents and application of R / 3 HR Support Packages 4.70
582528 4.6C HR upgrade for
SAP-Hinweis Nr. 522711
Nummer 522711
Version 75 vom 01.08.2003
Status Für Kunden freigegeben
Gesetzt am 01.08.2003
Sprache EN
Mastersprache DE
Kurztext Repairs for upgrade to Basis 620
Verantwortlich SAP
Komponente BC-UPG
Upgrade allgemein
Langtext
Symptom
You want to implement corrections for ABAP upgrade programs or update
control files.
This note is valid for all products based on SAP Web Application Server
Release 6.20.
Additional key words
620, upgrade, shadow system, shadow instance, SHD _ FIX _ IMP, TOOLIMP4 _ FIX,
TOOLIMP6 _ FIX, TOOLFIX _ CHK, IS _ MOVES.LST
Cause and prerequisites
This note describes how to add the repairs to the upgrade procedure.
Applying this note prevents the occurrence of various errors, upgrade
shutdowns, loss of data and long upgrade runtimes.
It is essential that you apply this note because, if you do not do so,
you risk losing data, data inconsistencies being created and the upgrade
shutting down.
Also refer to note 517731 for the correct R3up version.
Solution
The upgrade correction is provided as a SAR archive that you must
integrate into the upgrade. Caution:Each SAR archive is only valid for
one product (= exactly one delivered CD set). Therefore, there is
exactly one valid SAR archive for each product.You must reset the
upgrade if you apply the wrong archive.
The SAR archives are provided as note attachments in SAPNET.
Selecting the correction package
The following table tells you which archive you need and how to
integrate it into the upgrade. You can find the version of an archive in
file <PUTDIR> / bin / TOOLFIX _ STAMP.
Product Correction Version Integration
package name into the upgrade
WEB AS 6.20*) FIX _ WEBAS620.SAR 8 manually
R / 3E 4.70 FIX _ R3E470.SAR 21 manually
R / 3E 4.70 SR1 FIX _ R3E470SR1.SAR 24 automatically
BW 3.0B FIX _ BW30B.SAR 10 manually
BW 3.10 FIX _ BW310.SAR 16 manually
CRM 3.10 FIX _ CRM310.SAR 10 manually
CRM 4.0 FIX _ CRM400.SAR 14 automatically
EBP 3.5 FIX _ EBP350.SAR 8 manually
EBP 3.5 SR1 FIX _ EBP350SR1.SAR 12 manually
SCM 4.01 FIX _ SCM401.SAR 9 automatically
Comments:
- "SAP WEB AS 6.20" refers to the "Standalone" Web AS product,
on which no additional main component(s) is / are installed.Do
not confuse this with other products that are based on SAP WEB
AS 6.20.
- Higher quality service releases featuring improved upgrade
procedures are provided for the R / 3 Enterprise 4.70, BW and
EBP products.Always use the service release CDs for an
upgrade.
- The FIX _ R3E470 _ RAMP12.SAR package is provided for the R / 3
Enterprise 4.70 product, ramp-up Versions 1 and 2. It is
essential that you use ramp-up Version 3, or preferably R / 3
Enterprise 4.70 SR1.
- If you perform an upgrade to R / 3 Enterprise (FIX _ R3E470.SAR)
and you include less than 14 Basis Support Packages,
terminations occur later when you import Basis Support
Packages 14 (SAPKB62014) using transaction SPAM.Solution:Also
download the attached archive Y6AK029165.SAR and import the
Y6AK029165 request manually after the upgrade.
- If you perform an upgrade to R / 3 Enterprise (FIX _ R3E470.SAR),
do not use versions 52 (see also file TOOLFIX _ STAMP "date =
2003-5-9") to 58 (see also file TOOLFIX _ STAMP "date =
2003-5-15") (inclusive) of this note, because FIX _ R3E470.SAR1
contains a critical error in this case. The error results in a
loss of all customer objects and an upgrade that is started
with the error must be reset and restarted with the PREPARE.
-
Integration into the upgrade
Depending on the R3up version used, the correction package is either
automatically integrated or you must integrate it manually.
o Automatic integration
During the TOOLFIX _ CHK prepare phase (the "Import" or "Extension"
module), R3up searches the upgrade directory for the correct
correction package.If R3up is successful, the package is
automatically integrated into the upgrade.If R3up does not find a
valid package, the system displays a user dialog requesting that
you place the correction package in the upgrade directory.
You can use "Retry" to repeat the search or "Ignore" to continue
with the upgrade without integrating the correction package.
o Manual integration:
- Start PREPARE and run the "Parameter input", "Initialization"
and "Import" modules first.
- Place the SAR archive in the <DIR _ PUT> directory.
- Go to the <DIR _ PUT> directory:
cd <DIR _ PUT>
and unpack it there using the SAPCAR tool.
SAPCAR -xvf <SAR _ Archiv>
For iSeries, use also the option '-h', to avoid subsequent
authorization problems:
SAPCAR '-xvf <SAR _ Archiv> -h'
- Continue PREPARE with the "Extension" module or repeat the
"Extension" module. Caution:If you repeat the "Import" module,
control data is unpacked from the CD to the upgrade directory
and the corrections are undone.You must unpack the archive
again and continue the PREPARE using the "Extension" module.
The archive contains data files and cofiles for the transport requests,
buffers and control files of the upgrade.The corrections to the ABAP
tools of the source release are imported in the TOOLIMP4 _ FIX,
TOOLIMP6 _ FIX phases ("Extension" PREPARE module) (provided these exist),
while the corrections for the shadow system are imported in the
SHD _ FIX _ IMP phase (upgrade). The transport requests are imported
automatically. You must never manually import requests into the system.
Change history for transport requests and control files related to the
following notes:
Corrections to the source release ABAP tools:
SAPK620VTZ...484876 (Saving customer secondary indexes on SAP tables)
BCEK067486...576588 (ICNV Correction with Source Release 6.x)
BIOK016330 No note (Correction for all 4.* Source Releases: When you
receive an add-on, an out-of-date version is transferred.
B6AK005543, B6AK005582, BIOK015873...522391(corrections for RDDIT006 & Co)
SAPK620VTX, SAPK620VTY...No note
BIOK016320, B20K8A12BS...No note (fix for LANG _ SELECT, processing of D, E)
B20K8A12BT..............No note (SPDA fix)
BIOK016382, B20K8A13KM...No note (SPDA _ PREPARE _ PATCH)
BIOK016353..............No note (SUBST _ OBJECT _ DELIVERY _ INFO)
BIOK016384..............No note (RDDPURI2 correction)
BIOK016266..............No note (delete DDDTRENUPG for SDBA _ ACTID)
BIOK016283..............No note ()
Y9CK037922, Y6BK027466...619339 (error in DDL ICNV schema)
B20K8A14FY............. (Correction for Report RSTRESNC)
BIOK016393............. (Correction for RDDTAXIT for CRM)
MBBK000012............. (Correction for RDDTAXIT)
B20K8A13UX............. (Correction for RDDTAXIT 6.* source release)
BCEK072347............. (Correction for ICNV due to SP 1)
BCEK073119..............(Correction for ICNV)
MBCK000006..............(900 messages LSUGIF02)
MBCK000008..............(RDDPURI2 + RSTODIRM)
MBCK000014..............(LSUGITOP)
BIOK016425..............(R3TR FUGR SUGO)
B6AK005594..............(target release sr patches)
Corrections to the upgrade control files:
bin / TOOLFIX.TP0.........No note (change of the required steps in the
import process)
bin / DB2RUNPH.LST.........545281 (DB2: Optimizing DD activation)
bin / DB2CATSZ.LST.........No note (DB2: Optimization)
bin / DB2CHARX.LST.........No note (DB2: Optimization)
bin / TABLOC.DB2...........No note (DB2: Syntax error in SQL statement)
bin / IS _ MOVES.LST.........535107 (Information on add-on movements)
bin / TOOLCHECK.LST........537347 (Higher tp version for Windows)
bin / CUSTTA.XQL...........No note (Incorrect script for user data
classes)
cofiles / A620WH2.SAP......No note (Avoid XPRA errors with Support Package
cofiles / A620TD3.SAP, cofiles / A620TE3.SAP, cofiles / A620TF3.SAP...Nonote
(Avoid errors with first CRM Support Package)
cofiles / A620CCC.SAP + cofiles / A620CCI.SAP...No note (Avoid errors during
reimport)
bin / ALPXPOOL.LST.........No note (Adjustments for instance profile)
bin / TABEXCL.LST..........No note (Inserts TCP* tables)
bin / DIFFEXP*.TP0.........No note (R3trans "deletion=yes" used
for component upgrade)
bin / MINPATCHLV.LST...... (Required minimum patch level for SAP _ ABA)
bin / DBFALL.SPC.......... No note (Increase of free space requirement)
bin / NOXCONV.DAT......... No note (Avoid conversion for potentially large
tables)
cofiles / A620TDF.SAP......604728+569172 (problems with SXMSGLOBAL TABUs)
bin / IS _ PROTECT.LST.......No note (DEL-IS-OIL added)
Corrections for the shadow system:
B20K8A0XD2...541009 (Performance-optimization JOB _ RSUMOD03)
Y6BK006514...519440 (JOB _ UMOD20 _ UPG phase)
Y6BK012902...553337 (Customer objects after upgrade in transaction SPAU)
Y6BK013942...568454, 414633 (Merge activation, RDDMASGL)
Y6BK012629...551845 (Activation error with reference to classes)
Y6BK011413...545281 (DB2: Optimization ACT _ 620, part 1)
Y6BK011267...545281 (DB2: Optimization ACT _ 620, part 2)
B6AK005568...No note (DB6: Phase JOB _ RSUPDTEC, PARDIST _ SHD)
B6AK005546...No note (RSPTBFIL: Controlling the distributor)
B6AK005575...513536 (RSPTBFIL: Correction for ICNV, Source Release 3.1I)
Y6BK005387...495561 (Corrections for distribution process, PARDIST _ SHD
phase)
B6AK005565...No note (DB2: Optimization RUN _ RSPTBFIL _ PDIST)
B6AK005495...No note (Optimization for the RUN _ RSCPFROM phase)
B6AK005579...578180 (DB2: Termination with too old DBSL, RUN _ RSCPFROM)
B20K8A117V...No note (phase RUN _ RDDNT5MD)
Y6BK021240...No note (hide activation button in SE13)
Y6BK025003...No note (dump ITAB _ ILLEGAL _ COMPONENT at SPDD)
B6AK005585...No note (620 / 1, 2:data loss in XI adapter tables)
B20K8A126L...No note (620 / 3, 4:data loss in XI adapter tables)
B20K8A0XW7...No note ()
B20K8A133Q...No note (RSUMOD03)
B20K8A135Q...No note (RDDIT022 and UPGACTKORR)
B6AK005572...No note (RSCPFROM)
SAPK60UPGX...No note ()
Y6BK022204...No note (Optimization PARDIST _ SHD Informix)
Y6BK022550...No note (Optimization for DB6 Basis Support Package 20)
Y6BK023305...No note (Activation program errors for DDIC enhancement
DDIC category Basis Support Package 20)
Y6BK024611...No note (Version Management for SPDD)
Y6BK027779...No note (Search Help versions)
QO1K900008...533309 (SPDD / SPAU)
BCEK073118...No note (ICNV)
B20K8A15CC...No note (RSPTBFIL fix for logical pools)
B20K8A15KF...No note (DB2: Correction PARMVNT _ SHD)
Y6BK031375...No note (DB2: Optimizing, adjustment for v8.1)
Y6BK028932...No note (DB2: Optimizing, adjustment for v8.1)
Corrections for the system on target release
Y6BK016656...No note (Correcting the converter, PARCONV _ UPG phase)
B20K8A106C...571657 (Correcting the add-on administration, phase
RUN _ RDDIT022)
B20K8A10P8...571657 (Correcting the add-on administration, phase
RUN _ RDDIT022)
Y6BK021997...595298 (Termination RADDRDOC, Source Release 3.1I)
Source code corrections
Gültige Releases
Software Komponente Release
von bis
SAP _ BASIS SAP Basiskomponente 620 - 620
Hinweisattribute
Transaktionscodes SPDD
Verweise auf verwandte Hinweise
Nummer Kurztext
484876 Additional information on upgrading to SAP Web AS 6.20
490065 DB2 / 390: Additions upgrade to Web AS 6.20
493599 DB2 / 390: Additions upgrade to EBP 3.5
506339 DB2 / 390: Additions upgrade to BW 3.0B
447925 OCS: Known problems with Supp. Packages in Basis Rel.6.20
585941 DB2 / 390: Additions upgrade to R / 3 Enterprise 4.7 SR1
587896 Add. info on upgrade to SAP R / 3 Enterprise Core 4.70 SR1
513536 Add. information on upgrade to SAP R / 3 Enterprise Core 4.70
517278 DB2 / 390: Additions upgrade to CRM 3.1
517267 DB2 / 390: Additions upgrade to R / 3 Enterprise 4.7
517731 Corrections for the upgrade to systems with Basis 620
600824 DB2 / 390: Additions upgrade to CRM 4.0 / SRM Server 4.0
603278 DB2 / 390: Additions upgrade to SCM 4.0
603852 Additional information on upgrading to SAP SCM 4.0
604728 SAP CRM 4.0: Information on Upgrade
619339 ICNV: invalid end of SQL statement, SQL error -3014
633093 SCM release 4.0 (Installation / upgrade - system)
637683 Ergänzungen Upgrade auf SAP R / 3 Enterprise Core 4.70 Ext. 2
640223 Application error after 31I ->
640516 DB2 / 390: Additions upgrade to R / 3 4.7 ExtSet 2.00
535107 IS _ MOVES on sapserv
541009 Long runtime for the report RSUMOD03
544569 DB2 / 390: Additions upgrade to BW 3.10
545281 DB2 / 390: Performance of DD activation
551845 Activation error with reference to class / interface
569260 Upgrading to Solution Manager 2.2
571695 SAPBWNews BW 3.0B Support Package 14
575170 Duplicate key in RSRA _ BP _ OBJECTST upgrade from 2.x to 3.1
SAP-Hinweis Nr. 525677
Nummer 525677
Version 9 vom 28.04.2003
Status Für Kunden freigegeben
Gesetzt am 28.04.2003
Sprache EN
Mastersprache DE
Kurztext Problems with starting the shadow instance
Verantwortlich SAP
Komponente BC-UPG
Upgrade allgemein
Langtext
Symptom
The shadow instance does not start or an R3up connect is not possible
during the system switch upgrade.
Additional key words
START _ SHDI _ FIRST, ALTNTAB _ FILL, downtime minimized, resource minimized,
TEXTENV _ INVALID, TEXTENV _ CODEPAGE _ NOT _ ALLOWED
Cause and prerequisites
During the system switch upgrade, a SAP Web AS system (Basis system) is
started in the START _ SHDI _ FIRST phase of the target release.
This happens either
o Alternately for the production system (using the
resource-minimized strategy)
o In parallel (using the downtime-minimized strategy).
In rare cases, the process of starting the shadow instance may fail.This
note describes possible reasons for this.
Solution
1.) With HP-UX only:
With HP, the "SHLIB _ PATH" profile parameter is set to <DIR _ PUT> / exe in
the startsap script for the shadow instance in:
<DIR _ PUT> / SID / homeshd / SID
that is, on the new kernel directory.However, if the "LD _ LIBRARY _ PATH"
parameter is also being used in the environment, then this points to the
old kernel directory and overrides the old "SHLIB _ PATH" kernel
directory.
Solution:Use "unsetenv LD _ LIBRARY _ PATH" or also set this parameter in
the startsap / stopsap script for the shadow instance.
2.) On UNIX only: Using logical host names
If the rdisp / myname, SAPLOCALHOST and SAPLOCALHOSTFULL profile
parameters are set in the instance profile of the original instance and
if these point to the logical host names and not the physical host
names, the shadow system will boot up in phase START _ SHDI _ FIRST, but it
is not possible to log on in the next phase ALTNTAB _ FILL since the
physical host name is entered for these parameters in the instance
profile.
To correct these parameters, proceed as follows:
1. Stop the shadow system (see appendix)
2. Adjust the parameter in the default or instance profile of the
shadow system (see appendix)
3. Start the shadow system (see appendix)
The shadow instance should then run completely on the virtual host.
Now repeat the ALTNTAB _ FILL phase.
3.) With Source Release 31Ionly:
If you have no choice but to start the shadow instance manually (for
example, after a database crash), set the dbms _ type environment
parameter before you restart the shadow system.
4.) Target Release 6.20 only, resource-minimized strategy, UNIX:
Termination on AIX 5.x 64 bits - may also occur on other UNIX platforms.
If the shadow instance is not restarted in the 'START _ SHDI _ FIRST' phase,
log on as user <sid>adm and enter the following commands:
cd / usr / sap / put / <SID> / homeshd / <SID>
. / stopsap DVEBMGS <SHDSYSNO> r3
cleanipc <SYSNO> remove
cleanipc <SHDSYSNO> remove
where
SYSNO = number of the original instance and
SHDSYSNO = number of the shadow instance
Repeat the 'START _ SHDI _ FIRST' phase
5.) The process of starting the shadow system fails in the phase
START _ SHDI _ FIRST.The "TEXTENV _ INVALID" error message appears in the
trace files of the work processes (dev _ w*) of the shadow system.
Check to see whether the "zcsa / system _ language" profile parameter is set
to a value other than D or E in the instance or default profile of the
shadow system.If this is the case, correct this parameter to D or E.
Stop the shadow system (see appendix) and repeat the phase.
6.) An error message is displayed in the ALTNTAB _ FILL phase:
"RFC of "subst _ start _ report _ in _ batch" failed.
codepage 1100 is not released
In addition, the "TEXTENV _ CODEPAGE _ NOT _ ALLOWED" error message is
displayed in the trace files of the work processes (dev _ w*) for the
shadow system.
This is due to an error in the NLS configuration of the shadow system.If
the error occurs, proceed as follows:
Log on directly to the database.Use the user or database schema
of the standard SAP system (this is generally SAPR3 or SAP <SID>).
Insert the following row in the "TCPDB~" table:
INSERT "TCPDB~" VALUES ('1100', '1100');
for MSSQL: INSERT [TCPDB~] VALUES ('1100', '1100')
with final COMMIT
Stop and restart the shadow system (see appendix).Then continue
the upgrade.
7.) You are prompted to enter a new password when you first log on to
the shadow system as user DDIC.This error can only occur with UNIX and
the "Resource-minimized" upgrade strategy.The
"login / password _ expiration _ time" profile parameter in the DEFAULT.PFL
profile of the shadow instance is to blame here.Do not change the
password, instead stop the shadow instance (see appendix), comment out
this parameter, start the shadow instance and log on again.
8.) Error message:
Exception "VARIANT _ INSERT _ VARIANT _ LOCKED" raised,
variant is locked by another process.
The lock handler could not be reached. This is because the
"rdisp / myname" profile parameter is entered in the instance profile of
the shadow instance. This parameter is set in the profile default of the
shadow instance. You must therefore comment out this parameter in the
instance profile of the shadow instance. Stop and then start the shadow
instance as described in the appendix.
Appendix
o Starting the shadow instance
Call R3up as user <sid>adm as follows:
R3up startshd
Alternatively, the shadow instance can be started as follows:
<upgrade _ directory> / <SID> / homeshd / <SID> / startsap
DVEBMGS <SHDSYSNO> r3
where <SHDSYSNO> is the instance number of the shadow system.
o Stop the shadow instance
Call R3up as user <sid>adm as follows:
R3up stopshd
Alternatively, the shadow instance can be stopped as follows:
<upgrade _ directory> / <SID> / homeshd / <SID> / stopsap
DVEBMGS <SHDSYSNO> r3
where <SHDSYSNO> is the instance number of the shadow system.
o Configuring the shadow system:
- Kernel of the shadow system: <upgrade _ directory> / exe
- Profiles of the shadow system:
<upgrade _ directory> / <SID> / SYS / profile.
The default profile is DEFAULT.PFL, the instance profile is
<SID> _ DVEBMGS <SHDSYSNO> _ <hostname>
- Work directory (here you will find the trace files of the
message server, gateway, dispatcher and the work processes of
the shadow
system): <upgrade _ directory> / <SID> / DVEBMGS <SHDSYSNO> / work
- Scripts for starting and stopping the
system: <upgrade _ directory> / <SID> / homeshd / <SID>
Gültige Releases
Software Komponente Release
von bis
SAP _ BASIS SAP Basiskomponente 610 - 640
Verweise auf verwandte Hinweise
Nummer Kurztext
484876 Additional information on upgrading to SAP Web AS 6.20
500181 Strategy change from resource-minimized to downtime-minimize
401717 Additional info on upgrading to SAP Web AS 6.10 (Basis)
430318 Shadow instance on other operating system
96317 Host names for the R / 3 upgrade, tips & tricks
587896 Add. info on upgrade to SAP R / 3 Enterprise Core 4.70 SR1
518396 Profile während des Upgrades
603852 Additional information on upgrading to SAP SCM 4.0
637683 Ergänzungen Upgrade auf SAP R / 3 Enterprise Core 4.70 Ext. 2
|